Abstract
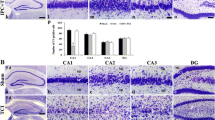
Previous studies indicated preconditioning of the brain with sublethal ischemic insults separated by many hours, protected tissues from a subsequent lethal insult. We recently reported neuroprotection by a rapid preconditioning paradigm where a sublethal ischemic insult preceded test ischemia by only 30 min. We hypothesize that neuroprotection caused by the rapid ischemic preconditioning (IPC) will result in lowered microglial, reactive astrocytes and increased normal neuronal cell counts. Wistar rats underwent normothermic (36.5–37 °C) global cerebral ischemia, produced by bilateral carotid artery ligation after lowering mean systemic blood pressure. The preconditioning ischemic insult lasted 2 min and was associated with a sufficient amount of time to provoke anoxic depolarization. After a 30-min reperfusion period, 10-min test ischemia was produced, and histopathology was assessed 3 and 7 days later. Normal neuronal cell counts for control rats at 3 days survival were significantly lower (by 58%) than in IPC animals. Although there was a trend toward protection in IPC rats at 7 days, the difference in normal neuronal cell count between the IPC and control groups was not significant. IPC rats at 3 days but not 7 days of survival showed a significantly lower microglial cell count (by 56%) than control rats. These results showed that the protection induced through IPC at 3 days of survival produced lower numbers of microglia, while maintaining normal neuronal cells. No significant differences between control and IPC groups were found in astrocytic cell count at any time of reperfusion in any region of the hippocampus studied. The beneficial effects of IPC may, therefore, involve anti-inflammatory processes that target microglial activation after cerebral ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 July 1998 / Revised: 30 September 1998 / Accepted: 21 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Pinzón, M., Vitro, T., Dietrich, W. et al. The effect of rapid preconditioning on the microglial, astrocytic and neuronal consequences of global cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 97, 495–501 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010051019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010051019