Abstract
Purpose
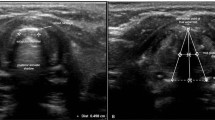
Ultrasonography of the airway has potential as an alternative, non-invasive, method to monitor patients with subglottic stenosis in an outpatient setting. This prospective, interventional, double-blinded study aimed to correlate ultrasound-based and laryngoscopy-based subglottic stenosis assessment in adults.
Methods
The study was conducted between July 2020 and March 2021 at a tertiary referral center. Consecutive adult patients with subglottic stenosis were evaluated using airway ultrasonography 1 day prior to scheduled laryngoscopy. The radiologist was blinded to the preoperative endoscopic findings, and the primary surgeon was blinded to the ultrasonographic measurements. The intraoperative subglottic diameter was defined as the outer diameter of an endotracheal tube passing through the subglottis without producing an air leak.
Results
Sixteen patients (11 females; age range, 17–66 years; mean = 44.06, SD = 12.79) were included. The ultrasonographic subglottic diameter ranged from 5.20 mm to 8.00 mm (mean = 6.24 mm, SD = 0.90). In 15 of 16 patients, the diameter difference between the ultrasonographic and intraoperative measurements ranged from -0.80 mm to 0.30 mm (mean = -0.20 mm, SD = 0.35). However, patient 6 had a difference of − 2.10 mm between the two measurements, which was attributed to thick laryngotracheal secretions interfering with the ultrasonographic air shadow. Data analysis of all 16 patients showed a statistically significant correlation between the readings obtained by the two techniques (r = 0.84, P = 0.000051).
Conclusion
This study found a significant correlation between ultrasonography-based and laryngoscopy-based subglottic stenosis assessment in adult patients. It provides a basis for an alternative and potentially reliable method to monitor patients with subglottic stenosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodsky MB, Levy MJ, Jedlanek E, Pandian V, Blackford B, Price C, Cole G, Hillel AT, Best SR, Akst LM (2018) Laryngeal injury and upper airway symptoms after oral endotracheal intubation with mechanical ventilation during critical care: a systematic review. Crit Care Med 46:2010–2017. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000003368
Jang M, Basa K, Levi J (2018) Risk factors for laryngeal trauma and granuloma formation in pediatric intubations. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 107:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.01.008
Schweiger C, Marostica PJ, Smith MM, Manica D, Carvalho PR, Kuhl G (2013) Incidence of post-intubation subglottic stenosis in children: prospective study. J Laryngol Otol 127:399–403. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002221511300025X
Boardman SJ, Albert DM (2008) Single-stage and multistage pediatric laryngotracheal reconstruction. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 41:947–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2008.04.002
Daniel SJ, Bertolizio G, McHugh T (2020) Airway ultrasound: point of care in children-the time is now. Paediatr Anaesth 30:347–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/pan.13823
Lun HM, Zhu SY, Liu RC, Gong JG, Liu YL (2016) Investigation of the upper airway anatomy with ultrasound. Ultrasound Q 32:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/RUQ.0000000000000163
Myer CM 3rd, O’Connor DM, Cotton RT (1994) Proposed grading system for subglottic stenosis based on endotracheal tube sizes. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 103:319–323. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949410300410
Wei JL, Bond J (2011) Management and prevention of endotracheal intubation injury in neonates. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 19:474–477. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0b013e32834c7b5c
Nouraei SAR, Dorman EB, Johnston J, Vokes DE (2019) Vocal fold fixation due to proximal stenosis progression complicating idiopathic subglottic stenosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276:2293–2300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05494-6
Gallo A, Pagliuca G, Greco A, Martellucci S, Mascelli A, Fusconi M, De Vincentiis M (2012) Laryngotracheal stenosis treated with multiple surgeries: experience, results and prognostic factors in 70 patients. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 32:182–188
Alshammari J, Monnier P (2012) Airway stenting with the LT-Mold™ for severe glotto-subglottic stenosis or intractable aspiration: experience in 65 cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:2531–2538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2080-x
George M, Jaquet Y, Ikonomidis C, Monnier P (2010) Management of severe pediatric subglottic stenosis with glottic involvement. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 139:411–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.05.010
Henes FO, Laudien M, Linsenhoff L, Bremer JP, Oqueka T, Adam G, Schön G, Bannas P (2018) Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for grading of subglottic stenosis in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis: correlation with pulmonary function tests and laryngoscopy. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 70:777–784. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.23332
Lakhal K, Delplace X, Cottier JP, Tranquart F, Sauvagnac X, Mercier C, Fusciardi J, Laffon M (2007) The feasibility of ultrasound to assess subglottic diameter. Anesth Analg 104:611–614. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000260136.53694.fe
Parida PK, Gupta AK (2008) Role of spiral computed tomography with 3-dimensional reconstruction in cases with laryngeal stenosis—a radioclinical correlation. Am J Otolaryngol 29:305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2007.09.006
Shitrit D, Valdsislav P, Grubstein A, Bendayan D, Cohen M, Kramer MR (2005) Accuracy of virtual bronchoscopy for grading tracheobronchial stenosis: correlation with pulmonary function test and fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Chest 128:3545–3550. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.128.5.3545
Jewett BS, Cook RD, Johnson KL, Logan TC, Rosbe KW, Mukherji SK, Shockley WW (1999) Subglottic stenosis: correlation between computed tomography and bronchoscopy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:837–841. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949910800904
Burke AJ, Vining DJ, McGuirt WF, Postma G, Browne JD (2000) Evaluation of airway obstruction using virtual endoscopy. Laryngoscope 110:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200001000-00005
You-Ten KE, Siddiqui N, Teoh WH, Kristensen MS (2018) Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) of the upper airway. Can J Anaesth 65:473–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12630-018-1064-8
Pillai R, Kumaran S, Jeyaseelan L, George SP, Sahajanandan R (2018) Usefulness of ultrasound-guided measurement of minimal transverse diameter of subglottic airway in determining the endotracheal tube size in children with congenital heart disease: a prospective observational study. Ann Card Anaesth 21:382–387. https://doi.org/10.4103/aca.ACA_220_17
Shibasaki M, Nakajima Y, Ishii S, Shimizu F, Shime N, Sessler DI (2010) Prediction of pediatric endotracheal tube size by ultrasonography. Anesthesiology 113:819–824. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181ef6757
Chan WH, Sung CW, Chang HCH, Ko PC, Huang EP, Lien WC, Huang CH (2020) Measurement of subglottic diameter and distance to pre-epiglottic space among Chinese adults. PLoS ONE 15:e0236364. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0236364
Ding LW, Wang HC, Wu HD, Chang CJ, Yang PC (2006) Laryngeal ultrasound: a useful method in predicting post-extubation stridor. A pilot study. Eur Respir J 27:384–389. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.06.00029605
Lambert EM, Tran HD, Ongkasuwan J (2020) Comparison of endoscopic and ultrasonographic measurements of the subglottic airway in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 163:1264–1269. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599820936249
Bell JR, Cohen AP, Graff JT, Fleck RJ, O’Hara S, de Alarcon A, Hart CK (2020) Pilot study to assess the use of ultrasound in evaluating the abnormal pediatric airway. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 162:950–953. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599820912034
Kristensen MS (2011) Ultrasonography in the management of the airway. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 55:1155–1173. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2011.02518.x
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Availability of data and material
Data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the institutional review board of king Saud university medical city (E-20-4778) and the study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Informed written consent was obtained from all recruited patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Meeting information
The 101st Annual Meeting of the American Broncho-Esophagological Association, occurring virtually with the Combined Otolaryngology Spring Meetings (COSM) on April 7–8, 2021.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aldriweesh, B., Khan, A., Aljasser, A. et al. Correlation of airway ultrasonography and laryngoscopy findings in adults with subglottic stenosis: a pilot study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 1989–1994 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07195-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07195-5