Abstract
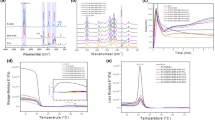
A new economical applied method has been developed to modify the polylactic acid (PLA) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) immiscible blends. The different molecular weights of polyethylene glycol (PEG) were adopted during processing. The morphology of PLA/ABS blends was successfully controlled by 10 wt% content of PEG, and the morphology results show remarkable changes at the PLA/ABS blend interface. A fluctuation of the storage modulus at the frequency lower than 0.1 rad/s of PLA/PEG/ABS blends also reflects the structure change in the system. The mechanical properties as well as the thermal and decomposition properties of the modified blends improve with increasing molecular weight of PEG. All the results of properties indicate that the interaction of polymer blend molecular chain decreases and the processability of the PLA/ABS blends increase both due to the addition of PEG.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lim LT, Auras R, Rubino M (2008) Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid. Prog Polym Sci 33(8):820–852. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.05.004
Ma P, Hristova-Bogaerds DG, Goossens JGP, Spoelstra AB, Zhang Y, Lemstra PJ (2012) Toughening of poly(lactic acid) by ethylene-co-vinyl acetate copolymer with different vinyl acetate contents. Eur Polym J 48(1):146–154. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2011.10.015
Zeng JB, Li KA, AK D (2015) Compatibilization strategies in poly(lactic acid)-based blends. RSC Adv 5(41):32546–32565. doi:10.1039/c5ra01655j
Xu Y, Li Q, Sun D, Zhang W, Chen G-X (2012) A strategy to functionalize the carbon nanotubes and the nanocomposites based on poly(l-lactide). Ind Eng Chem Res 51(42):13648–13654. doi:10.1021/ie300989w
Tymrak BM, Kreiger M, Pearce JM (2014) Mechanical properties of components fabricated with open-source 3-D printers under realistic environmental conditions. Mater Des 58:242–246. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.038
Xie L, Xu H, Niu B, Ji X, Chen J, Li ZM, Hsiao BS, Zhong GJ (2014) Unprecedented access to strong and ductile poly(lactic acid) by introducing in situ nanofibrillar poly(butylene succinate) for green packaging. Biomacromolecules 15(11):4054–4064. doi:10.1021/bm5010993
Rasal RM, Janorkar AV, Hirt DE (2010) Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci 35(3):338–356. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.12.003
Spinella S, Cai JL, Samuel C, Zhu JH, McCallum SA, Habibi Y, Raquez JM, Dubois P, Gross RA (2015) Polylactide/poly(omega-hydroxytetradecanoic acid) reactive blending: a green renewable approach to improving polylactide properties. Biomacromolecules 16(6):1818–1826. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00394
Urquijo J, Guerrica-Echevarria G, Eguiazabal JI (2015) Melt processed PLA/PCL blends: effect of processing method on phase structure, morphology, and mechanical properties. J Appl Polym Sci 132(42). doi:10.1002/app.42641
Li FJ, Liang JZ, Zhang SD, Zhu B (2015) Tensile properties of polylactide/poly(ethylene glycol) blends. J Polym Environ 23(3):407–415. doi:10.1007/s10924-015-0718-7
Liu HZ, Zhang JW (2011) Research progress in toughening modification of poly(lactic acid). J Polym Sci Pt B-Polym Phys 49(15):1051–1083. doi:10.1002/polb.22283
Sun S, Zhang M, Zhang H, Zhang X (2011) Polylactide toughening with epoxy-functionalized grafted acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene particles. J Appl Polym Sci 122(5):2992–2999. doi:10.1002/app.34111
Jo MY, Ryu YJ, Ko JH, Yoon J-S (2012) Effects of compatibilizers on the mechanical properties of ABS/PLA composites. J Appl Polym Sci 125(S2):E231–E238. doi:10.1002/app.36732
Nagarajan V, Zhang K, Misra M, Mohanty AK (2015) Overcoming the fundamental challenges in improving the impact strength and crystallinity of PLA biocomposites: influence of nucleating agent and mold temperature. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(21):11203–11214. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b01145
Arrieta MP, Lopez J, Rayon E, Jimenez A (2014) Disintegrability under composting conditions of plasticized PLA-PHB blends. Polym Degrad Stabil 108:307–318. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.01.034
Ge HH, Yang F, Hao YP, Wu GF, Zhang HL, Dong LS (2013) Thermal, mechanical, and rheological properties of plasticized poly(L-lactic acid). J Appl Polym Sci 127(4):2832–2839. doi:10.1002/app.37620
Ma H, Tong L, Xu Z, Fang Z (2007) Clay network in ABS-graft-MAH nanocomposites: rheology and flammability. Polym Degrad Stabil 92(8):1439–1445. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.05.013
Ji DY, Liu ZY, Lan XR, Wu F, Xie BH, Yang MB (2014) Morphology, rheology, crystallization behavior, and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate)/dicumyl peroxide reactive blends. J Appl Polym Sci 131(3). doi:10.1002/app.39580
Li Y, Shimizu H (2009) Improvement in toughness of poly(l-lactide) (PLLA) through reactive blending with acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene copolymer (ABS): morphology and properties. Eur Polym J 45(3):738–746. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2008.12.010
Sheth M, Kumar RA, Davé V, Gross RA, Mccarthy SP (1997) Biodegradable polymer blends of poly(lactic acid) and poly(ethylene glycol. J Appl Polym Sci 66(8):1495–1505
Bernabe GA, Kobelnik M, Almeida S, Ribeiro CA, Crespi MS (2013) Thermal behavior of lignin and cellulose from waste composting process. J Therm Anal Calorim 111:589–595. doi:10.1007/s10973-012-2276-8
Imre B, Bedo D, Domjan A, Schon P, Vancso GJ, Pukanszky B (2013) Structure, properties and interfacial interactions in poly (lactic acid)/polyurethane blends prepared by reactive processing. Eur Polym J 49(10):3104–3113. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.07.007
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the National Science Fund (No. 11372286, No. 51603192), Basic and advanced technology research project of Henan Province (No. 152300410033), International technological cooperation project (2015DFA30550) for their financial support of this project. The Project is sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry. The Project is supported by the Open Project of State Key Laboratory Cultivation Base for Nonmetal Composites and Functional Materials (15zxfk06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, S., Qiao, Y. et al. Effect of morphology designing on the structure and properties of PLA/PEG/ABS blends. Colloid Polym Sci 294, 1779–1787 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3940-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3940-5