Abstract
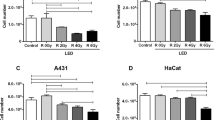
Clinical outcome of patients suffering from head neck squamous cell carcinomas is still poor due to recurrent disease and surgical limitations. There is still a demand for multimodality approaches and new therapeutic options. Hypericin is a promising phototoxic drug which was investigated for its effects on head neck squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro. FaDu cells incubated with or without hypericin were illuminated (450–700 nm, 50,000 lx) for different time periods. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide- and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assay were used to score metabolic and apoptotic activity. Even after the shortest illumination FaDu cells incubated with hypericin showed massive reduction of metabolism and excessive apoptosis. This was present even with the lowest hypericin concentration. Cells without hypericin or without illumination were not affected. These photosensitizing effects of hypericin could be suitable for clinical application and could lead to the development of an intraoperative photodynamic therapy of head neck squamous cell carcinomas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Kim AJ, Suh JD, Sercarz JA, Abemayor E, Head C et al (2007) Salvage surgery with free flap reconstruction: factors affecting outcome after treatment of recurrent head and neck squamous carcinoma. Laryngoscope 117:1019–1023
Juarranz A, Jaén P, Sanz-Rodríguez F, Cuevas J, González S (2008) Photodynamic therapy of cancer. Basic principles and applications. Clin Transl Oncol 10:148–154
Bredell MG, Besic E, Maake C, Walt H (2010) The application and challenges of clinical PD-PDT in the head and neck region: a short review. J Photochem Photobiol B 101:185–190
Brockmann H, Haschad MN, Maier K, Pohl F (1939) Hypericin, the photodynamically active pigment from Hypericum perforatum. Naturwissenschaften 27:550
Agostinis P, Vantieghem A, Merlevede W, de Witte PA (2002) Hypericin in cancer treatment: more light on the way. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34:221–241
Buytaert E, Dewaele M, Agostinis P (2007) Molecular effectors of multiple cell death pathways initiated by photodynamic therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1776:86–107
Siboni G, Weitman H, Freeman D, Mazur Y, Malik Z et al (2002) The correlation between hydrophilicity of hypericins and helianthrone: internalization mechanisms, subcellular distribution and photodynamic action in colon carcinoma cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 1:483–491
Kascakova S, Nadova Z, Mateasik A, Mikes J, Huntosova V et al (2008) High level of low-density lipoprotein receptors enhance hypericin uptake by U-87 MG cells in the presence of LDL. Photochem Photobiol 84:120–127
Huygens A, Kamuhabwa AR, Roskams T, Van Cleynenbreugel B, Van Poppel H et al (2005) Permeation of hypericin in spheroids composed of different grade transitional cell carcinoma cell lines and normal human urothelial cells. J Urol 174:69–72
Ali SM, Olivo M (2002) Bio-distribution and subcellular localization of hypericin and its role in PDT induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Int J Oncol 21:531–540
Karioti A, Bilia AR (2010) Hypericins as potential leads for new therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci 11:562–594
Rangan SR (1972) A new human cell line (FaDu) from a hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 29:117–121
Kubin A, Wierrani F, Burner U, Alth G, Grünberger W (2005) Hypericin—the facts about a controversial agent. Curr Pharm Des 11:233–253
Huygens A, Crnolatac I, Develter J, Van Cleynenbreugel B, Van der Kwast T et al (2008) Differential accumulation of hypericin in spheroids composed of T-24 transitional cell carcinoma cells expressing different levels of E-cadherin. J Urol 179:2014–2019
Seitz G, Warmann SW, Armeanu S, Heitmann H, Ruck P et al (2007) In vitro photodynamic therapy of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Int J Oncol 30:615–620
VanderWerf QM, Saxton RE, Chang A, Horton D, Paiva MB et al (1996) Hypericin: a new laser phototargeting agent for human cancer cells. Laryngoscope 106:479–483
Seitz G, Krause R, Fuchs J, Heitmann H, Armeanu S et al (2008) In vitro photodynamic therapy in pediatric epithelial liver tumors promoted by hypericin. Oncol Rep 20:1277–1282
Wessels JT, Busse AC, Rave-Fränk M, Zänker S, Hermann R et al (2008) Photosensitizing and radiosensitizing effects of hypericin on human renal carcinoma cells in vitro. Photochem Photobiol 84:228–235
Theodossiou TA, Hothersall JS, De Witte PA, Pantos A, Agostinis P (2009) The multifaceted photocytotoxic profile of hypericin. Mol Pharm 6:1775–1789
Wang X, Guo Y, Yang S, Wang C, Fu X et al (2010) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of photodynamic hypericin therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:847–853
Agostinis P, Assefa Z, Vantieghem A, Vandenheede JR, Merlevede W et al (2000) Apoptotic and anti-apoptotic signaling pathways induced by photodynamic therapy with hypericin. Adv Enzyme Regul 40:157–182
Sanovic R, Krammer B, Grumboeck S, Verwanger T (2009) Time-resolved gene expression profiling of human squamous cell carcinoma cells during the apoptosis process induced by photodynamic treatment with hypericin. Int J Oncol 35:921–939
Ali SM, Olivo M (2003) Mechanisms of action of phenanthroperylenequinones in photodynamic therapy (review). Int J Oncol 22:1181–1191
Blank M, Lavie G, Mandel M, Hazan S, Orenstein A et al (2004) Antimetastatic activity of the photodynamic agent hypericin in the dark. Int J Cancer 111:596–603
Martínez-Poveda B, Quesada AR, Medina MA (2005) Hypericin in the dark inhibits key steps of angiogenesis in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 516:97–103
Besic Gyenge E, Forny P, Lüscher D, Laass A, Walt H et al (2012) Effects of hypericin and a chlorin based photosensitizer alone or in combination in squamous cell carcinoma cells in the dark. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 9:321–331
Jerjes W, Upile T, Petrie A, Riskalla A, Hamdoon Z et al (2010) Clinicopathological parameters, recurrence, locoregional and distant metastasis in 115 T1–T2 oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Head Neck Oncol 2:9
Traynor NJ, Beattie PE, Ibbotson SH, Moseley H, Ferguson J et al (2005) Photogenotoxicity of hypericin in HaCaT keratinocytes: implications for St. John’s Wort supplements and high dose UVA-1 therapy. Toxicol Lett 158:220–224
Kah JC, Lau WK, Tan PH, Sheppard CJ, Olivo M (2008) Endoscopic image analysis of photosensitizer fluorescence as a promising noninvasive approach for pathological grading of bladder cancer in situ. J Biomed Opt 13:054022
Alecu M, Ursaciuc C, Hãlãlãu F, Coman G, Merlevede W et al (1998) Photodynamic treatment of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma with hypericin. Anticancer Res 18:4651–4654
Olivo M, Fu CY, Raghavan V, Lau WK (2012) New frontier in hypericin-mediated diagnosis of cancer with current optical technologies. Ann Biomed Eng 40:460–473
Ritz R, Müller M, Weller M, Dietz K, Kuci S et al (2005) Hypericin: a promising fluorescence marker for differentiating between glioblastoma and neurons in vitro. Int J Oncol 27:1543–1549
Ritz R, Daniels R, Noell S, Feigl GC, Schmidt V et al (2012) Hypericin for visualization of high grade gliomas: first clinical experience. Eur J Surg Oncol 38:352–360
Thong PS, Olivo M, Chin WW, Bhuvaneswari R, Mancer K et al (2009) Clinical application of fluorescence endoscopic imaging using hypericin for the diagnosis of human oral cavity lesions. Br J Cancer 101:1580–1584
Head CS, Luu Q, Sercarz J, Saxton R (2006) Photodynamic therapy and tumor imaging of hypericin-treated squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol 4:87
Gerstner AO, Laffers W, Schade G, Göke F, Martin R, Thies B (2012) Endoscopy of the larynx by hyperspectral imaging. HNO 60:1047–1052
Gerstner AO, Martin R, Westermann S, Mahlein AK, Schmidt K, Thies B, Laffers W (2013) Hyperspectral imaging in head & neck oncology. Laryngorhinootologie 92:453–457
Li J, Oyen R, Verbruggen A, Ni Y (2013) Small Molecule Sequential Dual-Targeting Theragnostic Strategy (SMSDTTS): from preclinical experiments towards possible clinical anticancer applications. J Cancer 4:133–145
Acknowledgments
This study was not supported by any grant.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laffers, W., Busse, AC., Mahrt, J. et al. Photosensitizing effects of hypericin on head neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 711–718 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2984-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2984-8