Abstract
Introduction
The accuracy of acetabular cup placement using conventional portable imageless navigation systems in total hip arthroplasty (THA) in the lateral decubitus position remains challenging. Several novel portable imageless navigation systems have been developed recently to improve cup placement accuracy in THA. This study compared the accuracy of acetabular cup placement using a conventional accelerometer-based portable navigation (c-APN) system and a novel accelerometer-based portable navigation (n-APN) system during THA in the lateral decubitus position.
Materials and methods
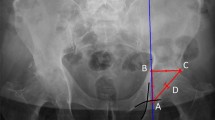
This retrospective cohort study compared 45 THAs using the c-APN and 45 THAs using the n-APN system. The primary outcomes were the absolute errors between the intraoperative and postoperative values of acetabular cup radiographic inclination and anteversion angles and the percentage of cases with absolute errors within 5°. Intraoperative values were shown on navigation systems, and postoperative measurements were conducted using computed tomography images.
Results
The median absolute errors of the cup inclination angles were significantly smaller in the n-APN group than in the c-APN group (3.9° [interquartile range 2.2°–6.0°] versus 2.2° [interquartile range 1.0°–3.3°]; P = 0.002). Additionally, the median absolute errors of the cup anteversion angles were significantly smaller in the n-APN group than in the c-APN group (4.4° [interquartile range 2.4°–6.5°] versus 1.9° [interquartile range 0.8°–2.7°]; P < 0.001). Significant differences were observed in the percentage of cases with absolute errors within 5° of inclination (c-APN group 67% versus n-APN group 84%; P = 0.049) and anteversion angles (c-APN group 62% versus n-APN group 91%; P = 0.001).
Conclusions
The n-APN system improved the accuracy of the cup placement compared to the c-APN system for THA in the lateral decubitus position.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Wasterlain AS, Buza JA 3rd, Thakkar SC, Schwarzkopf R, Vigdorchik J (2017) Navigation and robotics in total hip arthroplasty. JBJS Rev 5:e2. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.16.00046
Danoff JR, Bobman JT, Cunn G, Murtaugh T, Gorroochurn P, Geller JA, Macaulay W (2016) Redefining the Acetabular component safe zone for posterior Approach Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 31:506–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2015.09.010
Vigdorchik JM, Sharma AK, Buckland AJ, Elbuluk AM, Eftekhary N, Mayman DJ, Carroll KM, Jerabek SA (2021) 2021 Otto Aufranc Award: a simple hip- spine classification for total hip arthroplasty: validation and a large multicentre series. Bone Joint J 103–B:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.103B7
Hayashi S, Hashimoto S, Takayama K, Matsumoto T, Kamenaga T, Fujishiro T, Hiranaka T, Niikura T, Kuroda R (2020) Evaluation of the accuracy of acetabular cup orientation using the accelerometer-based portable navigation system. J Orthop Sci 25:612–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2019.09.012
Tanino H, Nishida Y, Mitsutake R, Ito H (2020) Portable accelerometer-based Navigation System for Cup Placement of total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. J Arthroplasty 35:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2019.08.044
Tanino H, Nishida Y, Mitsutake R, Ito H (2021) Accuracy of a portable accelerometer-based navigation system for cup placement and intraoperative leg length measurement in total hip arthroplasty: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 22:299. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04167-y
Kiyohara M, Hamai S, Shiomoto K, Harada S, Harada T, Motomura G, Ikemura S, Fujii M, Kawahara S, Nakashima Y (2022) Does accelerometer-based portable navigation provide more accurate and precise cup orientation without prosthetic impingement than conventional total hip arthroplasty? A randomized controlled study. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 17:1007–1015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02592-5
Tetsunaga T, Yamada K, Tetsunaga T, Furumatsu T, Sanki T, Kawamura Y, Ozaki T (2021) Comparison of the accuracy of CT- and accelerometer-based navigation systems for cup orientation in total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int 31:603–608. https://doi.org/10.1177/1120700020904940
Tetsunaga T, Yamada K, Tetsunaga T, Sanki T, Kawamura Y, Ozaki T (2020) An accelerometer-based navigation system provides acetabular cup orientation accuracy comparable to that of computed tomography-based navigation during total hip arthroplasty in the supine position. J Orthop Surg Res 15:147. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01673-y
Ong CB, Chiu YF, Premkumar A, Gonzalez Della Valle A (2023) Use of a novel imageless navigation system reduced fluoroscopy exposure and improved acetabular positioning in anterior approach total hip arthroplasty: a case–control study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143:2739–2745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04520-3
Hasegawa M, Naito Y, Tone S, Sudo A (2022) Accuracy of a novel accelerometer-based navigation (Naviswiss) for total hip arthroplasty in the supine position. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-022-05495-3
Ohyama Y, Sugama R, Kim Y, Ohta Y, Minoda Y, Nakamura H (2023) A new accelerometer-based portable navigation system provides high accuracy of acetabular cup placement in total hip arthroplasty in both the lateral decubitus and supine positions. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143:4473–4480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04675-z
Kuribayashi M, Takahashi KA, Fujioka M, Ueshima K, Inoue S, Kubo T (2010) Reliability and validity of the Japanese orthopaedic association hip score. J Orthop Sci 15:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-010-1490-0
Higuchi F, Gotoh M, Yamaguchi N, Suzuki R, Kunou Y, Ooishi K, Nagata K (2003) Minimally invasive uncemented total hip arthroplasty through an anterolateral approach with a shorter skin incision. J Orthop Sci 8:812–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-003-0715-x
Murray DW (1993) The definition and measurement of acetabular orientation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75:228–232. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.75b2.8444942
Ektas N, Scholes C, Ruiz AM, Ireland J (2020) Validity of intraoperative imageless navigation (Naviswiss) for component positioning accuracy in primary total hip arthroplasty: protocol for a prospective observational cohort study in a single-surgeon practice. BMJ Open 10:e037126. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037126
Widmer KH, Zurfluh B (2004) Compliant positioning of total hip components for optimal range of motion. J Orthop Res 22:815–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orthres.2003.11.001
Esposito CI, Miller TT, Kim HJ, Barlow BT, Wright TM, Padgett DE, Jerabek SA, Mayman DJ (2016) Does degenerative lumbar spine Disease Influence Femoroacetabular Flexion in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res 474:1788–1797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-016-4787-2
Tsukada S, Ogawa H, Hirasawa N, Nishino M, Aoyama H, Kurosaka K (2022) Augmented reality- vs accelerometer-based portable Navigation System to improve the Accuracy of Acetabular Cup Placement during Total Hip Arthroplasty in the lateral decubitus position. J Arthroplasty 37:488–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2021.11.004
Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, Compere CL, Zimmerman JR (1978) Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am 60:217–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5451-8_27
Callanan MC, Jarrett B, Bragdon CR, Zurakowski D, Rubash HE, Freiberg AA, Malchau H (2011) The John Charnley award: risk factors for cup malpositioning: quality improvement through a joint registry at a tertiary hospital. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:319–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1487-1
Iwakiri K, Kobayashi A, Ohta Y, Takaoka K (2017) Efficacy of the anatomical-pelvic-plane positioner in total hip arthroplasty in the lateral decubitus position. J Arthroplasty 32:1520–1524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2016.11.048
Schwarzkopf R, Muir JM, Paprosky WG, Seymour S, Cross MB, Vigdorchik JM (2017) Quantifying pelvic motion during total hip arthroplasty using a New Surgical Navigation device. J Arthroplasty 32:3056–3060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2017.04.046
Hayashi S, Hashimoto S, Kuroda Y, Nakano N, Matsumoto T, Ishida K, Shibanuma N, Kamenaga T, Kuroda R (2021) Accuracy of cup position following robot-assisted total hip arthroplasty may be associated with surgical approach and pelvic tilt. Sci Rep 11:7578. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86849-0
Acknowledgements
We thank Susumu Takemura and Shigekazu Mizokawa for the assistance of data collection of this study and the orthopedic surgery.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Yohei Ohyama. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yohei Ohyama and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in accordance with ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards, and the study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine.
Informed consent
All patients provided written informed consent prior to their participation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Device status/drug statement
The FDA or corresponding national agency approved the device(s)/drug(s) for this indication.
Competing of interests
Each author certifies that they have no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, or patent/licensing arrangements) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ohyama, Y., Minoda, Y., Sugama, R. et al. A novel imageless accelerometer-based navigation system improves acetabular cup placement accuracy during total hip arthroplasty in the lateral decubitus position. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-024-05376-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-024-05376-5