Abstract
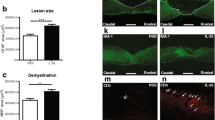
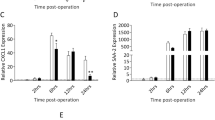
Post-traumatic inflammation response has been implicated in secondary injury mechanisms after spinal cord injury (SCI). Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a key inflammatory mediator that is increasingly expressed after SCI. The action of IL-1 is mediated through its functional receptor, type I interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1RI). However, whether this receptor is expressed after SCI remains to be elucidated. In the present study, the temporospatial expression of IL-1RI was detected in rats that received a moderate contusive SCI (a 10 g rod dropped at a height of 12.5 mm) at the ninth to tenth thoracic vertebral level using a widely used New York University impact device. Our study demonstrated that IL-1RI was slightly increased at 4 h post-injury compared to the normal or sham-operated controls, reached the peak at 8 h at mRNA level (4.44-fold, P<0.01) and 1 d at protein level (2.62-fold, P<0.01). IL-1RI remained at its elevated levels for a relatively long duration (4 h–7 days). Spatially, IL-1RI was observed throughout the entire length of a 10 mm-long cord segment containing the injury epicenter. Colocalization of IL-1RI was found in neurons, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and activated microglia. Our results suggest that the elevated expression of IL-1RI after SCI may contribute to posttraumatic inflammation responses of IL-1.




Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Albrecht PJ, Dahl JP, Stoltzfus OK, Levenson R, Levison SW (2002) Ciliary neurotrophic factor activates spinal cord astrocytes, stimulating their production and release of fibroblast growth factor-2, to increase motor neuron survival. Exp Neurol 173:46–62
Bartholdi D, Schwab ME (1995) Methylprednisolone inhibits early inflammatory processes but not ischemic cell death after experimental spinal cord lesion in the rat. Brain Res 672:177–186
Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC (1996) Graded histological and locomotor outcomes after spinal cord contusion using the NYU weight-drop device versus transaction. Exp Neurol 139:244–256
Basu A, Krady JK, Levison SW (2004) Interleukin-1: a master regulator of neuroinflammation. J Neurosci Res 78:151–156
Basu A, Krady JK, O’Malley M, Styren SD, DeKosky ST, Levison SW (2002) The type 1 interleukin-1 receptor is essential for the efficient activation of microglia and the induction of multiple proinflammatory mediators in response to brain injury. J Neurosci 22:6071–6082
Basu A, Lazovic J, Krady JK, Mauger DT, Rothstein RP Smith MB, Levison SW (2005) Interleukin-1 and the interleukin-1 type 1 receptor are essential for the progressive neurodegeneration that ensues subsequent to a mild hypoxic/ischemic injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:17–29
Berkenbosch F, van OJ, del RA, Tilders F, Besedovsky H (1987) Corticotropin-releasing factor-producing neurons in the rat activated by interleukin-1 Science. 238:524–526
Besedovsky H, del RA, Sorkin E, Dinarello CA (1986) Immunoregulatory feedback between interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones. Science 233:652–654
Blasi F, Riccio M, Brogi A, Strazza M, Taddei ML, Romagnoli S, Luddi A, D’Angelo R, Santi S, Costantino-Ceccarini E, Melli M (1999) Constitutive expression of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) in rat oligodendrocytes. Biol Chem 380:259–264
Bluthe RM, Laye S, Michaud B, Combe C, Dantzer R, Parnet P (2000) Role of interleukin-1beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness behaviour: a study with interleukin-1 type I receptor-deficient mice. Eur J Neurosci 12:4447–4456
Bossu P, Visconti U, Ruggiero P, Macchia G, Muda M, Bertini R, Bizzarri C, Colagrande A, Sabbatini V, Maurizi G (1995) Transfected type II interleukin-1 receptor impairs responsiveness of human keratinocytes to interleukin-1. Am J Pathol 147:1852–1861
Boutin H, LeFeuvre RA, Horai R, Asano M, Iwakura Y, Rothwell NJ (2001) Role of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta in ischemic brain damage. J Neurosci 21:5528–5534
Brenneman DE, Hill JM, Glazner GW, Gozes I, Phillips TW (1995) Interleukin-1 alpha and vasoactive intestinal peptide: enigmatic regulation of neuronal survival. Int J Dev Neurosci 13:187–200
Chung IY, Benveniste EN (1990) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by astrocytes. Induction by lipopolysaccharide, IFN-gamma, and IL-1 beta. J Immunol 144:2999–3007
Colotta F, Re F, Muzio M, Bertini R, Polentarutti N, Sironi M, Giri JG, Dower SK, Sims JE, Mantovani A (1993) Interleukin-1 type II receptor: a decoy target for IL-1 that is regulated by IL-4. Science 261:472–475
Cremona S, Laye S, Dantzer R, Parnet P (1998) Blockade of brain type II interleukin-1 receptors potentiates IL1beta-induced anorexia in mice. Neurosci Lett 246:101–104
Davies CA, Loddick SA, Toulmond S, Stroemer RP, Hunt J, Rothwell NJ (1999) The progression and topographic distribution of interleukin-1beta expression after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:87–98
Dziegielewska KM, Moller JE, Potter AM, Ek J, Lane MA, Saunders NR (2000) Acute-phase cytokines IL-1beta and TNF-alpha in brain development. Cell Tissue Res 299:335–345
Eriksson C, Van Dam AM, Lucassen PJ, Bol JG, Winblad B, Schultzberg M (1999) Immunohistochemical localization of interleukin-1beta, interleukin−1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-1beta converting enzyme/caspase-1 in the rat brain after peripheral administration of kainic acid. Neuroscience 93:915–930
Giulian D, Young DG, Woodward J, Brown DC, Lachman LB (1988) Interleukin-1 is an astroglial growth factor in the developing brain. J Neurosci 8:709–714
Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D, Decallonne B, Bouillon R, Mathieu C (2001) An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods 25:386–401
Gruner JA (1992) A monitored contusion model of spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 9:123–126
Hsu CY, Dimitrijevic MR (1990) Methylprednisolone in spinal cord injury: the possible mechanism of action. J Neurotrauma 7:115–119
John GR, Lee SC, Brosnan CF (2003) Cytokines: powerful regulators of glial cell activation. Neuroscientist 9:10–22
Johnson RW, Arkins S, Dantzer R, Kelley KW (1997) Hormones, lymphohemopoietic cytokines and the neuroimmune axis. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol 116:183–201
Konsman JP, Parnet P, Dantzer R (2002) Cytokine-induced sickness behaviour: mechanisms and implications. Trends Neurosci 25:154–159
Labow M, Shuster D, Zetterstrom M, Nunes P, Terry R, Cullinan EB, Bartfai T, Solorzano C, Moldawer LL, Chizzonite R, McIntyre KW (1997) Absence of IL-1 signaling and reduced inflammatory response in IL-1 type I receptor-deficient mice. J Immunol 159:2452–2461
Lee SC, Liu W, Brosnan CF, Dickson DW (1994) GM-CSF promotes proliferation of human fetal and adult microglia in primary cultures. Glia 12:309–318
Li C, Zienkiewicz J, Hawiger J (2005) Interactive sites in the MyD88 Toll/interleukin (IL) 1 receptor domain responsible for coupling to the IL1beta signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 280:26152–26159
Liberto CM, Albrecht PJ, Herx LM, Yong VW, Levison SW (2004) Pro-regenerative properties of cytokine-activated astrocytes. J Neurochem 89:1092–1100
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Loddick SA, Rothwell NJ (1996) Neuroprotective effects of human recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:932–940
Mason JL, Suzuki K, Chaplin DD, Matsushima GK (2001) Interleukin-1beta promotes repair of the CNS. J Neurosci 21:7046–7052
Nesic O, Xu GY, McAdoo D, High KW, Hulsebosch C, Perez-Pol R (2001) IL-1 receptor antagonist prevents apoptosis and caspase-3 activation after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 18:947–956
Norris JG, Tang LP, Sparacio SM, Benveniste EN (1994) Signal transduction pathways mediating astrocyte IL−6 induction by IL−1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol 152:841–850
O’Neill LA, Greene C (1998) Signal transduction pathways activated by the IL-1 receptor family: ancient signaling machinery in mammals, insects, and plants. J Leukoc Biol 63:650–657
Pan JZ, Ni L, Sodhi A, Aguanno A, Young W, Hart RP (2002) Cytokine activity contributes to induction of inflammatory cytokine mRNAs in spinal cord following contusion. J Neurosci Res 68:315–322
Parish CL, Finkelstein DI, Tripanichkul W, Satoskar AR, Drago J, Horne MK (2002) The role of interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and glia in inducing growth of neuronal terminal arbors in mice. J Neurosci 22:8034–8041
Parker LC, Luheshi GN, Rothwell NJ, Pinteaux E (2002) IL-1 beta signalling in glial cells in wildtype and IL-1RI deficient mice. Br J Pharmacol 136:312–320
Pearson VL, Rothwell NJ, Toulmond S (1999) Excitotoxic brain damage in the rat induces interleukin-1beta protein in microglia and astrocytes: correlation with the progression of cell death. Glia 25:311–323
Pinteaux E, Parker LC, Rothwell NJ, Luheshi GN (2002) Expression of interleukin-1 receptors and their role in interleukin-1 actions in murine microglial cells. J Neurochem 83:754–763
Rothwell NJ, Luheshi GN (2000) Interleukin 1 in the brain: biology, pathology and therapeutic target. Trends Neurosci 23:618–625
Samad TA, Moore KA, Sapirstein A, Billet S, Allchorne A, Poole S, Bonventre JV, Woolf CJ (2001) Interleukin-1beta-mediated induction of Cox-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 410:471–475
Sapolsky R, Rivier C, Yamamoto G, Plotsky P, Vale W (1987) Interleukin-1 stimulates the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Science 238:522–524
Sims JE, Gayle MA, Slack JL, Alderson MR, Bird TA, Giri JG, Colotta F, Re F, Mantovani A, Shanebeck K (1993) Interleukin 1 signaling occurs exclusively via the type I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6155–6159
Sung CS, Wen ZH, Chang WK, Ho ST, Tsai SK, Chang YC, Wong CS (2004) Intrathecal interleukin-1beta administration induces thermal hyperalgesia by activating inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the rat spinal cord. Brain Res 1015:145–153
Vitkovic L, Bockaert J, Jacque C (2000) “Inflammatory” cytokines: neuromodulators in normal brain? J Neurochem 74:457–471
Wang CX, Olschowka JA, Wrathall JR (1997) Increase of interleukin-1beta mRNA and protein in the spinal cord following experimental traumatic injury in the rat. Brain Res 759:190–196
Xu J, Fan G, Chen S, Wu Y, Xu XM, Hsu CY (1998) Methylprednisolone inhibition of TNF-alpha expression and NF-kB activation after spinal cord injury in rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 59:135–142
Yan P, Liu N, Kim GM, Xu J, Xu J, Li Q, Hsu CY, Xu XM (2003) Expression of the type 1 and type 2 receptors for tumor necrosis factor after traumatic spinal cord injury in adult rats. Exp Neurol 183:286–297
Yan P, Xu J, Li Q, Chen S, Kim GM, Hsu CY, Xu XM (1999) Glucocorticoid receptor expression in the spinal cord after traumatic injury in adult rats. J Neurosci 19:9355–9363
Yang L, Blumbergs PC, Jones NR, Manavis J, Sarvestani GT, Ghabriel MN (2004) Early expression and cellular localization of proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human traumatic spinal cord injury. Spine 29:966–971
Yang L, Jones NR, Blumbergs PC, Van Den HC, Moore EJ, Manavis J, Sarvestani GT, Ghabriel MN (2005) Severity-dependent expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in traumatic spinal cord injury in the rat. J Clin Neurosci 12:276–284
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant from Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Project) (2003CB515302) and Shanghai Science Development Fund (02JC14014). The authors thank Zhen Guan, research associate from the Spinal Cord Injury Research Center, Ohio State University, for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XF., Huang, LD., Yu, PP. et al. Upregulation of type I interleukin−1 receptor after traumatic spinal cord injury in adult rats. Acta Neuropathol 111, 220–228 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-0016-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-0016-x