Abstract
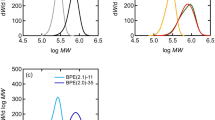
Low-density polyethylenes (LDPE) were synthesized in a laboratory-scale autoclave under high pressure. These samples were found to possess a high molar mass tail, resulting in a distinctly bimodal molar mass distribution and a lower concentration of long-chain branching than typical of commercial LDPEs. Rheological experiments in elongation showed that these samples exhibit a very pronounced strain hardening, which could be favorable for distinct processing operations. Although the samples have a rather high molar mass (\(M_{\rm w} = 2{\ldots}4 \times 10^{6}\) g/mol), their zero shear-rate viscosities η 0 and their shear thinning behavior are still in a range, where thermoplastic processing is possible. A qualitative understanding of the experimental results is tried by the model of the Cayley tree.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The fact that the injected mass is found within ±5% by the detectors is taken as a quality criterion of the measurement. Such an agreement is especially important considering the high molar masses of the CSTR-LDPEs, as they may contain insoluble (gelled) fractions.
This equation is only defined for monodisperse solutions. For polydisperse cases, a slightly different equation applies (Zimm and Stockmayer 1949).
A side-chain content s c of butyl chains of 27 wt.% would lead to an amorphous polymer.
Please note that η max = 500,000 Pa s was taken as η 0 for CSTR-LDPE 1.
LDPE 2 does not have a maximum in the strain hardening in the range under experimental investigation.
References
Bach A, Rasmussen HK, Hassager O (2003) Extensional viscosity for polymer melts measured in the filament stretching rheometer. J Rheol 47(2):429–441
Barroso VC, Ribeiro SP, Maia JM (2003) Stress relaxation after a step strain in uniaxial extension of polyisobutylene and polyethylene. Rheol Acta 42(4):345–354
Beer F, Capaccio G, Rose LJ (1999a) High molecular weight tail and long-chain branching in low density polyethylene. Polymer 80:2815–2822
Beer F, Capaccio G, Rose LJ (1999b) High molecular weight tail and long-chain branching in SRM 1476 polyethylene. J Appl Polym Sci 73(14):2807–2812
Buback M, Busch M, Lovis K, Mähling FO (1994) Development of a high-pressure high-temperature stirred vessel with incidence of light for continuous operation. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 66(4):510–513
Buback M, Busch M, Lovis K, Mähling FO (1995) Mini-pilot plant for continuous high pressure polymerisation. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 67(12):1652–1655
Buback M, Busch M, Lovis K, Mähling FO (1996) High-pressure free-radical copolymerization of ethene and butyl acrylate. Macromol Chem Phys 197(1):303–313
Burchard W (1974) Statistics of star-shaped molecules. II. Stars with polydisperse side chains. Macromolecules 7(6):841–846
Coll H, Gilding DK (1970) Universal calibration in gel-permeation chromatography: study of polystyrene, poly(α-methylstyrene), and polypropylene. J Polym Sci B, Polym Phys 8:89–103
Dealy J, Larson RG (2006) Structure and rheology of molten polymers—from structure to flow behavior and back again. Hanser, Munich
Frater DJ, Mays JW, Jackson C (1997) Synthesis and dilute solution properties of divinylbenzene-linked polystyrene stars with mixed arm lengths: evidence for coupled stars. J Polym Sci B, Polym Phys 35(1):141–151
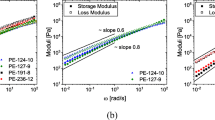
Gabriel C, Lilge D (2006) Molecular mass dependence of the zero shear-rate viscosity of LDPE melts: evidence of an exponential behaviour. Rheol Acta 45:992–1002
Gabriel C, Münstedt H (2002) Influence of long-chain branches in polyethylenes on linear viscoelastic flow properties in shear. Rheol Acta 41(3):232–244
Gabriel C, Münstedt H (2003) Strain hardening of various polyolefins in uniaxial elongational flow. J Rheol 47(3):619–630
Gabriel C, Kaschta J, Münstedt H (1998) Influence of molecular structure on rheological properties of polyethylenes I. Creep recovery measurements in shear. Rheol Acta 37(1):7–20
Hadjichristidis N, Xenidou M, Iatrou H, Pitsikalis M, Poulos Y, Avgeropoulos A, Sioula S, Paraskeva S, Velis G, Lohse DJ, Schulz DN, Fetters LJ, Wright PJ, Mendelson RA, Garcia-Franco CA, Sun T, Ruff CJ (2000) Well-defined, model long chain branched polyethylene. 1. Synthesis and characterization. Macromolecules 33(7):2424–2436
Laun HM, Münstedt H (1978) Elongational behaviour of a low density polyethylene melt I. Strain rate and stress dependence of viscosity and recoverable strain in the steady-state. Comparison with shear data. Influence of interfacial tension. Rheol Acta 17:415–425
Malmberg A, Gabriel C, Steffl T, Münstedt H, Löfgren B (2002) Long-chain branching in metallocene-catalyzed polyethylenes investigated by low oscillatory shear and uniaxial extensional rheometry. Macromolecules 35:1038–1048
Meissner J (1969) Rheometer for the study of mechanical properties of deformation of plastic melts under definite tensile stress. Rheol Acta 8(1):78–88
Münstedt H (1979) Elongational behavior of a low density polyethylene melt II. Transient behavior in constant stretching rate and tensile creep experiments. Comparison with shear data. Temperature dependence of the elongational properties. Rheol Acta 18:492–504
Münstedt H (1986) Polymerschmelzen. In: Kulicke W (ed) Fließverhalten von Stoffen und Stoffgemischen. Hüthig & Wepf, Basel, pp 238–279
Münstedt H, Auhl D (2005) Rheological measuring techniques and their relevance for the molecular characterization of polymers. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 128(1):62–69
Münstedt H, Schwetz M, Heindl M, Schmidt M (2001) Influence of molecular structure on secondary flow of polyolefin melts as investigated by laser-Doppler velocimetry. Rheol Acta 40:384–394
Münstedt H, Steffl T, Malmberg A (2005) Correlation between rheological behaviour in uniaxial elongation and film blowing properties of various polyethylenes. Rheol Acta 45(1):14–22
Piau JM, Agassant JF (1996) Rheology for melt processing. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Piel C, Stadler FJ, Kaschta J, Rulhoff S, Münstedt H, Kaminsky W (2006) Structure–property relationships of linear and long-chain branched metallocene high-density polyethylenes and SEC-MALLS. Macromol Chem Phys 207(1):26–38
Podzimek S, Vlcek T, Johann C (2001) Characterization of branched polymers by size exclusion chromatography coupled with multiangle light scattering detector. I. Size exclusion chromatography elution behavior of branched polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 81(7):1588–1594
Rubio P, Wagner MH (2000) LDPE melt rheology and the pom-pom model. Polymer 92:245–259
Scholte TG, Meijerink NLJ, Schoffeleers HM, Brands AMG (1984) Mark–Houwink equation and GPC calibration for linear short-chain branched polyolefins, including polypropylene and ethylene–propylene copolymers. J Appl Polym Sci 29:3763–3782
Schwetz M, Münstedt H, Heindl M, Merten A (2002) Investigations on the temperature dependence of the die entrance flow of various long-chain branched polyethylenes using laser-Doppler velocimetry. J Rheol 46(4):797–815
Stadler FJ, Bailly C (2008) A new method for the calculation of continuous relaxation spectra from dynamic-mechanical data. Rheol Acta doi:10.1007/s00397-008-0303-2
Stadler FJ, Münstedt H (2008a) Terminal viscous and elastic rheological characterization of ethene-/α-olefin copolymers. J Rheol 52(3):697–712. doi:10.1122/1.2892039
Stadler FJ, Münstedt H (2008b) Numerical description of shear viscosity functions of long-chain branched metallocene-catalyzed polyethylenes. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 151:129–135. doi:10.1016/j.jnnfm.2008.01.010
Stadler FJ, Piel C, Kaminsky W, Münstedt H (2006a) Rheological characterization of long-chain branched polyethylenes and comparison with classical analytical methods. Macromol Symp 236(1):209–218
Stadler FJ, Piel C, Kaschta J, Rulhoff S, Kaminsky W, Münstedt H (2006b) Dependence of the zero shear-rate viscosity and the viscosity function of linear high density polyethylenes on the mass-average molar mass and polydispersity. Rheol Acta 45(5):755–764
Stadler FJ, Piel C, Klimke K, Kaschta J, Parkinson M, Wilhelm M, Kaminsky W, Münstedt H (2006c) Influence of type and content of very long comonomers on long-chain branching of ethene-/α-olefin copolymers. Macromolecules 39(4):1474–1482
Stadler FJ, Nishioka A, Stange J, Koyama K, Münstedt H (2007) Comparison of the elongational behavior of various polyolefins in uniaxial and equibiaxial flows. Rheol Acta 46(7):1003–1012. doi:10.1007/s00397-007-0190-y
Tackx P, Tacx JCJF (1998) Chain architecture of LDPE as a function of molar mass using size exclusion chromatography and multi-angle laser light scattering (SEC-MALLS). Polymer 39(14):3109–3113
Utracki LA, Schlund B (1987) Linear low density polyethylenes and their blends. Part 2. Shear flow of LLDPE’s. Polym Eng Sci 27(5):367–379
Wagner MH, Bastian H, Hachmann P, Meissner J, Kurzbeck S, Münstedt H, Langouche F (2000) The strain hardening behaviour of linear and long-chain-branched polyolefin melts in extensional flows. Rheol Acta 39:97–109
Wagner MH, Rubio P, Bastian H (2001) The molecular stress function model for polydisperse polymer melts with dissipative convective constraint release. J Rheol 45(6):1387–1412
Ye XN, Sridhar T (2001) Shear and extensional properties of three-arm polystyrene solutions. Macromolecules 34(23):8270–8277
Zimm BHM, Stockmayer WH (1949) The dimensions of molecules containing branching and rings. J Chem Phys 17(12):1301–1314
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs. I. Herzer (University Erlangen-Nürnberg) for the GPC–MALLS measurements and J. Stange (University Erlangen-Nürnberg, now Bayer Material Science) for scientific input into this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stadler, F.J., Kaschta, J., Münstedt, H. et al. Influence of molar mass distribution and long-chain branching on strain hardening of low density polyethylene. Rheol Acta 48, 479–490 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-008-0334-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-008-0334-8