Abstract
Purpose
To compare the tonsillectomy operations performed with bipolar radiofrequency clamp (BRC), plasma blade (PB), and cold dissection (CD) techniques in terms of postoperative pain and collateral tissue damage.
Methods
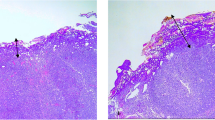
This is a prospective randomized comparative cohort study conducted in a tertiary hospital. A total of 50 patients who underwent tonsillectomy in our institution met the inclusion criteria. Based on the tonsillectomy technique, patients were randomly divided into 3 groups as BRC (CURIS®) (n:20), PB (PEAK Surgical) (n:20), and CD (n:10). The patients were given a visual analog scale (VAS) for pain evaluation on the 1st postoperative day (3rd h) and on the 3rd and 6th days after discharge. The deepest and the most superficial necrosis depths were examined under the light microscope (Olympus BX53, Japan) by the same single blinded pathologist.
Results
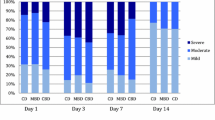
The age of the patients included in the study ranged from 5 to 45 years. The mean age was 14.5 years. Twenty-four of the patients were female, 26 were male. Mean 3rd h and 3rd day VAS scores for pain in the BRC group were significantly higher than the other two groups (p < 0.001). Although PB group had higher VAS scores compared with CD group, the difference was not significant (p > 0.05). The deepest necrosis depths (dND) in patients who were operated with BRC was significantly greater compared to patients operated with PB (p < 0.01), whereas no significant difference was observed between the techniques regarding the most superficial necrosis depth (msND) (p > 0.05). For patients operated with CD technique, only ischemic fields were observed.
Conclusion
Both BRC and PB techniques seem to not provide significant advantage compared with conventional CD technique in terms of postoperative pain. Necrosis depths in tonsillectomy specimens due to thermal damage positively correlate with the postoperative pain level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leinbach RF, Markwell SJ, Colliver JA, Lin SY (2003) Hot versus cold tonsillectomy: a systematic review of the literature. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:360–364
Baugh RF, Archer SM, Mitchell RB, Rosenfeld RM, Amin R, Burns JJ, et al (2011) Clinical practice guideline: tonsillectomy in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144:S1–S30
D'Eredità R1, Bozzola L (2009) Molecular resonance vs. coblation tonsillectomy in children. Laryngoscope 119:1897–1901
Bhattacharyya N, Kepnes LJ (2014) Revisits and postoperative hemorrhage after adult tonsillectomy. Laryngoscope 124:1554–1556
Pynnonen M, Brinkmeier JV, Thorne MC, Chong LY, Burton MJ (2017) Coblation versus other surgical techniques for tonsillectomy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 8:CD004619
Thottam PJ, Christenson JR, Cohen DS, Metz CM, Saraiya SS, Haupert MS (2014) The utility of common surgical instruments for pediatric adenotonsillectomy. Laryngoscope 125:475–479
Spektor Z, Kay DJ, Mandell DL (2016) Prospective comparative study of pulsed-electron avalanche knife (PEAK) and bipolar radiofrequency ablation (coblation) pediatric tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Am J Otolaryngol 37:528–533
Erickson BK, Larson DR, St Sauver JL, Meverden RA, Orvidas LJ (2009) Changes in incidence and indications of tonsillectomy and adenotonsillectomy, 1970–2005. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140:894–901
Galindo Torres BP, De Miguel García F, Whyte Orozco J (2018) Tonsillectomy in adults: Analysis of indications and complications. Auris Nasus Larynx 45:517–521
Chimona T, Proimos E, Mamoulakis C, Tzanakakis M, Skoulakis CE, Papadakis CE (2008) Multiparametric comparison of cold knife tonsillectomy, radiofrequency excision and thermal welding tonsillectomy in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 72:1431–1436
Sutters KA, Isaacson G (2014) Posttonsillectomy pain in children. Am J Nurs 114:36–42 (quiz 43)
Elinder K, Söderman AC, Stalfors J, Knutsson J (2016) Factors influencing morbidity after paediatric tonsillectomy: a study of 18,712 patients in the National Tonsil Surgery Register in Sweden. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273:2249–2256
Tan GX, Tunkel DE (2017) Control of pain after tonsillectomy in children: a review. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143:937–942
Windfuhr JP, Toepfner N, Steffen G et al (2016) Clinical practice guideline: tonsillitis II. Surgical management. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273:989–1009
Alexiou VG, Salazar-Salvia MS, Jervis PN, Falagas ME (2011) Modern technology-assisted vs conventional tonsillectomy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:558–570
Ozkul MH, Bayram O, Balikci HH, Karakas M, Bayram AA, Gurdal MM, Chatzi T (2014) Impedance-controlled radiofrequency vs. cold dissection tonsillectomy. B-ENT 10:285–289
Philpott CM, Wild DC, Mehta D, Daniel M, Banerjee AR (2005) A double-blinded randomized controlled trial of coblation versus conventional dissection tonsillectomy on post-operative symptoms. Clin Otolaryngol 30:143–148
Polites N, Joniau S, Wabnitz D, Fassina R, Smythe C, Varley P, Carney AS (2006) Postoperative pain following coblation tonsillectomy: randomized clinical trial. ANZ J Surg 76:226
Mitic S, Tvinnereim M, Lie E, Saltyte BJ (2007) A pilot randomized controlled trial of coblation tonsillectomy versus dissection tonsillectomy with bipolar diathermy haemostasis. Clin Otolaryngol 32:261–267
Metcalfe C, Muzaffar J, Daultrey C, Coulson C (2017) Coblation tonsillectomy: a systematic review and descriptive analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274:2637–2647
Timms MS, Temple RH (2002) Coblation tonsillectomy: a double blind randomized controlled study. J Laryngol Otol 116:450–452
Wiltshire D, Cronin M, Lintern N, Fraser-Kirk K, Anderson S, Barr R, Bennett D, Bond C (2018) The debate continues: a prospective, randomised, single-blind study comparing Coblation and bipolar tonsillectomy techniques. J Laryngol Otol 132:240–245
Shah UK, Dunham B (2007) Coblation for tonsillectomy: an evidence-based review. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 69:349–357
Magdy EA, Elwany S, el-Daly AS, Abdel-Hadi M, Morshedy MA (2008) Coblation tonsillectomy: a prospective, double-blind, randomised, clinical and histopathological comparison with dissection-ligation, monopolar electrocautery and laser tonsillectomies. J Laryngol Otol 122:282–290
Funding
The authors have no funding to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All patients were informed about their disease and its treatment, and the surgical method to be applied was explained in detail. All patients provided informed consent.
Human and animal rights statement
The study has been performed according to the ethical standards of the Helsinki Declaration. We declare that all authors have contributed to it, read and approved the final manuscript for submission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boğrul, M.F., Ünal, A., Yılmaz, F. et al. Comparison of two modern and conventional tonsillectomy techniques in terms of postoperative pain and collateral tissue damage. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 2061–2067 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05464-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05464-y