Abstract
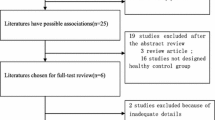
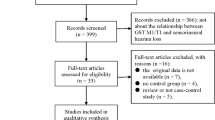
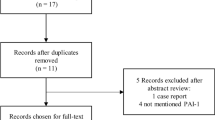
A variety of epidemiological studies have evaluated the association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene C677T polymorphism and sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL), but the results were inconsistent. The aim of this meta-analysis was to clarify more accurately the association of this polymorphism with SSNHL. A systematic literature search of the associated studies up to May 1, 2014, was conducted using the following electronic databases: PubMed, Embase, Medline, and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure. Statistical analyses were performed by STATA12.0 software, with odds ratios (ORs) and their 95 % confidence intervals (CIs). Six eligible studies including covering 1,271 objects were identified. A pooled analysis of these studies showed no significant association between C677T polymorphism and risk of SSNHL: T vs. C (OR = 1.334, POR = 0.105); TT vs. CC (OR = 1.580, POR = 0.231); CT vs. CC (OR = 1.500, POR = 0.123); TT vs. CC + CT (OR = 1.326, POR = 0.293); and TT + CT vs. CC (OR = 1.540, POR = 0.102). But in subgroup analysis, a significant association was found in European populations (T vs. C, OR = 1.542, 95 % CI 1.008–2.359, P = 0.046; TT vs. CT + CC, OR = 1.856, 95 % CI 1.245–2.767, P = 0.002). There was no significant association in any model in the Asian populations. The present meta-analysis suggests that MTHFR gene C677T polymorphism is significantly associated with increased risk of SSNHL disease in European populations, but no statistically significant association was found between the MTHFR C677T gene mutation and SSNHL in Asian. Further large and well-designed studies are needed to confirm this association.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Kleyn A (1944) Sudden complete or partial loss of function of the octavus system in apparently normal persons. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 32:409–429
Fusconi M, Chistolini A, Angelosanto N, Pignoloni P, Tombolini M, De Virgilio A, Pagliarella M, de Vincentiis M (2011) Role of genetic and acquired prothrombotic risk factors in genesis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Audiol Neurootol 16(3):185–190
Nosrati-Zarenoe R, Arlinger S, Hultcrantz E (2007) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: results drawn from the Swedish national database. Acta Otolaryngol 127(11):1168–1175
Wilson WR, Veltri RW, Laird N, Sprinkle PM (1983) Viral and epidemiologic studies of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 91(6):653–658
Hultcrantz E, Stenquist M, Lyttkens L (1994) Sudden deafness: a retrospective evaluation of dextran therapy. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 56(3):137–142
Kellerhals B (1972) Acoustic trauma and cochlear microcirculation. An experimental and clinical study on pathogenesis and treatment of inner ear lesions after acute noise exposure. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 18:91–168
Probst R, Tschopp K, Lüdin E, Kellerhals B, Podvinec M, Pfaltz CR (1992) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of dextran/pentoxifylline medication in acute acoustic trauma and sudden hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol 112(3):435–443
Campbell KCM, Klemens JJ (2000) Sudden hearing loss and autoimmune inner ear disease. J Am Acad Audiol 11:361–367
Goodhill V (1971) Sudden deafness and round window rupture. Laryngoscope 81(9):1462–1474
Uchida Y, Sugiura S, Ando F, Shimokata H, Nakashima T (2010) Association of the C677T polymorphism in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 120(4):791–795
Capaccio P, Ottaviani F, Cuccarini V, Bottero A, Schindler A, Cesana BM, Censuales S, Pignataro L (2007) Genetic and acquired prothrombotic risk factors and sudden hearing loss. Laryngoscope 117(3):547–551
Frosst P, Blom HJ, Milos R, Goyette P, Sheppard CA, Matthews RG, Boers GJ, den Heijer M, Kluijtmans LA, van den Heuvel LP et al (1995) A candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat Genet 10(1):111–113
Pereira TV, Rudnicki M, Pereira AC, Pombo-de-Oliveira MS, Franco RF (2006) 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms and acute lymphoblastic leukemia risk: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15(10):1956–1963
Yang S, Zhang J, Feng C, Huang G (2013) MTHFR 677T variant contributes to diabetic nephropathy risk in Caucasian individuals with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Metabolism 62(4):586–594
Zhong S, Yang JH, Liu K, Jiao BH, Chang ZJ (2012) Quantitative assessment of the association between MTHFR C677T polymorphism and colorectal cancer risk in East Asians. Tumour Biol 33(6):2041–2051
Little J, Bradley L, Bray MS, Clyne M, Dorman J, Ellsworth DL, Hanson J, Khoury M, Lau J, O’Brien TR, Rothman N, Stroup D, Taioli E, Thomas D, Vainio H, Wacholder S, Weinberg C (2002) Reporting, appraising, and integrating data on genotype prevalence and gene-disease associations. Am J Epidemiol 156:300–310
Wang L, Teng Z, Cai S, Wang D, Zhao X, Yu K (2013) The association between the PPARγ2 Pro12Ala polymorphism and nephropathy susceptibility in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis based on 9,176 subjects. Diagn Pathol 8(1):118
Gong T, Yang M, Qi L, Shen M, Du Y (2013) Association of MCP-1 −2518A/G and −362G/C variants and tuberculosis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Infect Genet Evol 20:1–7
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Yu Y, Wang W, Zhai S, Dang S, Sun M (2012) IL6 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis and review. Mol Biol Rep 39(8):8457–8463
Rudack C, Langer C, Junker R (2004) Platelet GPIaC807T polymorphism is associated with negative outcome of sudden hearing loss. Hear Res 191(1–2):41–48
Cadoni G, Scipione S, Rocca B, Agostino S, La Greca C, Bonvissuto D, Paludetti G (2006) Lack of association between inherited thrombophilic risk factors and idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in Italian patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 115(3):195–200
Gross M, Friedman G, Eliashar R, Koren-Morag N, Goldschmidt N, Atta IA, Ben-Yehuda A (2006) Impact of methionine synthase gene and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms on the risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Audiol Neurootol 11(5):287–293
Fusconi M, Chistolini A, de Virgilio A, Greco A, Massaro F, Turchetta R, Benincasa AT, Tombolini M, de Vincentiis M (2012) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a vascular cause? Analysis of prothrombotic risk factors in head and neck. Int J Audiol 51(11):800–805
Lee EJ, Cho YJ, Yoon YJ (2010) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T gene mutation as risk factor for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: association with plasma homocysteine, folate and cholesterol concentrations. J Laryngol Otol 124(12):1268–1273
Capaccio P, Ottaviani F, Cuccarini V, Ambrosetti U, Fagnani E, Bottero A, Cenzuales S, Cesana BM, Pignataro L (2005) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene mutations as risk factors for sudden hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol 26(6):383–387
Pollak A, Mueller-Malesinska M, Lechowicz U, Skorka A, Korniszewski L, Sobczyk-Kopciol A, Waskiewicz A, Broda G, Iwanicka-Pronicka K, Oldak M, Skarzynski H, Płoski R (2012) MTHFR 677T is a strong determinant of the degree of hearing loss among Polish males with postlingual sensorineural hearing impairment. DNA Cell Biol 31(7):1267–1273
Marcucci R, Alessandrello Liotta A, Cellai AP, Rogolino A, Berloco P, Leprini E, Pagnini P, Abbate R, Prisco D (2005) Cardiovascular and thrombophilic risk factors for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J Thromb Haemost 3(5):929–934
Coppola A, Davi G, De Stefano V, Mancini FP, Cerbone AM, Di Minno G (2000) Homocysteine, coagulation, platelet function, and thrombosis. Semin Thromb Hemost 26(3):243–254
Zhang MJ, Li JC, Yin YW, Li BH, Liu Y, Liao SQ, Gao CY, Zhang LL (2014) Association of MTHFR C677T polymorphism and risk of cerebrovascular disease in Chinese population: an updated meta-analysis. J Neurol 261(5):925–935
Acknowledgments
This work was not supported by any funds.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, J., Yin, S., Tan, AZ. et al. Association between the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene C677T polymorphism and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 2267–2274 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3198-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3198-9