Abstract
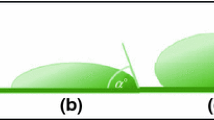
Contact angle (CA) hysteresis is the difference between the maximum (advancing) and minimum (receding) water CA. Hysteresis is caused by adhesion hysteresis in the solid–water contact area (2D effect) and by pinning of the solid–water–air triple line due to the surface roughness (1D effect). In this work, we show that CA hysteresis is present also in more complex systems, such as an organic liquid (oil) in contact with a solid immersed in water. In order to decouple the 1D and 2D effects, we study CA hysteresis in solid–water–air (droplet), solid–air–water (bubble), solid–water–oil, and solid–water–air–oil systems involving rough and microstructured surfaces. The comparative analysis of these systems allows decoupling the 1D and 2D effects as well as hydrogen bonding and entropic forces (water–air tension) and dispersion forces (oil–air tension).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young T (1805) Phil Trans R Soc Lond 95:65–87
Cammarata RC (1994) Prog Surf Sci 46:1–38
Krasovitski B, Marmur A (2005) Langmuir 21:3881–3885
Rayleigh L (1891) Nature 43:437–439
Pockels A (1914) Physik Z 15:39–46
Ablett R (1923) Phil Mag 46:224
Adam NK, Jessop G (1925) J Chem Soc 127:1863
Good RJ (1952) J Am Chem Soc 79:5041
Shepard JW, Bartell FEJ (1953) J Phys Chem 57:458
Nosonovsky M (2007) J Chem Phys 126:224701
Carré A, Mittal KL (2009) Superhydrophobic surfaces. VSP/Brill, Leiden
Jin M, Feng X, Feng L, Sun T, Zhai J, Li T, Jiang L (2005) Adv Mater 17:1977–1981
Nosonovsky M, Bhushan B (2008) Multiscale dissipative mechanisms and hierarchical surfaces: Friction, superhydrophobicity and biomimetics. Springer, Verlag
Bormashenko E, Stein T, Pogreb R, Aurbach D, Phys J (2009) Chem C 113:5568–5572
Li W, Amirfazli A (2007) Adv Mater 19:3421–3422
Gao L, McCarthy TJ (2008) Langmuir 24:9184–9188
Wang S, Jiang L (2007) Adv Mater 19:3423–3424
Chang FM, Hong SJ, Sheng YJ, Tsao HK (2009) Appl Phys Lett 95:064102
Bormashenko E, Bormashenko Y, Stein T, Whyman G, Pogreb R (2007) Langmuir 23:4378–4382
Xia F, Jiang L (2008) Adv Mater 20:2842–2858
Wenzel RN (1936) Ind Eng Chem 28:988
Cassie ABD, Baxter S (1944) Trans Faraday Soc 40:546–551
Feng L, Zhang Y, Xi J, Zhu Y, Wang N, Xia F, Jiang L (2008) Langmuir 24:4114–4119
McHale G (2009) Langmuir 25:7185–7187
Bhushan B, Nosonovsky M (2010) Phil Trans R Soc A 368:4713–4728
Bormashenko E. (2012) J Colloid Polym Sci, in press.
Hejazi V, Nosonovsky M (2011) Langmuir. Vol 28:2173–2180
de Gennes PG, Brochard-Wyart F, Quéré D (2004) Capillarity and wetting phenomena: Drops, bubbles, pearls, waves. Springer
Extrand CW (1998) J Colloid Interface Sci 207:11–19
Bormashenko E, Bormashenko Y, Whyman G, Pogreb R, Musin A, Jager R, Barkay Z (2008) Langmuir 24(8):4020–4025
Nosonovsky M, Bhushan B (2008) J Phys: Condens Matter 20, 395005
Nosonovsky M, Bhushan B (2009) Phil Trans Royal Soc A367:1511–1539
Nosonovsky M, Hejazi V, Nyong AE, Rohatgi PK (2011) Langmuir 27:14419–14424
Hejazi V, Nyong AE, Rohatgi PK, Nosonovsky M (2012) Adv Mater. doi:10.1002/adma.201202516
Wong T-S, Kang SH, Tang SKY, Smythe EJ, Hatton BD, Grinthal A, Aizenburg J (2011) Nature 477:443–447
Nosonovsky M (2011) Nature 477:412–413
Bormashenko E (2010) Am J Phys 78:1309–1311
Israelachvili JN (2011) Intermolecular and surface forces, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Contact Angle Hysteresis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hejazi, V., Nosonovsky, M. Contact angle hysteresis in multiphase systems. Colloid Polym Sci 291, 329–338 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2838-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2838-0