Abstract
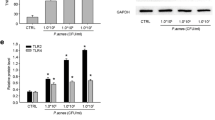
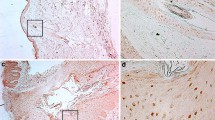
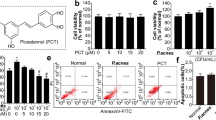
Propionibacterium acnes plays an important role in the pathogenesis of acne and it is established that this bacteria is involved in the induction and maintenance of the inflammatory phase of acne. The aim of our work was to determine if P. acnes extracts could modulate integrins and filaggrin in vitro expression by keratinocytes. Integrins and filaggrin expression was examined using immunohistochemistry technique both on Normal Human Epiderminal Keratinocytes (NHEK) and on deep-frozen sections of normal human skin explants incubated with three different P. acnes extracts. In addition, the expression of filaggrin was investigated on biopsies of acne lesions and by western-blot associated with its precursor profilaggrin. We demonstrated that P. acnes extracts induced β1 integrin expression significantly on both proliferating keratinocytes and differentiated keratinocytes. In addition, P. acnes induced α3, α6s and αVβ6 integrin expression and filaggrin expression on differentiated keratinocytes. Finally P. acnes extracts increased filaggrin expression by suprabasal layer of epidermis of explants. Western-blot confirmed that total amount of filaggrin was increased. These results indicate that P. acnes extracts are directly able to modulate the differentiation of keratinocytes suggesting that this bacteria play a role not only in the development of inflammatory acne lesions but also in the formation of the microcomedo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brakebusch C, Fassler R (2005) β1 integrin function in vivo: adhesion, migration and more. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24:403–411
Bruggemann H, Henne A, Hoster F et al (2004) The complete genome sequence of Propionibacterium acnes, a commensal of human skin. Science 305:671–673
Cunliffe WJ, Holland DB, Clark SM, Stables GI (2000) Comedogenesis: some new aetiological, clinical and therapeutic strategies. Br J Dermatol 142:1084–1091
Dale BA (1985) Filaggrin, the matrix protein of keratin. Am J Dermatopathol 7:65–68
Graham GM, Farrar MD, Cruse-Sawyer JE, Holland KT, Ingham E (2004) Proinflammatory cytokine production by human keratinocytes stimulated with Propionibacterium acnes and P. acnes GroEL. Br J Dermatol 150:421–428
Guy R, Kealey T (1998) The effects of inflammatory cytokines on the isolated human sebaceous infundibulum. J Invest Dermatol 110:410–415
Jeremy AH, Holland DB, Roberts SG, Thomson KF, Cunliffe WJ (2003) Inflammatory events are involved in acne lesion initiation. J Invest Dermatol 121:20–27
Jugeau S, Tenaud I, Knol AC et al (2005) Induction of toll-like receptors by Propionibacterium acnes. Br J Dermatol 153:1105–1113
Kurokawa I, Mayer-da-Silva A, Gollnick H, Orfanos CE (1988) Monoclonal antibody labeling for cytokeratins and filaggrin in the human pilosebaceous unit of normal, seborrhoeic and acne skin. J Invest Dermatol 91:566–571
Leyden JJ, McGinley KJ, Vowels B (1998) Propionibacterium acnes colonization in acne and nonacne. Dermatology 196:55–58
Nagy I, Pivarcsi A, Koreck A, Szell M, Urban E, Kemeny L (2005) Distinct strains of Propionibacterium acnes induce selective human beta-defensin-2 and interleukin-8 expression in human keratinocytes through toll-like receptors. J Invest Dermatol 124:931–938
Schaller M, Loewenstein M, Borelli C et al (2005) Induction of a chemoattractive proinflammatory cytokine response after stimulation of keratinocytes with Propionibacterium acnes and coproporphyrin III. Br J Dermatol 153:66–71
Simon M, Sebbag M, Haftek M et al (1995) Monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal filaggrin, some not recognizing profilaggrin. J Invest Dermatol 105:432–437
van der Flier A, Sonnenberg A (2001) Function and interactions of integrins. Cell Tissue Res 305:285–298
Watt FM (2002) Role of integrins in regulating epidermal adhesion, growth and differentiation. Embo J 21:3919–3926
Watt FM (2002) The stem cell compartment in human interfollicular epidermis. J Dermatol Sci 28:173–180
Zouboulis CC (2001) Is acne vulgaris a genuine inflammatory disease? Dermatology 203:277–279
Acknowledgments
Financial support and P. acnes extracts were provided by Pierre Fabre Laboratories (Toulouse, France). No conflicts of interest exist. We thank surgeons from the plastic surgery Department of Nantes Hospital for abdominal skin samples and the pediatric surgery Department of Nantes Hospital for foreskin samples. The authors thank Simon M. (Toulouse) for antibodies AHF2 and AHF7 gift.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jarrousse, V., Castex-Rizzi, N., Khammari, A. et al. Modulation of integrins and filaggrin expression by Propionibacterium acnes extracts on keratinocytes. Arch Dermatol Res 299, 441–447 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-007-0774-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-007-0774-5