Abstract.
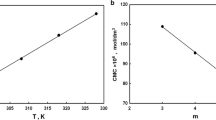
The interfacial and thermodynamic properties of a non-ionic surfactant, poly[oxyethylene(10)] lauryl ether, [C12H25(OCH2CH2)10OH], in aqueous solution in the presence of amino acids have been investigated. Critical micelle concentrations (cmcs) were determined by surface tension measurements at different additive concentrations and temperatures using a du Nouy tensiometer. From the surface tension data, the surface excess concentration (τ), the minimum area per molecule (Amin), and the surface pressure at the cmc(πcmc) were evaluated. Thermodynamic parameters of adsorption and micellization were evaluated and discussed. The other solution properties of this surfactant like the cloud point viscosity, and foaming have been determined in the presence of different concentrations of alanine and glycine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakshit, A., Sharma, B. The effect of amino acids on the surface and thermodynamic properties of poly[oxyethylene(10)] lauryl ether in aqueous solution. Colloid Polym Sci 281, 45–51 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-002-0743-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-002-0743-7