Abstract
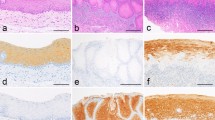
Immunohistochemistry with monospecific antibodies was used to study the expression patterns of cytokeratins (Cks) and vimentin in non-dysplastic lesions of the oral cavity, including lichen planus and fibromas. In hyperplastic lesions, Ck expression did not deviate significantly from the normal non-keratinizing squamous epithelium of the oral cavity. Hyperkeratotic lesions showed pronounced aberrations in their Ck profile. These lesions were characterized by extended expression of the keratinization marker Ck 10, the basal cell Ck 14 and the hyperproliferation-associated Ck 16 in the suprabasal compartment. The stratification markers Cks 4 and 13 showed a decreased expression. Coexpression of Cks and vimentin was found in lesions having accumulations of inflammatory cells in the subepithelial cell layer. These changes are felt to characterize benign mucosal lesions without dysplasia and might be helpful for distinguishing these lesions from potentially malignant ones.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 September 1998 / Accepted: 5 February 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Velden, LA., Manni, J., Ramaekers, F. et al. Expression of intermediate filament proteins in benign lesions of the oral mucosa. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 256, 514–519 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004050050202
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004050050202