Abstract.
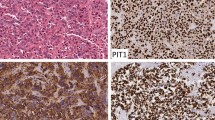
A 67-year-old woman presented with clinical features of hypercortisolism in association with an invasive pituitary macroadenoma. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-dependent Cushing's disease was documented, and the resected tumor was chromophobic, weakly positive with periodic-Schiff reagent, and showed immunostaining for ACTH and β-endorphin in a minority of adenoma cells. Both luteinizing hormone and α-subunit staining were also observed, but no follicle-stimulating hormone reactivity was seen. Ultrastructurally, the tumor showed typical features of a gonadotroph adenoma of female type. Immunoelectron microscopy showed that ACTH was not produced in corticotrophs, but in cells with the characteristic features of gonadotrophs. This represents the second report of a plurihormonal gonadotroph adenoma producing sufficient ACTH to result in pituitary-dependent Cushing's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Revised, accepted: 29 January 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Egensperger, .R., Scheithauer, .B., Horvath, .E. et al. Cushing's disease due to plurihormonal adrenocorticotropic hormone and gonadotropin-producing pituitary adenoma. Acta Neuropathol 102, 398–403 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010100376
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010100376