Abstract
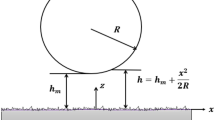
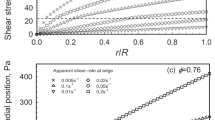
Two principal squeeze flow modes are investigated for yield stress and Newtonian materials squeezed by a constant force, F, between plates of equal or unequal diameters. In mode A, the material fills the space between the plates and is extruded at their periphery as their separation decreases. Experiments are described to measure the contribution to F from the extrudate. In mode B, all the material remains in contact with the planes of the plates as their separation decreases; there is no extrudate. The results of mode B experiments agree closely with the predictions of theory and give rheological parameters in fair agreement with those measured by the rotational vane method. The material properties and extrusion behaviour which complicate mode A experiments are discussed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MJ, Edmondson B, Caughey DG, Yahya R (1994) An experimental and theoretical study of the squeeze-film deformation and flow of elastoplastic fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 51:61–78
Barnes HA, Nguyen QD (2001) Rotating vane rheometry—a review. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 98:1–14
Bertola V (2009) Wicking with a yield stress fluid. J Phys: Condens Matter 21:1–6
Covey GH, Stanmore BR (1981) Use of the parallel-plate plastometer for the characterisation of viscous fluids with a yield stress. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 8:249–260
Engmann J, Servais C, Burbidge AS (2005) Squeeze flow theory and applications to rheometry: a review. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 132:1–27
Karapetsas G, Tsamopoulos J (2006) Transient squeeze flow of viscoplastic materials. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 133:35–56
Laun HM (1992) Rheometry towards complex flows: squeeze flow technique. Makromol Chem Macromol Symp 56:55–66
Liddell PV, Boger DV (1996) Yield stress measurements with the vane. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 63:235–261
Meeten GH (2000) Yield stress of structured fluids measured by squeeze flow. Rheol Acta 39:399–408
Meeten GH (2002) Constant-force squeeze flow of soft solids. Rheol Acta 41:557–566
Meeten GH (2004a) Squeeze flow of soft solids between rough surfaces. Rheol Acta 43:6–16
Meeten GH (2004b) Effects of plate roughness in squeeze flow rheometry. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 124:51–60
Meeten GH (2008) Squeeze-flow and vane rheometry of a gas–liquid foam. Rheol Acta 47:883–894
Patil YP, Senador A, Mather PT, Shaw MT (2007) Rheological characterization of asphalt in a temperature-gradient combinatorial squeeze flow setup. Rheol Acta 46:1075–1082
Rabideau BD, Lanos C, Coussot P (2009) An investigation of squeeze flow as a viable technique for determining the yield stress. Rheol Acta 48:517–526
Sherwood JD, Meeten GH (1991) The use of the vane to measure the shear modulus of linear elastic solids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 41:101–118
Acknowledgement
I thank John Sherwood (Schlumberger Cambridge Research) for discussions on this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meeten, G.H. Comparison of squeeze flow and vane rheometry for yield stress and viscous fluids. Rheol Acta 49, 45–52 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-009-0391-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-009-0391-7