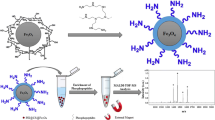
Abstract
The magnetic separation technique based on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MNPs) has potential applications in protein adsorption and purification, enzyme immobilization, cell sorting, nucleic acid detachment, and drug release. However, the naked MNPs are often insufficient for their hydrophilicity, colloidal stability, and further functionalization. To overcome these limitations, chitosan was firstly carboxymethylated and then covalently conjugated on the surface of the MNPs ranging in size from about 5 to 15 nm, which were prepared by co-precipitating iron (II) and iron (III) in alkaline solution and then treating under hydrothermal conditions. It was found that such modification did not result in the phase change of the MNPs, and the resultant modified nanoparticles were still superparamagnetic. In particular, the colloidal stability of MNPs in aqueous suspension was improved after the surface modification. By investigating the adsorption of bovine serum albumin (BSA) on the modified MNPs, it was observed that the adsorption capacity of the BSA on the modified MNPs increased rapidly within several minutes and then reached the maximum value at about 10 min. The adsorption equilibrium isotherm could be fitted well by the Langmuir model. The medium pH affected greatly the adsorption of the BSA. The maximum adsorption of the BSA occurred at the pH value close to the isoelectric point of the BSA, with a saturation adsorption amount of 94.45 mg/g (25 °C). For the BSA feed concentration of 1.017 mg/ml, a high desorption percentage of 91.5% could be achieved under an alkaline condition (pH 9.4).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abudiab T, Beitle RR Jr (1998) J Chromatogr A 795:211–215
Peng ZG, Hidajat K, Uddin MS (2004) J Colloid Interface Sci 271:277–283
Liao MH, Chen DH (2001) Biotechnol Lett 23:1723–1727
Ito A, Shinkai M, Honda H, Kobayashi T (2005) J Biosci Bioeng 100:1–11
Neuberger T, Schöpf B, Hofmann H, Hofmann M, Rechenberg B (2005) J Magn Magn Mater 293:483–496
Gupta AK, Curtis ASG (2004) J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:493–496
Perez JM, O’Loughin T, Simeone FJ, Weissleder R, Josephson L (2002) J Am Chem Soc 124:2856–2857
Dyal A, Loos K, Noto M, Chang SW, Spagnoli C, Shafi KV, Ulman A, Cowman M, Gross RA (2003) J Am Chem Soc 125:1684–1685
Gelinas S, Finch JA, Bohme P (2000) Colloids Surf A 172:103–112
Gu HW, Yang ZM, Gao JH, Chang CK, Xu B (2005) J Am Chem Soc 127:34–35
Wang DS, He JB, Rosenzweig N, Rosenzweig Z (2004) Nano Lett 4:409–413
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Biomaterials 26:3995–4021
Bacri JC, Perzynski R, Salin D, Cabuil V, Massart R (1990) J Magn Magn Mater 85:27–32
Shen L, Stachowiak A, Fateen SEK, Laibinis PE, Hatton TA (2001) Langmuir 17:288–299
Mendenhall GD, Geng Y, Hwang J (1996) J Colloid Interface Sci 184:519–526
Lee J, Isobe T, Senna M (1996) J Colloid Interface Sci 177:490–494
Harris LA, Goff JD, Carmichael AY, Riffle JS, Harburn JJ, St Pierre TG, Saunders M (2003) Chem Mater 15:1367–1377
Si S, Kotal A, Mandal TK, Giri S, Nakamura H, Kohara T (2004) Chem Mater 16:3489–3496
Yu S, Chow GM (2004) J Mater Chem 14:2781–2786
Kim BS, Qiu JM, Wang JP, Taton TA (2005) Nano Lett 5:1987–1991
Ditsch A, Laibinis PE, Wang DIC, Hatton TA (2005) Langmuir 21:6006–6018
Zhang Y, Kohler N, Zhang M (2002) Biomaterials 23:1553–1561
Kohler N, Fryxell GE, Zhang MA (2004) J Am Chem Soc 126:7206–7211
Hu F, Neoh KG, Cen L, Kang ET (2006) Biomacromolecules 7:809–816
Veiseh O, Sun C, Gunn J, Kohler N, Gabikian P, Lee D, Bhattarai N, Ellenbogen R, Sze R, Hallahan A, Olson J, Zhang M (2005) Nano Lett 5:1003–1008
Martino AD, Sittinger M, Risbud MV (2005) Biomaterials 26:5983–5990
Majeti NV, Ravi K (2000) React Funct Polym 46:1–27
Wang GH, Zhang LM (2006) J Phys Chem B 110:24864–24868
Kim DK, Mikhaylova M, Zhang Y, Muhammed M (2003) Chem Mater 15:1617–1627
Chen XG, Park H (2003) Carbohydr Polym 53:355–357
Chang YC, Chen DH (2005) J Colloid Interface Sci 283:446–451
Haruma K (2000) Prog Polym Sci 25:1171–1210
Saravanan P, Alam S, Mathur GN (2003) J Mater Sci Lett 22:1283–1285
Huang SH, Liao MH, Chen DH (2003) Biotechnol Prog 19:1095–1100
Flesch C, Bourgeat-Lami E, Mornet S, Duguet E, Delaite C, Dumas P (2005) J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 43:3221–3231
Kamruzzaman Selim KM, Ha YS, Kim SJ, Chang Y, Kim TJ, Lee JH, Kang IK (2007) Biomaterials 28:710–716
Tanyolac D, Ozdural AR (2001) J Appl Polym Sci 80:707–715
Zhang LM, Chen DQ (2002) Colloids Surf A 205:231–236
Zhang LM, Zhou YJ, Wang Y (2006) J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:799–804
Bajpai AK (2000) J Appl Polym Sci 78:933–940
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NSFC (20273086; 30470476; 20676155), NSFG (5003252; 039184; 6023103), Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province (2004B33101003), and NCET Program (NCET-04-0810) in Universities of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, YY., Zhang, LM., Li, W. et al. Polysaccharide-modified iron oxide nanoparticles as an effective magnetic affinity adsorbent for bovine serum albumin. Colloid Polym Sci 285, 1193–1199 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-007-1672-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-007-1672-2