Abstract
Introduction
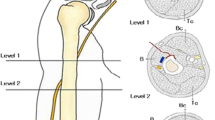
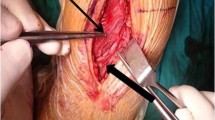
Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPPO) is increasingly favored for treating humeral shaft fractures (HSFs). However, conventional MIPPO techniques pose challenges in fixing fractures near fossa olecranon and carry a risk of iatrogenic radial nerve palsy. A novel technique using a medial MIPPO for treating humeral shaft fractures (HSFs) is described. Results of clinical follow-up are presented.
Materials and methods
This study is a retrospective case series study. Twenty-one patients (mean age 43.9 ± 17.66 [22‒81] years) with HSFs were treated with the novel MIPPO fixation method. Clinical outcomes including time for radiographic consolidation, Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) score, and complications were assessed at the last follow-up. The mean follow-up was 26 ± 17.12 (range 12–67) months.
Results
All patients had a bony union at a mean of 15.76 ± 6.74 (range 8–40) weeks based on X-ray with an early and aggressive range of motion. The complication rate was 0. The mean DASH score was3.29 ± 4.09 (range 0–14.17) at the time of the last follow-up. The mean screw density was 0.49 ± 0.1 (range 0.2–0.65).
Conclusion
This novel surgical technique for HSFs is a viable alternative to previously described methods with the advantage of being less prone to nerve injury and easy to fix distal extra-articular HSFs. The learning curve is short.
Level of evidence
IV.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Klenerman L (1966) Fractures of the shaft of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br 48(1):105–111
Shields E, Sundem L, Childs S et al (2016) The impact of residual angulation on patient reported functional outcome scores after non-operative treatment for humeral shaft fractures. Injury 47(4):914–918
Crespo AMKS, Egol KA (2018) Set it and forget it: diaphyseal fractures of the humerus undergo minimal change in angulation after functional brace application. Iowa Orthop J 38:73–77 (PMID: 30104927; PMCID: PMC6047395)
Gallusser N, Barimani B, Vauclair F (2021) Humeral shaft fractures. EFORT Open Reviews 6(1):24–34
Ramo L, Sumrein BO, Lepola V et al (2020) Effect of surgery vs functional bracing on functional outcome among patients with closed displaced humeral shaft fractures: the FISH randomized clinical trial. JAMA 323(18):1792–1801
Matsunaga FTTM, Matsumoto MH, Netto NA et al (2017) Minimally invasive osteosynthesis with a bridge plate versus a functional brace for humeral shaft fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 99(7):583–592
Kocialkowski C, Sheridan B (2020) Humeral shaft fractures: how effective really is functional bracing? Should Elb 13(6):620–626
van de Wall BJM, Theus C, Link BC et al (2019) Absolute or relative stability in plate fixation for simple humeral shaft fractures. Injury 50(11):1986–1991
Beeres FJ, Diwersi N, Houwert MR et al (2021) ORIF versus MIPPO for humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized clinical trials and observational studies. Injury 52(4):653–663
Keshav K, Baghel A, Kumar V et al (2021) Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis better than conventional open plating for humeral shaft fractures? A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Indian J Orthop 55:283–303
Giordano M, Giordano V, Gameiro VS, Belangero W, Livani B, Giannoudis PV, Krettek C (2021) Anterior minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis technique (MIPPO) for humeral shaft fractures: an anatomical study of neuromuscular structures at risk. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 31(3):449–458
Lee T, Yoon J (2016) Newly designed minimally invasive plating of a humerus shaft fracture; a different introduction of the plate. Int Orthop 40(12):2597–2602
Gallucci G, Boretto J, Vujovich A, Alfie V, Donndorff A, De Carli P (2014) Posterior minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fractures. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg 18(1):25–30
Lu S, Wu J, Xu S, Fu B, Dong J, Yang Y, Wang G, Xin M, Li Q, He TC, Wang F, Zhou D (2016) Medial approach to treat humeral mid-shaft fractures: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res 17(11):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-016-0366-1
Sanjay M et al (2017) Medial plating of humerus shaft fractures through anterolateral approach. IOSR JDMS 16(4):18–23. e-ISSN: 2279–0853, p-ISSN: 2279–0861
Meinberg EG, Agel J, Roberts CS, Karam MD, Kellam JF (2018) Fracture and dislocation classification compendium-2018. J Orthop Trauma 32(Suppl 1):S1–S170
Zogaib RK, Morgan S, Belangero PS et al (2014) Minimal invasive ostheosintesis for treatment of diaphiseal transverse humeral shaft fractures. Acta Ortopédica Brasileira 22(2):94–98
Sargeant HW, Farrow L, Barker S et al (2019) Operative versus non-operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review. Should Elb 12(4):229–242
Gomes GS, Zderic I, Ahrend M-D et al (2021) Is bridge plating of comminuted humeral shaft fractures advantageous when using compression plates with three versus two screws per fragment? A biomechanical cadaveric study. Biomed Res Int 2021:1–10 (PMID: 33748273; PMCID: PMC7960035)
Antoniac I, Stoia D, Ghiban B et al (2019) Failure analysis of a humeral shaft locking compression plate—surface investigation and simulation by finite element method. Materials 12(7):1128–1146
Lin J, Hou S-M (2000) Rotational alignment of humerus after closed locked nailing. J Trauma 49(5):854–859
Tan J, Lee H-J, Aminata I et al (2015) Radiographic landmark for humeral head rotation: a new radiographic landmark for humeral fracture fixation. Injury 46(4):666–670
Malavolta EA, Assunção JH, Pagotto RA et al (2016) The rotation of the humeral head does not alter radiographic evaluation of the head-shaft angle. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25(4):543–547
Oliver WM, Molyneux SG, White TO et al (2022) Routine fixation of humeral shaft fractures is cost-effective: cost-utility analysis of 215 patients at a mean of five years following nonoperative management. Bone Jt Open 3(7):566–572
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DL performed all the surgeries and is the major contributor in development of the surgical technique, and was responsible for the concept of study, the assembly, analysis and interpretation of the data, and the drafting of the article; JL collected and analyzed the datasets of the study; HY and ZL contributed to the writing of the article and was responsible for data and pictures collection; YZ was the independent observer who performed the clinical and radiological assessment. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or nonfinancial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was waived by the local Ethics Committee in view of the retrospective nature of the study and all the procedures being performed were part of the routine care.
Consent for publication
All the authors gave their consent to publish this final form of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 8442 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MP4 5333 KB)





Supplementary file8 (MP4 5025 KB)
Supplementary file9 (MP4 7275 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Liang, J., Yang, H. et al. Medial minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fractures: a case series and novel technique description. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143, 6657–6664 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-04992-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-04992-x