Abstract
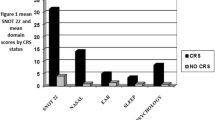
Quality of Life (QoL) studies are increasingly being used as the primary outcome measure in chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) globally. However, little is known about QoL and the interplay of identifiable factors on QoL in CRS in sub-Saharan Africa. This study investigated the correlation between disease severity and QoL in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. A total of 147 adults with subjective severity rating of CRS were studied. Participants were assessed using designed questionnaire, Individual Rhinosinusitis Symptom Severity Score Assessment (IRSSSA) and Rhinosinusitis Disability Index (RSDI) questionnaires to elicit socio-demographic/clinical profile, CRS symptom severity and QoL, respectively. The mean age of the participants was 36.86 ± 11.91 years. The mean severity score of all 147 CRS cases was 3.8 ± 1.13. The majority of participants (N = 80; 54.4 %) had moderate disease. The RSDI mean scores for the participants for overall HRQoL were 40.6 ± 19.8. (Median = 40; Range = 77), for physical domain 15.2 ± 7.7, functional domain 12.1 ± 6.4 and emotional domain 13.2 ± 8.2. The trend of association between the disease severity scores and the overall HRQoL on Pearson linear correlation indicates a positive linear association of worsening overall HRQoL with increasing disease severity (R = 0.83; P < 0.0001). The severity of CRS impacted negatively on the HRQoL. All domains were significantly affected by the disease severity particularly the physical domain. Patients adjudged severity of their disease and its’ impact on their quality of life should be considered in the determination of the line of their management which could include psychosocial intervention.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballenger JJ (1996) Clinical anatomy and physiology of the nose and Paranasal sinuses. In Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery 15th Edition Ballenger JJ, Snow Jr S B, eds Williams & Wilkins, USA, pp 3–18
Scadding G (1996) Rhinitis: common debilitating and treatable. Practitioner 240:48–53
Okafor BC (1983) Otolaryngology in south eastern Nigeria II. Pattern of disease of the nose. Niger Med Pract 13:21–29
Anand VK (2004) Epidemiology and economic impact of rhinosinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 193:3–5
United States census bureau, international data base 2004 Available at www.cureresearch.com
Iseh KR, Makusidi M (2010) Rhinosinusitis: a retrospective analysis of clinical pattern and outcome in north western Nigeria. Ann Afr Med 9:20–26
Somefun OA, Nwawolo CC, Mazai AE (2005) An evaluation of sinusitis in Lagos, Nigeria. Niger Med J 46:53–56
Fasunla AJ, Nwaorgu OGB (2011) Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: spectrum of clinical features in a Tertiary Health Institution and Literature review. East Cent Afr J Surg 16:12–18
Ray NF, Baruniak JN, Thamer M et al (1999) Healthcare expenditures for sinusitis in 1996: contributions of Asthma, rhinitis, and other airway disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol 103:408–414
Brook I, Gooch WM, Jerikins SG et al (2000) Medical management of acute Bacterial sinusitis. Recommendation of a clinical advisory committee on paediatric and adult sinusitis. Ann otol rhinol Laryngol 182:2–20
Metson RB, Glicklich RE (2000) Clinical outcomes in patients with chronic sinusitis. Laryngoscope 3:24–28
Alobid I, Benitez P, Bernal-sprkelsen M, Roca J, Alonso J, Picado C (2005) Nasal polyposis and its impact on quality of life: comparison between the effects of medical and surgical treatments. Allergy 60:452–458
Bousquet J, Bullinger M, Fayol C, Marquis P, Valentin B, Burtin B (1994) Assessment of quality of life in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis with the French version of the SF-36 Health Status Questionnaire. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1:182–188
Fairley JW, Yardley MPJ, Durhan LH (1993) Reliability and validity of a nasal symptom questionnaire for use as an outcome measure in clinical research and audit of functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Clin Otolaryngol 18:436–437
Cunningham JM, Chiu EJ, Landgraf JM, Gliklich RE (2000) The health impact of chronic recurrent rhinosinusitis in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:1363–1368
Fahmy F, McCombe A, Hicklin L (2000) Outcome measures for endoscopic sinus surgery. Proceedings of the 4th European Congress of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Monduzzi Editore, Milano 1, pp 397–402
Piccirillo JF (1995) Psychometric and clinimetric validity of the 31-item rhinosinusitis outcome measure. Am J Rhinol 9:297–306
Anderson ER, Murphy MP, Weymuller EA Jr (1999) Clinimetric evaluation of the Sinonasal Outcome Test-16. Student Research Award 1998. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121:702–707
Benninger MS, Senior BA (1997) The development of the rhinosinusitis disability index. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123:1175–1179
Catalano P, Roffman E (2003) Outcome in patients with chronic sinusitis after the minimally invasive sinus technique. Am J Rhinol 17:17–22
Birch DS, Saleh HA, Wodehouse T, Simpson IN, Mackay IS (2001) Assessing the quality of life for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis using the “Rhinosinusitis Disability Index”. Rhinology 39(4):191–196
Mace J, Michael YL, Carlson NE, Litvack JR, Smith TL (2008) Effects of depression on quality of life improvement after endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope 118:528–534
Soler ZM, Mace J, Smith T (2008) Fibromyalgia and chronic rhinosinusitis: outcomes after endoscopic sinus surgery. Am J Rhinol 22:427–432
Hobbs T. Individual Rhinosinusitis symptoms: Severity Scoring Assessment at www.peytonmanning.stvincent.org.
Lanzer D, Kennedy DW (1997) Adult rhinosinusitis defined. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 117(3):51–57
Fisher A, Laing J, Stoekel J, Townnsend J (1983) Sampling and sample size determination: Handbook for family planning operations. Research and Design (2nd Ed). The population council New York 45
da Lilly-Tariah OB (2006) Patterns of clinical features of simple chronic rhinosinusitis in Portharcourt. Niger J Clin Pract 9:142–146
Bhattacharyya N (2003) The economic burden and symptom manifestations of chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol 17:27–32
Seybt MW, McMain KC, Kountakis SE (2007) The prevalence and effect of asthma on adults with chronic rhinitis. Ear Nose Throat J 86(7):409–411
Bresciani M, Paradis L, Des Roches A et al (2001) Rhinosinusitis in severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immuol 107:73–80
Joe SA, Thakkar K (2008) Chronic rhinosinusitis and asthma. Otlaryngol Clin North Am 41:297–309
Stammberger H, Posawetz G (1990) Functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Concept, indications and results of the Messerklinger technique. Eur Arch Otorhinolarngol 247:63–76
Birch DS, Saleh HA, Wodehouse T, Simpson IN, Mackay IS (2001) Assessing the quality of life for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis using the “Rhinosinusitis Disability Index”. Rhinology 39(4):191–196
Atlas SJ, Metson RB, Singer DE, Wu YA, Gliklich RE (2005) Validity of a new health-related quality of life instrument for patient with chronic sinusitis. Laryongoscope 115:846–854
Chen H, Katz PP, Eisner MD, Yelin EH, Blanc PD (2004) Health-related quality of life in adult rhinitis: the role of perceived control disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 15:15–20
Lange B, Holst R, Thilsing T, Baelum J, Kjeldsen A (2013) Quality of life and associated factors in persons with chronic rhinosinusitis in the general population. A prospective questionnaire and clinical cross-sectional study. Clin Otlaryngol 38(6):474–480
Pa Chun W, Chin-Jaan T, Min-Shung L, Chin-Chen C, Shu-Cheng L (2003) Quality of life in Taiwanese adult with chronic rhinosinusitis. Qual Life Res 12:443–448
Dotlic J, Marinkovic J (2009) Health-related quality of life in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Srp Arh Celok Lek 137:470–474
Conflict of interest
The authors report no sponsorship for this study and no conflict of interties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olowosusi, O.Z., Asoegwu, C.N., Olagunju, A.T. et al. A cross-sectional evaluation of the correlation between disease severity and quality of life in chronic rhinosinusitis patients in Nigeria. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 2341–2346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3348-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3348-0