Abstract
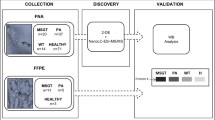
The objective of this study is to perform proteomic analysis of pleomorphic adenoma (PA) in the human parotid gland (PG) with comparison of normal PG. This is an individual prospective randomized controlled trial. This study was performed in a tertiary referral center. Tissue samples of PG and PA were taken after surgical excision of PG from 13 patients. Protein extracts were prepared and protein pools created from the soluble extracts were subjected to 2D-DIGE analysis. Proteins displaying regulation in their abundance were determined and identified using MALDIT-OF/TOF analysis. The identified proteins were subjected to STRING analysis for classification of the proteins based on their biological roles in metabolic pathways. Fifteen proteins, carbonic anhydrase 1, carbonic anhydrase 2, fibrinogen beta chain, alpha-amylase 1, heats hock protein hsp 90-alpha, clusterin, 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein, endoplasmin, alpha-amylase 2b, ATP synthase subunit alpha (mitochondrial), elongation factor 1-gamma, malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic, triosephosphate isomerase, receptor of activated protein c kinase 1, and aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial were down-regulated, whereas 11 proteins including ig kappa chain c region, serotransferrin, vimentin, annexin a5, glial fibrillary acidic protein, calreticulin, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, microfibril-associated glycoprotein 4, 14-3-3 protein epsilon, fibulin-5, and f-box only protein 2 were up-regulated in PA samples in comparison to healthy parotid tissue. This study described the differences observed in protein expression patterns of the PA and normal PG. The results may provide new insights into the pathogenesis and diagnosis of PA in human PG.
Level of evidence: 1b.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spiro RH (1986) Salivary neoplasms: overview of a 35-year experience with 2807 patients. Head Neck Surg 8:177–184
Rossi ED, Wong LO, Bizzarro T, Petrone G, Mule A, Fadda G, Baloch ZM (2016) The impact of FNAC in the management of salivary gland lesions: institutional experiences leading to a risk-based classification scheme. Cancer Cytopathol 124(6):388–396
Jain R, Gupta R, Kudesia M, Singh S (2013) Fine needle aspiration cytology in diagnosis of salivary gland lesions: a study with histologic comparison. Cyto J 10:5
Donadio E, Giusti L, Seccia V, Ciregia F, da Valle Y, Dallan I et al (2013) A new insight into benign tumors of major salivary glands by proteomic approach. PLoS One 8(8):71874
Akpinar G, Kasap M, Aksoy A, Duruksu G, Gacar G, Karaoz E (2014) Phenotypic and proteomic characteristics of human dental pulp derived mesenchymal stem cells from a natal, an exfoliated deciduous, and an impacted third molar tooth. Stem Cells Int 2014:457059
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J et al (2015) STRING v10: protein–protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43:447–452
Mi H, Muruganujan A, Casagrande JT (2013) Thomas PD Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system. Nat Protoc 8(8):1551–1566
Chopra DP, Xue-Hu IC (1993) Secretion of alpha-amylase in human parotid gland epithelial cell culture. J Cell Physiol 155(2):223–233
Morley DJ (1988) Hodes ME amylase expression in human parotid neoplasms: evidence by in situ hybridization for lack of transcription of the amylase gene. J Histochem Cytochem 36(5):487–491
Prasad KN, Carvalho E, Edwards-Prasad J, La Rosa FG, Kumar S, Kim JH et al (1994) Establishment of human parotid pleomorphic adenoma cells in culture: morphological and biochemical characterization. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 30(5):312–320
Pucci S, Bonanno E, Pichiorri F, Angeloni C, Spagnoli LG (2004) Modulation of different clusterin isoforms in human colon tumorogenesis. Oncogene 23(13):2298–2304
Leskov KS, Klokov DY, Li J, Kinsella TJ, Boothman DA (2003) Synthesis and functional analysis of nuclear clusterin, a cell death protein. J Biol Chem 278(13):11590–11600
Xie D, Sham JS, Zeng WF, Che LH, Zhang M, Wu HX et al (2005) Oncogenic role of clusterin overexpression in multistage colorectal tumorogenesis and progression. World J Gastroenterol 11(21):3285–3289
Yu SY, Hong LC, Feng J, Wu YT, Zhang YZ (2016) Integrative proteomics and transcriptomics identify novel invasive-related biomarkers of non-functioning pituitary adenomas. Tumour Biol 37(7):8923–8930
Vanmuylder N, Evrard L, Daelemans P, Dourov N (2000) Chaperones in the parotid gland: localization of heat shock proteins in human adult salivary glands. Cells Tissues Organs 167(2–3):199–205
Wang G, Gu X, Chen L, Wang Y, Cao B, Qun E (2013) Comparison of the expression of 5 heat shock proteins in benign and malignant salivary gland tumor tissues. Oncol Lett 5(4):1363–1369
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Liu J (2001) Prognostic significance of heat shock proteins 70 and p27 protein in patients with mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 36(6):467–470
Morrison DK (2009) The 14-3-3 proteins: integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and cancer development. Trends Cell Biol 19(1):16–22
Sofiadis A, Becker S, Hellman U, Hultin-Rosenberg L, Dinets A, Hulchiy M et al (2012) Proteomic profiling of follicular and papillary thyroid tumors. Eur J Endocrinol 166(4):657–667
Leader M, Collins M, Patel J, Henry K (1987) Vimentin: an evaluation of its role as a tumour marker. Histopathology 11(1):63–72
Sedassari BT, Dos Santos HT, Mariano FV, da Silva Lascane NA, Altemani A, Sousa S (2015) Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of minor salivary glands with major epithelial–myoepithelial component: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 3 cases. Ann Diagn Pathol 19(3):164–168
Burns BF, Dardick I, Parks WR (1988) Intermediate filament expression in normal parotid glands and pleomorphic adenomas. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 413(2):103–112
Wittchow R, Landas SK (1991) Glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in pleomorphic adenoma, chordoma, and astrocytoma. A comparison of three antibodies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 115(10):1030–1033
Stead RH, Qizilbash AH, Kontozoglou T, Daya AD, Riddell RH (1988) An immunohistochemical study of pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary gland: glial fibrillaryacidic protein-like immunoreactivity identifies a major myoepithelial component. Hum Pathol 19(1):32–40
Takahashi H, Fujita S, Tsuda N, Tezuka F, Okabe H (1991) Iron-binding proteins in adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary glands: an immunohistochemical study. Tohoku J Exp Med 163(1):1–16
Blankenberg FG (2008) In vivo detection of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 49(2):81–95
Thongwatchara P, Promwikorn W, Srisomsap C, Chokchaichamnankit D, Boonyaphiphat P, Thongsuksai P (2012) Differential protein expression in primary breast cancer and matched axillary node metastasis. Oncol Rep 26(1):185–191
Acknowledgements
The Scientific Research Unit of Kocaeli University supports this study as a scientific research project (Project Number: 2015/41).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mutlu, A., Ozturk, M., Akpinar, G. et al. Proteomics analysis of pleomorphic adenoma of the human parotid gland. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 3183–3195 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4608-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4608-6