Abstract
Purpose
The main aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of intratympanic administration of dexamethasone and resveratrol in preventing cisplatin ototoxicity by measuring acoustic brainstem response (ABR) and distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE).
Methods
Forty rats (80 ears) were divided into five groups. Cisplatin was administered intraperitoneally to the first group (n = 8). Group 2 (n = 8) received cisplatin after resveratrol had been administered intratympanically. Group 3 (n = 8) received cisplatin after dexamethasone had been administered intratympanically. Group 4 (n = 8) received cisplatin after sodium chloride (NaCl) had been given intratympanically. Group 5 (n = 8) received cisplatin after dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) had been given intratympanically. ABR and DPOAE tests were performed on all groups before and 72 h after the procedure.
Results
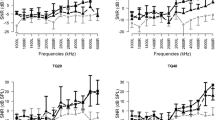
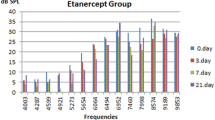
ABR threshold values in rats that received dexamethasone and resveratrol were found to be less affected than those observed in the other post-cisplatin groups. ABR-IV and ABR-I–IV interval values were significantly reduced in rats that had been given dexamethasone and resveratrol compared to the other groups. After cisplatin treatment, otoacoustic emission (OAE) amplitudes were significantly decreased in Groups 1, 4, and 5 for all frequencies, while OAE values were sustained in the resveratrol and dexamethasone groups (Groups 2 and 3). At OAE frequency 5652, dexamethasone was more significantly associated with protective than resveratrol was, while no significant difference was found between the two groups at other OAE frequencies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intratympanic dexamethasone and intratympanic resveratrol treatments may provide a significant protection against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganesan P, Schmiedge J, Manchaiah V, Swapna S, Dhandayutham S, Kothandaraman PP (2018) Ototoxicity: a challenge in diagnosis and treatment. J Audiol Otol 22(2):59–68
Campbell KCM, Le Prell CG (2018) Drug-induced ototoxicity: diagnosis and monitoring. Drug Saf 41(5):451–464
Liu W, Staecker H, Stupak H, Malgrange B, Lefebvre P, Van De Water TR (1998) Caspase inhibitors prevent cisplatin-induced apoptosis of auditory sensory cells. NeuroReport 9:2609–2614
McKeage MJ (1995) Comparative adverse effect profiles of platinum drugs. Drug Saf 13:228–244
Liang F, Schulte BA, Qu C, Hu W, Shen Z (2005) Inhibition of the calcium and voltage-dependent big conductance potassium channel ameliorates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in spiral ligament fibrocytes of the cochlea. Neuroscience 135:263–271
Doyle KJ, Bauch C, Battista R et al (2004) Intratympanic steroid treatment: a review. Otol Neurotol 25:1034–1039
Simşek G, Tokgoz SA, Vuralkan E, Caliskan M, Besalti O, Akin I (2013) Protective effects of resveratrol on cisplatin-dependent inner-ear damage in rats. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270(6):1789–1793
Yumusakhuylu AC, Yazici M, Sari M, Binnetoglu A, Kosemihal E et al (2012) Protective role of resveratrol against cisplatin induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76(3):404–408
Lee SH, Kim HS, An YS, Chang J, Choi J, Im GJ (2015) Protective effect of resveratrol against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in HEI-OC1 auditory cells. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79(1):58–62
Dinh CT, Chen S, Dinh J, Goncalves S, Bas E et al (2017) Effects of intratympanic dexamethasone on high-dose radiation ototoxicity in vivo. Otol Neurotol 38(2):180–186
Seligmann H, Podoshin L, Ben-David J, Fradis M, Goldsher M (1996) Drug-induced tinnitus and other hearing disorders. Drug Saf 14:198–212 (review)
Taş BM, Simşek G (2017) Cisplatin ototoxicity. KÜ Tıp Fak Derg 19(1):30–36. https://doi.org/10.24938/kutfd.306905
Bokemeyer C, Berger CC, Hartmann JT, Kollmannsberger C, Schmoll HJ et al (1998) Analysis of risk factors for cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in patients with testicular cancer. Br J Cancer 77:1355–1362
Huang E, Teh BS, Strother DR et al (2002) Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for pediatric medulloblastoma: early report on the reduction of ototoxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1(52):599–605
Reavis KM, McMillan GP, Dille MF, Konrad-Martin D (2015) Meta-analysis of distortion product otoacoustic emission retest variability for serial monitoring of cochlear function in adults. Ear Heart 36(5):e251–e260
Martín-Saldaña S, Palao-Suay R, Trinidad A, Aguilar MR, Ramírez-Camacho R et al (2016) Otoprotective properties of 6α-methylprednisolone-loaded nanoparticles against cisplatin: in vitro and in vivo correlation. Nanomedicine 12:965–976
Hargunani CA, Kempton JB, DeGagne JM, Trune DR (2006) Intratympanic injection of dexamethasone: time course of inner ear distribution and conversion to its active form. Otol Neurotol 27:564–569
Palmer RM, Bridge L, Foxwell NA et al (1992) The role of nitric oxide in endothelial cell damage and its inhibition by glucocorticoids. Br J Pharmacol 105:11–12
Kiliç R, Safak MA, Oğuz H, Kargin S, Demirci M et al (2007) Intratympanic methylprednisolone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 3:312–316
Han X, Yin X, Du X, Sun C (2017) Combined intratympanic and systemic use of steroids as a first-line treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis of randomized. Control Trials Otol Neurotol 38(4):487–495
Lee JJ, Jang JH, Choo OS, Lim HJ, Choung YH (2017) Steroid intracochlear distribution differs by administration method: systemic versus intratympanic injection. Laryngoscope 128(1):189–194. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.26562
Hill GW, Morest DK, Parham K (2008) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: effect of intratympanic dexamethasone injections. Otol Neurotol 29(7):1005–1011
Marshak T, Steiner M, Kaminer M, Levy L, Shupak A (2014) Prevention of cisplatin-induced hearing loss by intratympanic dexamethasone: a randomized controlled study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 150(6):983–990
Vidavalur R, Otani H, Singal PK, Maulik N (2006) Significance of wine and resveratrol in cardiovascular disease: French paradox revisited. Exp Clin Cardiol 11(3):217–225
García-Alcántara F, Murillo-Cuesta S, Pulido S, Bermúdez-Muñoz JM, Martínez-Vega R et al (2018) The expression of oxidative stress response genes is modulated by a combination of resveratrol and N-acetylcysteine to ameliorate ototoxicity in the rat cochlea. Hear Res 358:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2017.12.004
Yan Y, Yang J, Chen G, Mou Y, Zhao Y, Pan L, Ma C, Liu X, Wu C (2011) Protection of resveratrol and its analogues against ethanol-induced oxidative DNA damage in human peripheral lymphocytes. Mutat Res 721(2):171–177
Avcı D, Erkan M, Sönmez MF, Kökoğlu K, Güneş MS et al (2016) A prospective experimental study on the protective effect of resveratrol against amikacin-induced ototoxicity in rats. J Int Adv Otol 12(3):290–297
Erdem T, Bayindir T, Filiz A, Iraz M, Selimoglu E (2012) The effect of resveratrol on the prevention of cisplatin ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(10):2185–2188
Erkan SO, Tuhanioğlu B, Gürgen SG, Özdaş T, Taştekin B et al (2019) The effect of resveratrol on the histologic characteristics of the cochlea in diabetic rats. Laryngoscope 129(1):E1–E6. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27253
Funding
The authors declare that this article did not receive any financial support during the research and authorship process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they had no conflict of interest during the preparation and publication of this article.
Ethical approval
This study was carried out with the approval of the ethics of the Experimental Animal Research Center of Kırıkkale University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simsek, G., Taş, B.M., Muluk, N.B. et al. Comparison of the protective efficacy between intratympanic dexamethasone and resveratrol treatments against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: an experimental study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 3287–3293 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05635-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05635-x