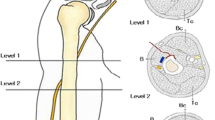
Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to evaluate the neuromuscular structures at risk during modified anterior minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis technique (Belangero–Livani) for humeral shaft fractures.
Methods
Eight fresh-frozen human specimens ranging from 38 to 82 years old were used. Specimens were positioned supine with the shoulder in 70° abduction and the forearm in full supination. Anterior minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis technique according to Belangero–Livani technique was performed in each specimen. Under radioscopic control, the plate was introduced in retrograde fashion through the subbrachialis path. Anatomical structures were inspected and different anatomical parameters were measured after dissection at the end of the surgical procedures. Measurements were performed using a high digital caliper. Statistical analysis was performed using the Pearson’s correlation coefficient test. A p value of < 0.05 was used to define statistical significance.
Results
There were no macroscopic lesions of myotendinous or neurovascular structures in any specimen. The mean distance between the radial nerve to the distal lateral end of the plate was 8.63 mm (range 4.14–13.83 mm). The mean total length of the humerus was 328.59 mm. We found a significant direct correlation between the total length of the humerus and both specimen height and weight.
Conclusion
The modified Belangero–Livani anterior MIPO technique for humeral shaft fractures performed in retrograde fashion is safe and useful, without major risk to the soft tissue of the anterior compartment of the arm, including the radial nerve in the lateral intermuscular septum. Intraoperative dissection, avoiding deep lateral retraction on the distal approach, minimizes the risk of radial nerve damage. Strict surgical planning and appreciation for the anatomic landmarks can reduce the risk of damage to neuromuscular structures.
Level of evidence
Level IV; Case series with no comparison group; Treatment study









Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Z, Zeng B, He X, Chen Q, Hu S (2010) Plating osteosynthesis of mild-distal humeral shaft fractures: minimally invasive versus conventional open reduction technique. Int Orthop 34(1):131–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0753-x
Apivatthakakul T, Arpornchayanon O, Bavornratanavech S (2005) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture is it possible? a cadaveric study and preliminary report. Injury 36(4):530–538
Benninger E, Meier C (2017) Minimally invasive lateral plate placement for metadiaphyseal fractures of the humerus and its implications for the distal insertion—it is not only about the radial nerve a cadaveric study. Injury 48(3):615–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2017.01.026
Chen J, Wu S, Ren J (2014) Ultrasonographic reference values for assessing normal radial nerve ultrasonography in the normal population. Neural Regen Res 9(20):1844–1849. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.143433
Chiarapattanakom P, Leechavengvongs S, Witoonchart K, Uerpairojkit C, Thuvasethakul P (1998) Anatomy and internal topography of the musculocutaneous nerve: the nerves to the biceps and brachialis muscle. J Hand Surg Am 23(2):250–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0363-5023(98)80122-6
Chou PH, Shyu JF, Ma HL, Wang ST, Chen TH (2008) Courses of the radial nerve differ between Chinese and Caucasians clinical implications. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:135–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-007-0019-0
Dell’Oca AAF (2002) The principle of helical implants unusual ideas worth considering. Injury 33(1):S-A1–S-A27. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-1383(02)00064-5
Dell’Oca AAF (2002) Case studies. Injury 33(Suppl1):29–40
Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Lorich DG (2005) Helical plating of the proximal humerus. Injury 36(10):1197–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2005.06.038
Guse TR, Ostrum RF (1995) The surgical anatomy of the radial nerve around the humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 320:149–153
Hohman E, Glatt V, Tetsworth K (2016) Minimally invasive plating versus either open reduction and plate fixation or intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Shoulder Elb Surg 25(10):1634–1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2016.05.014
Hu X, Xu S, Lu H, Chen B, Zhou X, He X et al (2016) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis vs conventional fixation techniques for surgically treated humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 11:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-016-0394-x
International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) (2020) Recommendations of good practice for the donation and study of human bodies and tissues for anatomical examination. January 2012:45. Plexus: Newsletter of the IFAA. https://www.ifaa.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/plexus_jan_2012-screen.pdf. Accessed 1 Apr 2020
Jiamton C, Ratreprasatsuk N, Jarayabhand R, Kritsaneephaiboon A, Apivatthakakul T (2019) The safety and feasibility of minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the posterior aspect of the humerus: a cadaveric study. Clin Anat 32(2):176–182. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.23220
Kim JW, Oh CW, Byun YS, Kim JJ, Park KC (2015) A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Orthop Trauma 29(4):189–194. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000232
Livani B, Belangero WD (2004) Osteosynthesis of the humeral shaft fractures, with bridge plate. Acta Ortop Bras 12(2):113–117. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-78522004000200007
Livani B, Belangero WD (2004) Bridging plate osteosynthesis of humeral shaft fractures. Injury 35(6):587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2003.12.003
Livani B, Belangero W, Andrade K, Zuiani G, Pratali R (2009) Is MIPO in humeral shaft fractures really safe? postoperative ultrasonographic evaluation. Int Orthop 33(6):1719–1723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0616-x
Mahajan AS, Kim YG, Kim JH, Dsa P, Lakhani A, Ok HS (2016) Is anterior bridge plating for mid-shaft humeral fractures a suitable option for patients predominantly involved in overhead activities? a functional outcome study in athletes and manual laborers. Clin Orthop Surg 8(4):358–366
Rayegani SM, Azadi A (2007) Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve injury induced by phlebotomy. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj 2:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-7221-2-6
Tetsworth K, Hohmann E, Glatt V (2018) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of humeral shaft fractures: current state of the art. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 26(18):652–661. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00238
Uzun Ö, Yeginoğlu G, Kalkışım SN, Öksüz CE, Zihni NB (2018) Evaluation of upper extremity anthropometric measurements in terms of sex estimation. Int J Res Med Sci 6(1):42–50. https://doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20175709
Wang C, Li J, Li Y, Dai G, Wang M (2015) Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture advantageous compared with the conventional open technique? J Shoulder Elb Surg 24(11):1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.07.032
Wilke J, Krause F, Niederer D, Engeroff T, Nürnberger F, Vogt L et al (2015) Appraising the methodological quality of cadaveric studies: validation of the QUACS scale. J Anat 226(5):440–446. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.12292
Ziran BH, Belangero W, Livani B, Pesantez R (2007) Percutaneous plating of the humerus with locked plating: technique and case report. J Trauma 63(1):205–210. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ta.0000231870.11908.3e
Zogaib RK, Morgan S, Belangero PS, Fernandes HJA, Belangero WD, Livani B (2014) Minimal invasive ostheosintesis for treatment of diaphyseal transverse humeral shaft fractures. Acta Ortop Bras 22(2):94–98. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-78522014220200698
Funding
The authors did not receive Grants or outside funding in support of their research for or preparation of this manuscript. Authors and any member of their families did not receive payments or other benefits or a commitment or agreement to provide such benefits from a commercial entity. No commercial entity paid or directed, or agreed to pay or direct, any benefits to any research fund, foundation, educational institution, or other charitable or nonprofit organization with which the authors are affiliated or associated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MG and VG were involved in conceptualization, data curation, investigation, and visualization. MG, VG, and CK were contributed to formal analysis, project administration, resources, supervision, and validation. VG was involved in writing—original draft. MG, VG, VSG, WB, BL, PVG, and CK were involved in writing—review and editing. Methodology was contributed by MG, VG, WB, CK. Funding acquisition was contributed by no one.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Vincenzo Giordano has the following disclosures: Zimmer Biomet: paid consultant and unpaid consultant. Peter V. Giannoudis has the following disclosures: Injury: Editorial or governing board. Christian Krettek has the following disclosures: Traumastiftung: Board or committee member; Springer: Publishing royalties, financial or material support; DFG: research support; AO: research support; BMBF: research support; Else Krömer: research support; Traumstiftung: research support. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study was performed according to the ethical procedures recommended by the international federation of associations of anatomists (IFAA) and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Klinik für Unfallchirurgie–MHH.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giordano, M., Giordano, V., Gameiro, V.S. et al. Anterior minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis technique (MIPO) for humeral shaft fractures: an anatomical study of neuromuscular structures at risk. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 31, 449–458 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-020-02792-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-020-02792-2