Abstract
Introduction
Periprosthetic fractures are difficult to manage. Plating technique has been considered a reliable form of management of periprosthetic fractures with a well-fixed stem, but a dependable and stable method of plate fixation to the bone is lacking. This study reports the clinical results using a locking attachment plate (LAP) instead of cable fixation to fix locking plates to a periprosthetic femoral shaft fracture.
Materials and methods
Nineteen patients with periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures around well-fixed stemmed implants were studied between August 2012 and December 2014. Patients were followed up for at least 1 year postoperatively. Median age was 74 years (range 56–96 years). Fractures were classified according to the Unified Classification System, Vancouver classification, and Su classification.
Procedure
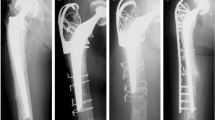
Open reduction was performed under minimal incision and the locking plate was fixed to the lateral cortex of the femoral shaft. The part of the shaft without a stem was fixed to the plate using 5.0-mm locking screws, and the part with an underlying stem was fixed using 3.5-mm locking screws through the LAP instead of cables. Postoperatively, patients were managed using general principles for femoral shaft fractures.
Results
Average follow-up was 16 months (range 12–36 months). All cases achieved fracture healing without loss of reduction. There were no cases of implant breakage or stem loosening at final follow-up. The average number of LAPs per fixation construct was 2.1 (range 1–4), and the average number of 3.5-mm locking screws through each LAP was 3.3 (range 2–4). The average value of plate screw density was 0.55 (range 0.37–0.8), and the average working length was four holes (range 2–8).
Conclusions
Using the LAP to manage periprosthetic fractures with a well-fixed stem could obviate the need for cable around the stem area and yield acceptable outcomes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fredin HO, Lindberg H, Carlsson AS (1987) Femoral fracture following hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand 58:20–22
Haidukewych GJ, Ricci W (2008) Locked plating in orthopaedic trauma: a clinical update. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 16:347–355
Haidukewych GJ, Langford JR, Liporace FA (2013) Revision for periprosthetic fractures of the hip and knee. Instr Course Lect 62:333–340
Haddad FS, Duncan CP, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG, Gross AE, Chandler HP (2002) Periprosthetic femoral fractures around well-fixed implants: use of cortical onlay allografts with or without a plate. J Bone Jt Surg Am 84-A:945–950
Wahnert D, Schroder R, Schulze M, Westerhoff P, Raschke M, Stange R (2014) Biomechanical comparison of two angular stable plate constructions for periprosthetic femur fracture fixation. Int Orthop 38:47–53
Pike J, Davidson D, Garbuz D, Duncan CP, O’Brien PJ, Masri BA (2009) Principles of treatment for periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures around well-fixed total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 17:677–688
Fulkerson E, Tejwani N, Stuchin S, Egol K (2007) Management of periprosthetic femur fractures with a first generation locking plate. Injury 38:965–972
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Oden A, Garellick G (2006) Risk factors for failure after treatment of a periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Bone Jt Surg Br 88:26–30
Ricci WM, Haidukewych GJ (2009) Periprosthetic femoral fractures. Instr Course Lect 58:105–115
O’Toole RV, Gobezie R, Hwang R, Chandler AR, Smith RM, Estok DM 2nd, Vrahas MS (2006) Low complication rate of LISS for femur fractures adjacent to stable hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 450:203–210
Graham SM, Mak JH, Moazen M, Leonidou A, Jones AC, Wilcox RK (2015) Periprosthetic femoral fracture fixation: a biomechanical comparison between proximal locking screws and cables. J Orthop Sci 20:875–880
Lenz M, Windolf M, Muckley T, Hofmann GO, Wagner M, Richards RG (2012) The locking attachment plate for proximal fixation of periprosthetic femur fractures–a biomechanical comparison of two techniques. Int Orthop 36:1915–1921
Dumpies CW, Conrad T, Marintschev I, Hofmann GO (2012) Locking attachment plate—first experience. Z Orthop Unfall 150:302–308
Kammerlander C, Kates SL, Wagner M, Roth T, Blauth M (2013) Minimally invasive periprosthetic plate osteosynthesis using the locking attachment plate. Oper Orthop Traumatol 25(398–408):410
Duncan CP, Haddad FS (2014) The Unified Classification System (UCS): improving our understanding of periprosthetic fractures. Bone Joint J 96-B:713–716
Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP (1999) Classification of the hip. Orthop Clin N Am 30:215–220
Su ET, DeWal H, Di Cesare PE (2004) Periprosthetic femoral fractures above total knee replacements. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 12:12–20
Tp R, Wm M (2000) AO Principles of Fracture Management. Thieme, New York
Egol KA, Kubiak EN, Fulkerson E, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ (2004) Biomechanics of locked plates and screws. J Orthop Trauma 18:488–493
Spina M, Rocca G, Canella A, Scalvi A (2014) Causes of failure in periprosthetic fractures of the hip at 1- to 14-year follow-up. Injury 45(Suppl 6):S85–S92
Bhattacharyya T, Chang D, Meigs JB, Estok DM 2nd, Malchau H (2007) Mortality after periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Bone Jt Surg Am 89:2658–2662
Konstantinidis L, Hauschild O, Beckmann NA, Hirschmüller A, Südkamp NP, Helwig P (2010) Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures with two different minimal invasive angle-stable plates: biomechanical comparison studies on cadaveric bones. Injury 41:1256–1261
Gautier E, Sommer C (2003) Guidelines for the clinical application of the LCP. Injury 34(Suppl 2):B63–B76
Hurkmans HL, Bussmann JB, Selles RW, Benda E, Stam HJ, Verhaar JA (2007) The difference between actual and prescribed weight bearing of total hip patients with a trochanteric osteotomy: long-term vertical force measurements inside and outside the hospital. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 88:200–206
Hustedt JW, Blizzard DJ, Baumgaertner MR, Leslie MP, Grauer JN (2012) Is it possible to train patients to limit weight bearing on a lower extremity? Orthopedics 35:e31–e37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
There is no funding source.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.B., Cho, JW., Lee, Y.H. et al. Locking attachment plate fixation around a well-fixed stem in periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137, 1193–1200 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2745-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2745-4