Abstract
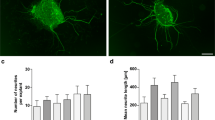
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) is a growth factor of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily. Members of this protein family are involved in the development of various mammalian tissues, including the inner ear. As their notations indicate, they also have well-known effects on bone formation and regeneration. In this study, we examined the influence of rhBMP-2 on spiral ganglion (SG) neurite growth in vitro and showed the presence of its most preferred receptor BMPR-IB in spiral ganglion cells both in vitro and in vivo. SG explants of postnatal day 4 rats were analysed for neurite length and number after organotypical cell culture for 72 h, fixation and immunolabeling. Different concentrations of rhBMP-2 were used in a serum-free culture media. Neurite growth was compared with control groups that lacked stimulative effects; with neutrophin-3 (NT-3), which is a well-established positive stimulus on neurite length and number; and with combinations of these parameters. The results display that neurite number and total neurite length per explant in particular concentrations of rhBMP-2 increased by a maximum factor of two, while the mean neurite length was not affected. NT-3 demonstrated a much more potent effect, delivering a maximum increase of a factor of five. Furthermore, a combination of both growth factors shows a predominant effect on NT-3. Immunohistological detection of BMPR-IB was successful both in cell culture explants and in paraffin-embedded sections of animals of different ages. The results show that rhBMP-2 is, among other growth factors, a positive stimulus for SG neurite growth in vitro. Most growth factors are unstable and cannot be attached to surfaces without loss of their biological function. In contrast, rhBMP-2 can be attached to metal surfaces without loss of activity. Our findings suggest in vivo studies and a future clinical application of rhBMP-2 in cochlear implant technology to improve the tissue/electrode interface.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pettingill LN, Richardson RT, Wise AK, O’Leary SJ, Shepherd RK (2007) Neurotrophic factors and neural prostheses: potential clinical applications based upon findings in the auditory system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54:1138–1148
Firszt JB, Holden LK, Skinner MW, Tobey EA, Peterson A, Gaggl W, Runge-Samuelson CL, Wackym PA (2004) Recognition of speech presented at soft to loud levels by adult cochlear implant recipients of three cochlear implant systems. Ear Hear 25:375–387
Arnoldner C, Riss D, Baumgartner WD, Kaider A, Hamzavi JS (2007) Cochlear implant channel separation and its influence on speech perception—implications for a new electrode design. Audiol Neurootol 12:313–324
Bhattacharya A, Zeng FG (2007) Companding to improve cochlear-implant speech recognition in speech-shaped noise. J Acoust Soc Am 122:1079–1089
Chen GD (2006) Prestin gene expression in the rat cochlea following intense noise exposure. Hear Res 222:54–61
Lautermann J, Dehne N, Schacht J, Jahnke K (2004) Aminoglycoside- and cisplatin-ototoxicity: from basic science to clinics. Laryngol 83:317–323
Liu XZ, Yan D (2007) Ageing and hearing loss. J Pathos 211:188–197
Schwander M, Sczaniecka A, Grillet N, Bailey JS, Avenarius M, Najmabadi H, Steffy BM, Federe GC, Lagler EA, Banan R, Hice R, Grabowski-Boase L, Keithley EM, Ryan AF, Housley GD, Wiltshire T, Smith RJ, Tarantino LM, Muller U (2007) A forward genetics screen in mice identifies recessive deafness traits and reveals that pejvakin is essential for outer hair cell function. J Neurosci 27:2163–2175
Glueckert R, Pfaller K, Kinnefors A, Rask-Andersen H, Schrott-Fischer A (2005) The human spiral ganglion: new insights into ultrastructure, survival rate and implications for cochlear implants. Audiol Neurootol 10:258–273
Dodson HC, Mohuiddin A (2000) Response of spiral ganglion neurones to cochlear hair cell destruction in the guinea pig. J Neurocytol 29:525–537
Friedmann TB, Griffith AJ (2003) Human nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 4:341–402
Lawner BE, Harding GW, Bohne BA (1997) Time course of nerve-fiber regeneration in the noise-damaged mammalian cochlea. Int J Dev Neurosci 15:601–617
Staecker H, Gabaizadeh R, Federoff H, Van De Water TR (1998) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene therapy prevents spiral ganglion degeneration after hair cell loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:7–13
McGuinness SL, Shepherd RK (2005) Exogenous BDNF rescues rat spiral ganglion neurons in vivo. Otol Neurotol 23:1064–1072
Whitlon DS, Grover M, Tristano J, Williams T, Coulson MT (2007) Culture conditions determine the prevalence of bipolar and monopolar neurons in cultures of dissociated spiral ganglion. Neuroscience 146:833–840
Shepherd RK, Coco A, Epp SB, Crook JM (2005) Chronic depolarization enhances the trophic effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rescuing auditory neurons following a sensorineural hearing loss. J Comp Neurol 486:145–158
Dazert S, Battaglia A, Ryan AF (1997) Transfection of neonatal rat cochlear cells in vitro with an adenovirus vector. Int J Dev Neurosci 15:595–600
Stöver T, Paasche G, Lenarz T, Ripken T, Breitenfeld P, Lubatschowski H, Fabian T (2007) Development of a drug delivery device: using the femtosecond laser to modify cochlear implant electrodes. Cochlear Implants Int 8:38–52
Plontke SK, Siedow N, Wegener R, Zenner HP, Salt AN (2007) Cochlear pharmacokinetics with local inner ear drug delivery using a three-dimensional finite-element computer model. Audiol Neurootol 12:37–48
Shoji F, Yamasoba T, Magal E, Dolan DF, Altschuler RA, Miller JM (2000) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor has a dose dependent influence on noise-induced hearing loss in the guinea pig cochlea. Hear Res 142:41–55
Stover T, Yagi M, Raphael Y (2000) Transduction of the contralateral ear after adenovirus-mediated cochlear gene transfer. Gene Ther 7:377–383
Dazert S, Kim D, Luo L, Aletsee C, Garfunkel S, Maciag T, Baird A, Ryan AF (1998) Focal delivery of fibroblast growth factor-1 by transfected cells induces spiral ganglion neurite targeting in vitro. J Cell Physiol 177:123–129
Aletsee C, Brors D, Mlynski R, Ryan AF, Dazert S (2003) Branching of spiral ganglion neurites is induced by focal application of fibroblast growth factor-1. Laryngoscope 113:791–796
Miller JM, Le Prell CG, Prieskorn DM, Wys NL, Altschuler RA (2007) Delayed neurotrophin treatment following deafness rescues spiral ganglion cells from death and promotes regrowth of auditory nerve peripheral processes: effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and fibroblast growth factor. J Neurosci Res 85:1959–1969
Staecker H, Kopke R, Malgrange B, Lefebvre P, Van de Water TR (1996) NT-3 and/or BDNF therapy prevents loss of auditory neurons following loss of hair cells. Neuroreport 7:889–894
Jennissen HP, Zumbrink T, Chatzinikolaidou M, Steppuhn J (1999) Biocoating of implants with mediator molecules: surface enhancement of metals by treatment with chromosulfuric acid. Materialwiss Werkst 30:838–845
Jennissen HP (2002) Accelerated and improved osteointegration of implants biocoated with bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2). Ann NY Acad Sci 961:139–142
Becker J, Kirsch A, Schwarz F, Chatzinikolaidou M, Rothamel D, Lekovic V, Laub M, Jennissen HP (2006) Bone apposition to titanium implants biocoated with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). A pilot study in dogs. Clin Oral Investig 10:217–224
Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR (2004) Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors 22:233–241
Pujades C, Kamaid A, Alsina B, Giraldez F (2006) BMP-signaling regulates the generation of hair-cells. Dev Biol 292:55–67
Dazert S, Schick B, Hartensuer R, Volkenstein S, Aletsee C, Hansen S, Shehata-Dieler WE, EIgenthaler M, Walter U, Ryan AF, Brors D (2007) Hearing development and spiral ganglion neurite growth in VASP deficient mice. Brain Res 1178:73–82
Brors D, Bodmer D, Pak K, Aletsee C, Schäfers M, Dazert S, Ryan AF (2003) EphA4 provides repulsive signals to developing cochlear ganglion neurites mediated through ephrin-B2 and -B3. J Comp Neurol 462:90–100
Rumpf HM, Dopp E, Rettenmeier AW, Chatzinikolaidou M, Jennissen HP (2003) Absence of genotoxic effects after exposure of mammalian cells to the recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) prepared from E. coli. Materialwiss Werkst 34:1101–1105
Wiemann M, Rumpf HM, Bingmann D, Jennissen HP (2001) The binding of rhBMP-2 to the receptors of viable MC3T3-E1 cells and the question of cooperativity. Materialwiss Werkst 32:931–936
Mlynski R, Volkenstein S, Hansen S, Brors D, Ebmeyer J, Dazert S (2007) Interaction of cochlear nucleus explants with semiconductor materials. Laryngoscope 117:1216–1222
Mlynski R, Brors D, Aletsee C, Dazert S (2002) Histomorphometric assessment of spiral ganglion neurite outgrowth in vitro. Laryngol 81:184–188
Bilsland J, Rigby M, Young L, Harper S (1999) A rapid method for semi-quantitative analysis of neurite outgrowth from chick DRG explants using image analysis. J Neurosci Methods 92:75–85
Oh SH, Johnson R, Wu DK (1996) Differential expression of bone morphogenetic proteins in the developing vestibular and auditory sensory organs. J Neurosci 16:6463–6475
Thomadakis G, Ramoshebi LN, Crooks J, Rueger DC, Ripamonti U (1999) Immunolocalization of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -3 and osteogenic protein-1 during murine tooth root morphogenesis and in other craniofacial structures. Eur J Oral Sci 107:368–377
Chang W, ten Dijke P, Wu DK (2002) BMP pathways are involved in otic capsule formation and epithelial–mesenchymal signaling in the developing chicken inner ear. Dev Biol 251:380–394
Liu W, Oh SH, Kang YkY, Li G, Doan TM, Little M, Li L, Ahn K, Crenshaw EB 3rd, Frenz DA (2003) Bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4): a regulator of capsule chondrogenesis in the developing mouse inner ear. Dev Dyn 226:427–438
Marzella PL, Gillespie LN (2002) Role of trophic factors in the development, survival and repair of primary auditory neurons. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 29:363–371
Whitlon DS, Ketels KV, Coulson MT, Williams T, Grover M, Edpao W, Richter CP (2006) Survival and morphology of auditory neurons in dissociated cultures of newborn mouse spiral ganglion. Neuroscience 138:653–662
Marzella PL, Gillespie LN, Clark GM, Bartlett PF, Kilpatrick TJ (1999) The neurotrophins act synergistically with LIF and members of the TGF-beta superfamily to promote the survival of spiral ganglia neurons in vitro. Hear Res 138:73–80
Brors D, Aletsee C, Schwager K, Mlynski R, Hansen S, Schäfers M, Ryan AF, Dazert S (2002) Interaction of spiral ganglion neuron processes with alloplastic materials in vitro(1). Hear Res 167:110–121
Roehm PC, Hansen MR (2005) Strategies to preserve or regenerate spiral ganglion neurons. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13:294–300
Lefebvre PP, Malgrange B, Staecker H, Moghadass M, Van de Water TR, Moonen G (1994) Neurotrophins affect survival and neuritogenesis by adult injured auditory neurons in vitro. Neuroreport 5:865–868
Wei D, Jin Z, Järlebark L, Scarfone E, Ulfendahl M (2007) Survival, synaptogenesis, and regeneration of adult mouse spiral ganglion neurons in vitro. Dev Neurobiol 67:108–122
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. Susanne Kanabey for technical assistance in histology and immunolabeling and Patrick Hsu for his comments on the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volkenstein, S., Brors, D., Hansen, S. et al. Influence of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on spiral ganglion neurite growth in vitro. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266, 1381–1389 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-0930-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-0930-y