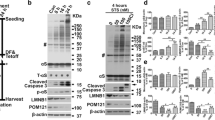
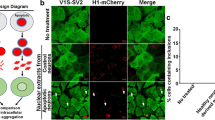
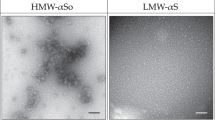
Abstract
Ample in vitro and in vivo experimental evidence supports the hypothesis that intercellular transmission of α-synuclein (αS) is a mechanism underlying the spread of αS pathology in Parkinson’s disease and related disorders. What remains unexplained is where and how initial transmissible αS aggregates form. In a previous study, we demonstrated that αS aggregates rapidly form in neurons with impaired nuclear membrane integrity due to the interaction between nuclear proaggregant factor(s) and αS and that such aggregates may serve as a source for αS seeding. In the present study, we identify histones as a potential nuclear proaggregant factor for αS aggregation in both apoptotic neurons and brains with αS pathology. We further demonstrate that histone-induced aggregates contain a range of αS oligomers, including protofibrils and mature fibrils, and that these αS aggregates can seed additional aggregation. Importantly, we demonstrate transmissibility in mouse brains from stereotaxic injection. This study provides new clues to the mechanism underlying initial pathological aggregation of αS in PD and related disorders, and could lead to novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolton SJ, Perry VH (1997) Histone H1; a neuronal protein that binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Neurocytol 26:823–831
Brix K, Summa W, Lottspeich F, Herzog V (1998) Extracellularly occurring histone H1 mediates the binding of thyroglobulin to the cell surface of mouse macrophages. J Clin Invest 102:283–293. doi:10.1172/JCI1614
Chase A (2015) Parkinson disease: traumatic brain injury increases the risk of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 11:184. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2015.39
Chen R, Kang R, Fan XG, Tang D (2014) Release and activity of histone in diseases. Cell Death Dis 5:e1370. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.337
Danzer KM, Kranich LR, Ruf WP, Cagsal-Getkin O, Winslow AR, Zhu L, Vanderburg CR, McLean PJ (2012) Exosomal cell-to-cell transmission of alpha synuclein oligomers. Mol Neurodegener 7:42. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-7-42
Desplats P, Lee HJ, Bae EJ, Patrick C, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Spencer B, Masliah E, Lee SJ (2009) Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13010–13015. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903691106
Dickson DW, Liu W, Hardy J, Farrer M, Mehta N, Uitti R, Mark M, Zimmerman T, Golbe L, Sage J, Sima A, D’Amato C, Albin R, Gilman S, Yen SH (1999) Widespread alterations of alpha-synuclein in multiple system atrophy. Am J Pathol 155:1241–1251
Emmanouilidou E, Elenis D, Papasilekas T, Stranjalis G, Gerozissis K, Ioannou PC, Vekrellis K (2011) Assessment of alpha-synuclein secretion in mouse and human brain parenchyma. PLoS ONE 6:e22225. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022225
Gabler C, Blank N, Hieronymus T, Schiller M, Berden JH, Kalden JR, Lorenz HM (2004) Extranuclear detection of histones and nucleosomes in activated human lymphoblasts as an early event in apoptosis. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1135–1144. doi:10.1136/ard.2003.011452
Gardner RC, Burke JF, Nettiksimmons J, Goldman S, Tanner CM, Yaffe K (2015) Traumatic brain injury in later life increases risk for Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 77:987–995. doi:10.1002/ana.24396
Goers J, Manning-Bog AB, McCormack AL, Millett IS, Doniach S, Di Monte DA, Uversky VN, Fink AL (2003) Nuclear localization of alpha-synuclein and its interaction with histones. Biochemistry 42:8465–8471. doi:10.1021/bi0341152
Hariton-Gazal E, Rosenbluh J, Graessmann A, Gilon C, Loyter A (2003) Direct translocation of histone molecules across cell membranes. J Cell Sci 116:4577–4586. doi:10.1242/jcs.00757
Iwatsubo T (2003) Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 250 Suppl 3:III11–14. doi:10.1007/s00415-003-1303-x
Jang A, Lee HJ, Suk JE, Jung JW, Kim KP, Lee SJ (2010) Non-classical exocytosis of alpha-synuclein is sensitive to folding states and promoted under stress conditions. J Neurochem 113:1263–1274. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06695.x
Jiang P, Gan M, Ebrahim AS, Castanedes-Casey M, Dickson DW, Yen SH (2013) Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase overactivation leads to accumulation of alpha-synuclein oligomers and decrease of neurites. Neurobiol Aging 34:1504–1515. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.11.001
Jiang P, Gan M, Yen SH, Moussaud S, McLean PJ, Dickson DW (2016) Proaggregant nuclear factor(s) trigger rapid formation of alpha-synuclein aggregates in apoptotic neurons. Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-016-1542-4
Jiang P, Ko LW, Jansen KR, Golde TE, Yen SH (2008) Using leucine zipper to facilitate alpha-synuclein assembly. Faseb J 22:3165–3174. doi:10.1096/fj.08-108365
Ko LW, Ko HH, Lin WL, Kulathingal JG, Yen SH (2008) Aggregates assembled from overexpression of wild-type alpha-synuclein are not toxic to human neuronal cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:1084–1096. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e31818c3618
Kramer ML, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ (2007) Presynaptic alpha-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurosci 27:1405–1410. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4564-06.2007
Kutcher ME, Xu J, Vilardi RF, Ho C, Esmon CT, Cohen MJ (2012) Extracellular histone release in response to traumatic injury: implications for a compensatory role of activated protein C. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 73:1389–1394. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e318270d595
Lee HJ, Patel S, Lee SJ (2005) Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of alpha-synuclein and its aggregates. J Neurosci 25:6016–6024. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0692-05.2005
Lee HJ, Shin SY, Choi C, Lee YH, Lee SJ (2002) Formation and removal of alpha-synuclein aggregates in cells exposed to mitochondrial inhibitors. J Biol Chem 277:5411–5417. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105326200
Lotharius J, Barg S, Wiekop P, Lundberg C, Raymon HK, Brundin P (2002) Effect of mutant alpha-synuclein on dopamine homeostasis in a new human mesencephalic cell line. J Biol Chem 277:38884–38894. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205518200
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 338:949–953. doi:10.1126/science.1227157
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Intracerebral inoculation of pathological alpha-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative alpha-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 209:975–986. doi:10.1084/jem.20112457
Mason DM, Nouraei N, Pant DB, Miner KM, Hutchison DF, Luk KC, Stolz JF, Leak RK (2016) Transmission of alpha-synucleinopathy from olfactory structures deep into the temporal lobe. Mol Neurodegener 11:49. doi:10.1186/s13024-016-0113-4
Masuda-Suzukake M, Nonaka T, Hosokawa M, Oikawa T, Arai T, Akiyama H, Mann DM, Hasegawa M (2013) Prion-like spreading of pathological alpha-synuclein in brain. Brain 136:1128–1138. doi:10.1093/brain/awt037
Mishra B, von der Ohe M, Schulze C, Bian S, Makhina T, Loers G, Kleene R, Schachner M (2010) Functional role of the interaction between polysialic acid and extracellular histone H1. J Neurosci 30:12400–12413. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6407-09.2010
Nonaka T, Watanabe ST, Iwatsubo T, Hasegawa M (2010) Seeded aggregation and toxicity of {alpha}-synuclein and tau: cellular models of neurodegenerative diseases. J Biol Chem 285:34885–34898. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.148460
Ramakrishnan V (1997) Histone structure and the organization of the nucleosome. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 26:83–112. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.26.1.83
Rockenstein E, Nuber S, Overk CR, Ubhi K, Mante M, Patrick C, Adame A, Trejo-Morales M, Gerez J, Picotti P, Jensen PH, Campioni S, Riek R, Winkler J, Gage FH, Winner B, Masliah E (2014) Accumulation of oligomer-prone alpha-synuclein exacerbates synaptic and neuronal degeneration in vivo. Brain 137:1496–1513. doi:10.1093/brain/awu057
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL, Goedert M (1998) Filamentous alpha-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci Lett 251:205–208
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Hasegawa M, Goedert M (1998) alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6469–6473
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Lee VM (2014) Addition of exogenous alpha-synuclein preformed fibrils to primary neuronal cultures to seed recruitment of endogenous alpha-synuclein to Lewy body and Lewy neurite-like aggregates. Nat Protoc 9:2135–2146. doi:10.1038/nprot.2014.143
Watson K, Edwards RJ, Shaunak S, Parmelee DC, Sarraf C, Gooderham NJ, Davies DS (1995) Extra-nuclear location of histones in activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes and cultured T-cells. Biochem Pharmacol 50:299–309
Wu D, Ingram A, Lahti JH, Mazza B, Grenet J, Kapoor A, Liu L, Kidd VJ, Tang D (2002) Apoptotic release of histones from nucleosomes. J Biol Chem 277:12001–12008. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109219200
Zhang H, Griggs A, Rochet JC, Stanciu LA (2013) In vitro study of alpha-synuclein protofibrils by cryo-EM suggests a Cu(2 +)-dependent aggregation pathway. Biophys J 104:2706–2713. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2013.04.050
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Monica Castanedes-Casey, Virginia Phillips for their histologic supports. This study was supported by the National Institute of Health (P50-NS072187, R01-NS073740 and R21-NS099757), the Mangurian Foundation Lewy Body Dementia Program at Mayo Clinic (Dickson, Jiang & Yen). All authors have no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, P., Gan, M., Yen, SH. et al. Histones facilitate α-synuclein aggregation during neuronal apoptosis. Acta Neuropathol 133, 547–558 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1660-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1660-z