Abstract
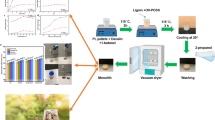
The three-dimensional polylactide (PLA)/kapok monolith with hierarchical porous structures was first prepared via the non-solvent-induced phase separation (NIPS) method. Kapok fibers were preferred to be used as oil adsorbing materials due to their extensive resource, low cost, and excellent oil sorption capacity. However, the fibrous assemblies of kapok formed by adhesives could not be degraded naturally. In this study, PLA and kapok fibers could be regarded as dispersed medium and dispersed phase, respectively. PLA and kapok fibers were physically combined without any binder. The resulting PLA/kapok monoliths exhibited the integrated properties of superior hydrophobicity with a water contact angle of 141°, rapid absorption rate, high oil absorption of 17.34 g/g and reutilization. The degradability of raw materials, excellent oil absorption performance, and simplicity of the preparation technology make the monolith have potential in oil/water separation and oil pollution treatment.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
References
Yeh SK, Tsai YB, Gebremedhin KF, Chien TY, Chang RY, Tung KL (2021) Preparation of polypropylene/high-melt-strength PP open-cell foam for oil absorption. Polym Eng Sci 61:1139–1149. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25654
Zhang Y, Wang B, Wang B, Yang X, Ma S, Feng Y, Liu C, Shen C (2022) Super-hydrophobic graphene-coated thermoplastic polyurethane porous monolith with superior photothermal effect for solar-assisted efficient cleanup of crude oil spill. Appl Surf Sci 605:154701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154701
Lei W, Portehault D, Liu D, Qin S, Chen Y (2013) Porous boron nitride nanosheets for effective water cleaning. Nat Commun 4:1777. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2818
Li B, Wu L, Li L, Seeger S, Zhang J, Wang A (2014) Superwetting double-layer polyester materials for effective removal of both insoluble oils and soluble dyes in water. ACS Appl Mater Inter 6:11581–11588. https://doi.org/10.1021/am502313h
Dong T, Wang F, Xu G (2015) Sorption kinetics and mechanism of various oils into kapok assembly. Mar Pollut Bull 91:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.11.044
Xu Z, Miyazaki K, Hori T (2016) Fabrication of polydopamine-coated superhydrophobic fabrics for oil/water separation and self-cleaning. Appl Surf Sci 370:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.135
Zhang P, Tian R, Lv R, Na B, Liu Q (2015) Water-permeable polylactide blend membranes for hydrophilicity-based separation. Chem Eng J 269:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.111
Hu X, Xiao CF, Zhao J, Fen Y, Xu NK (2013) Preparation of plma/pu blend fiber and its absorption properties. Chem J Chinese U 34:1985–1992. https://doi.org/10.7503/cjcu20130222
Dong T, Cao S, Xu G (2016) Highly porous oil sorbent based on hollow fibers as the interceptor for oil on static and running water. J Hazard Mater 305:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.11.030
Si Y, Fu Q, Wang X, Zhu J, Yu J, Sun G, Ding B (2015) Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 9:3791–3799. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn506633b
Hu H, Zhao Z, Wan W, Gogotsi Y, Qiu J (2013) Ultralight and highly compressible graphene aerogels. Adv Mater 25:2219–2223. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201204530
Wang B, Yang X, Sha D, Shi K, Xu J, Ji X (2020) Silane functionalized polyvinyl-alcohol formaldehyde sponges on fast oil absorption. ACS Appl Polym Mater 2:5309–5317. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.0c01052
Lu Z, Song J, Pan K, Meng J, Xin Z, Liu Y, Zhao Z, Gong RH, Li J (2019) Ecoflex sponge with ultrahigh oil absorption capacity. ACS Appl Mater Inter 11:20037–20044. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b04446
Wang G, Uyama H (2016) Facile synthesis of flexible macroporous polypropylene sponges for separation of oil and water. Sci Rep 6:21265. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21265
Su C (2009) Highly hydrophobic and oleophilic foam for selective absorption. Appl Surf Sci 256:1413–1418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.08.098
Xu T, Miszuk JM, Zhao Y, Sun H, Fong H (2015) Electrospun polycaprolactone 3D nanofibrous scaffold with interconnected and hierarchically structured pores for bone tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater 4:2238–2246. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201500345
Liu Y, Huang G, Gao C, Zhang L, Chen M, Xu X, Gao J, Pan C, Yang N, Liu Y (2015) Biodegradable polylactic acid porous monoliths as effective oil sorbents. Compos Sci Technol 118:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2015.08.005
Wang G, Niu J, Asoh TA, Uyama H (2019) Fabrication of compressible polyolefin monoliths and their applications. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 105:166–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.09.025
Zhao J, Ren W, Cheng HM (2012) Graphene sponge for efficient and repeatable adsorption and desorption of water contaminations. J Mater Chem 22:20197–20202. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm34128j
Shen Y, Fang Q, Chen B (2015) Environmental applications of three-dimensional graphene-based macrostructures: adsorption, transformation, and detection. Environ Sci Technol 49:67–84. https://doi.org/10.1021/es504421y
Sun X, Fujimoto T, Uyama H (2013) Fabrication of a poly(vinyl alcohol) monolith via thermally impacted non-solvent-induced phase separation. Polym J 45:1101–1106. https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2013.18
Kang Y, Wang C, Qiao Y, Gu J, Zhang H, Peijs T, Kong J, Zhang G, Shi X (2019) Tissue-engineered trachea consisting of electrospun patterned scPLA/GO-g-IL fibrous membranes with antibacterial property and 3D-printed skeletons with elasticity. Biomacromol 20:1765–1776. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.9b00160
Sai H, Tan KW, Hur K et al (2013) Hierarchical porous polymer scaffolds from block copolymers. Science 341:530–534. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1238159
Morariu MD, Voicu NE, Schaffer E, Lin ZQ, Russell TP, Steiner U (2003) Hierarchical structure formation and pattern replication induced by an electric field. Nat Mater 2:48–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat789
Okada K, Nandi M, Maruyama J, Oka T, Tsujimoto T, Kondoh K, Uyama H (2011) Fabrication of mesoporous polymer monolith: a template-free approach. Chem Commun 47:7422–7424. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc12402a
Onde OC, Yilgor E, Yilgor I (2016) Fabrication of rigid poly(lactic acid) foams via thermally induced phase separation. Polymer 107:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2016.11.025
Wang G, Xin Y, Uyama H (2015) Facile fabrication of mesoporous poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol)/chitosan blend monoliths. Carbohyd Polym 132:345–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.040
Chen M, Qiao J, Sun X, Chen W, Uyama H, Wang X (2019) A green and facile strategy for hierarchically porous poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) monolithic composites. J Mater Res 34:2990–2999. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.214
Zheng Y, Wang J, Zhu Y et al (2015) Research and application of kapok fiber as an absorbing material: a mini review. J Environ Sci 27:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.09.026
Rengasamy RS, Das D, Karan CP (2011) Study of oil sorption behavior of filled and structured fiber assemblies made from polypropylene, kapok and milkweed fibers. J Hazard Mater 186:526–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.031
Rezabeigi E, Wood-Adams PM, Drew RAL (2014) Production of porous polylactic acid monoliths via nonsolvent induced phase separation. Polymer 55:6743–6753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2014.10.063
Qin X, Wang B, Zhang X, Shi Y, Ye S, Feng Y, Liu C, Shen C (2019) Superelastic and durable hierarchical porous thermoplastic polyurethane monolith with excellent hydrophobicity for highly efficient oil/water separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:20291–20299. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b03717
Wang B, Chen W, Zhang L, Li Z, Liu C, Chen J, Shen C (2017) Hydrophobic polycarbonate monolith with mesoporous nest-like structure: an effective oil sorbent. Mater Lett 188:201–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.11.015
Ridgway CJ, PaC G, Schoelkopf J (2002) Effect of capillary element aspect ratio on the dynamic imbibition within porous networks. J Colloid Interf Sci 252:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2002.8468
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 52203056], and the Graduate Student Innovation Fund of Donghua University [No. CUSF-DH-D-2020020].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mingjing Chen wrote the main manuscript text. Hiroshi Uyama, Xinhou Wang, and Xiaoxia Sun provided guiding suggestions for the experimental plan and the theories involved in the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Uyama, H., Wang, X. et al. A green and facile approach to prepare polylactide/kapok monoliths for a sustainable and reusable oil sorbent. Colloid Polym Sci 301, 1261–1270 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05147-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05147-5