Abstract
Introduction
In this study we aimed to compare the efficacy of peritonsillar injection of bupivacaine and intravenous acetaminophen on post-tonsillectomy pain in children.
Materials and methods
In this randomized double-blind clinical trial study 60 children with ASA = I–II aged 5–12 years undergoing tonsillectomy were involved. The first group received bupivacaine at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg that was injected into the bed and the anterior crease of each tonsil. The second group was given intravenous acetaminophen at a dose of 12.5 mg/kg. The patient’s pain score at 10, 30, 60 min after his/her admission to recovery room and 120, 240 and 360 min after the surgery was recorded using CHEOPS. Patient’s sedation score, nausea or vomiting, the time of the first request for analgesia and the time of starting oral feeding were recorded and analyzed too.
Results
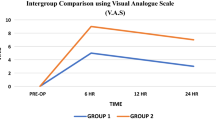
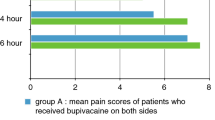
There was no significant differences in mean age (p value = 0.44), gender (p value = 0.79), weight (p value = 0.36), height (p value = 0.17), anesthesia duration (p.value = 0.85) and surgery duration (p.value = 0.73) between two groups. Postoperative pain was significantly less in the bupivacaine group at 240 and 360 min after the surgery. The mean sedation score was higher in the bupivacaine group but not significantly. There was no significant difference between groups regarding the nausea and vomiting, the first analgesics request time and the start time of oral feeding.
Conclusion
According to the results of the present study, since administration of peritonsillar bupivacaine compared to acetaminophen had a better effect on managing postoperative pain and improving sedation and also since no complications were reported; therefore, peritonsillar infiltration with bupivacaine is suggested for pediatric tonsillectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohebbi S, Nia FH, Kelantari F, Nejad SE, Hamedi Y, Abd R (2014) Efficacy of honey in reduction of post tonsillectomy pain, randomized clinical trial. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 78(11):1886–1889
Ekici NY, Özdoğan H (2020) Comparing local anesthetic infiltration of the peritonsillar region and glossotonsillar sulcus for post-tonsillectomy pain management. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277(1):255–260
Chen M-q, Chen C, Li L (2017) Effect of baricity of bupivacaine on median effective doses for motor block. Med Sci Monit 23:4699
Rajput SD, Patel AV, Prajapati MB, Padavi DS (2019) Role of Preincisional Peritonsillar infiltration of bupivacaine in postoperative pain relief in tonsillectomy patients. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71(1):610–613
Bowman B, Sanchez L, Sarangarm P (2018) Perioperative intravenous acetaminophen in pediatric tonsillectomies. Hosp Pharm 53(5):316–320
Chisholm AG, Sathyamoorthy M, Seals SR, Carron JD (2019) Does intravenous acetaminophen reduce perioperative opioid use in pediatric tonsillectomy? Am J Otolaryngol 40(6):102294
Kilinc L, Türk B, Türk HS, Cinar S, Turgut S, İslamoğlu S (2019) Peritonsillar dexamethasone–bupivacaine vs. bupivacaine infiltration for post-tonsillectomy pain relief in children: a randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276(7):2081–2089
Ayatollahi V, Behdad S, Hatami M, Moshtaghiun H, Baghianimoghadam B (2012) Comparison of peritonsillar infiltration effects of ketamine and tramadol on post tonsillectomy pain: a doubleblinded randomized lacebocontrolled clinical trial. Croat Med J 53(2):155–161
Heiba M, Atef A, Mosleh M, Mohamed R, El-Hamamsy M (2012) Comparison of peritonsillar infiltration of tramadol and lidocaine for the relief of post-tonsillectomy pain. J Laryngol Otol 126(11):1138
Dahi-Taleghani M, Mousavifard S, Tahmoureszade S, Dabbagh A (2011) Rectal acetaminophen versus peritonsillar infiltration of bupivacaine for postoperative analgesia after adenotonsillectomy in children. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268(4):581–584
Junaid M, Halim MS, Onali MAS, Qadeer S, Khan HU, Ali NS (2020) Intraoperative use of analgesics in tonsillar fossa and postoperative evaluation with visual analogue scale scores-a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 24(1):e62–e67
Teunkens A, Vermeulen K, Peters M, Fieuws S, Van de Velde M, Rex S (2019) Bupivacaine infiltration in children for postoperative analgesia after tonsillectomy: a randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol 36(3):206–214
DeHart AN, Potter J, Anderson J, Russo-Menna I, Lee JH, Chapman DA et al (2019) Perioperative interdisciplinary approach for reduction of opioid use in pediatric tonsillectomy: protocol using dexmedetomidine and bupivicaine as adjunct agents. Am J Otolaryngol 40(3):382–388
Newcomb W, Lincourt A, Hope W, Schmelzer T, Sing R, Kercher K et al (2007) Prospective, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled comparison of local anesthetic and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for postoperative pain management after laparoscopic surgery. Am Surg 73(6):618–625
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Study protocol was in accordance with the latest Declaration of Helsinki for medical research involving human subjects and was approved by the local ethics committee.
Human/animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, H., Shariatmadari, M., Ayatollahi, V. et al. Comparing the efficacy of peritonsillar injection of bupivacaine and intravenous acetaminophen on post-tonsillectomy pain in children. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 2599–2602 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07049-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07049-0