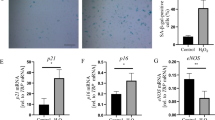
Abstract
Availability of adiponectin plays a crucial role in cardiovascular function. The present study was conducted to evaluate the presence, alterations and impact of the various adiponectin isoforms in vascular tissue under clinically relevant in vitro conditions (cold storage). Presence of various adiponectin isoforms in vascular smooth muscle cells and their regulation during cold storage was evaluated by PCR, western blot, ELISA and immunohistochemistry. The impact of the various isoforms for vessel preservation was assessed using isometric force measurement as an in vitro assay for vascular function. Adiponectin is expressed in smooth muscle cells from murine aortae and human saphenous veins. Following 2 days of cold storage adiponectin mRNA expression in mouse aorta is reduced, which appears to be regulated indirectly by miR-292-3p. Despite the reduced mRNA expression, adiponectin accumulated in cold storage supernatant over 2 days indicating a net release of adiponectin. Two days of cold storage resulted in an impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation which was prevented by addition of full-length adiponectin in concentrations similar to normal plasma levels during storage. In contrast, addition of recombinant adiponectin which is unable to form high order multimers failed to improve vessel function. High concentrations (20 μg/mL) of this trimeric isoform even reduced the vasorelaxation response and facilitated uncoupling of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Endothelial injury by cold storage may partly be prevented by addition of high-molecular-weight adiponectin. This effect may support graft patency to avoid coagulation- and atherosclerosis-associated impairment of perfusion.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albinsson S, Skoura A, Yu J, DiLorenzo A, Fernandez-Hernando C, Offermanns S, Miano JM, Sessa WC (2011) Smooth muscle miRNAs are critical for post-natal regulation of blood pressure and vascular function. PLoS ONE 6:e18869
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (1999) Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257:79–83
Bork S, Horn P, Castoldi M, Hellwig I, Ho AD, Wagner W (2011) Adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells is down-regulated by microRNA-369-5p and up-regulated by microRNA-371. J Cell Physiol 226:2226–2234
Cao Y, Tao L, Yuan Y, Jiao X, Lau WB, Wang Y, Christopher T, Lopez B, Chan L, Goldstein B, Ma XL (2009) Endothelial dysfunction in adiponectin deficiency and its mechanisms involved. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46:413–419
Ding M, Carrao AC, Wagner RJ, Xie Y, Jin Y, Rzucidlo EM, Yu J, Li W, Tellides G, Hwa J, Aprahamian TR, Martin KA (2012) Vascular smooth muscle cell-derived adiponectin: a paracrine regulator of contractile phenotype. J Mol Cell Cardiol 52:474–484
Dschietzig T, Brecht A, Bartsch C, Baumann G, Stangl K, Alexiou K (2012) Relaxin improves TNF-alpha-induced endothelial dysfunction: the role of glucocorticoid receptor and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signalling. Cardiovasc Res 95:97–107
Ebner A, Poitz DM, Augstein A, Strasser RH, Deussen A (2012) Functional, morphologic, and molecular characterization of cold storage injury. J Vasc Surg
Fasshauer M, Paschke R (2003) Regulation of adipocytokines and insulin resistance. Diabetologia 46:1594–1603
Fleming I (2010) Molecular mechanisms underlying the activation of eNOS. Pflugers Arch 459:793–806
Fruebis J, Tsao TS, Javorschi S, Ebbets-Reed D, Erickson MR, Yen FT, Bihain BE, Lodish HF (2001) Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight loss in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2005–2010
Fujimoto N, Matsuo N, Sumiyoshi H, Yamaguchi K, Saikawa T, Yoshimatsu H, Yoshioka H (2005) Adiponectin is expressed in the brown adipose tissue and surrounding immature tissues in mouse embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta 1731:1–12
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M, Shimomura I (2004) Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 114:1752–1761
Garbe S, Zatschler B, Muller B, Dieterich P, Ebner A, Rauen U, Matschke K, Deussen A (2011) Preservation of human artery function following prolonged cold storage with a new solution. J Vasc Surg 53:1063–1070
Houbaviy HB, Dennis L, Jaenisch R, Sharp PA (2005) Characterization of a highly variable eutherian microRNA gene. RNA 11:1245–1257
Hug C, Wang J, Ahmad NS, Bogan JS, Tsao TS, Lodish HF (2004) T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10308–10313
Khong SM, Andrews KL, Huynh NN, Venardos K, Aprico A, Michell DL, Zarei M, Moe KT, Dusting GJ, Kaye DM, Chin-Dusting JP (2012) Arginase II inhibition prevents nitrate tolerance. Br J Pharmacol 166:2015–2023
Kloting N, Berthold S, Kovacs P, Schon MR, Fasshauer M, Ruschke K, Stumvoll M, Bluher M (2009) MicroRNA expression in human omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 4:e4699
Komura N, Kihara S, Sonoda M, Kumada M, Fujita K, Hiuge A, Okada T, Nakagawa Y, Tamba S, Kuroda Y, Hayashi N, Sumitsuji S, Kawamoto T, Matsumoto S, Ouchi N, Arita Y, Okamoto Y, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2008) Clinical significance of high-molecular weight form of adiponectin in male patients with coronary artery disease. Circ J 72:23–28
Komura N, Kihara S, Sonoda M, Maeda N, Tochino Y, Funahashi T, Shimomura I (2010) Increment and impairment of adiponectin in renal failure. Cardiovasc Res 86:471–477
Kumada M, Kihara S, Sumitsuji S, Kawamoto T, Matsumoto S, Ouchi N, Arita Y, Okamoto Y, Shimomura I, Hiraoka H, Nakamura T, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Association of hypoadiponectinemia with coronary artery disease in men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:85–89
Lehle K, Hoenicka M, Jacobs VR, Schmid FX, Birnbaum DE (2006) Identification and reduction of cryoinjury in endothelial cells: a first step toward establishing a cell bank for vascular tissue engineering. Tissue Eng 12:3439–3447
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (1999) Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 100:2473–2476
Ouchi N, Ohishi M, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Nakamura T, Nagaretani H, Kumada M, Ohashi K, Okamoto Y, Nishizawa H, Kishida K, Maeda N, Nagasawa A, Kobayashi H, Hiraoka H, Komai N, Kaibe M, Rakugi H, Ogihara T, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Association of hypoadiponectinemia with impaired vasoreactivity. Hypertension 42:231–234
Owens CD, Kim JM, Hevelone ND, Hamdan A, Raffetto JD, Creager MA, Conte MS (2010) Novel adipokines, high molecular weight adiponectin and resisting, are associated with outcomes following lower extremity revascularization with autogenous vein. J Vasc Surg 51:1152–1159
Pajvani UB, Du X, Combs TP, Berg AH, Rajala MW, Schulthess T, Engel J, Brownlee M, Scherer PE (2003) Structure-function studies of the adipocyte-secreted hormone Acrp30/adiponectin. Implications fpr metabolic regulation and bioactivity. J Biol Chem 278:9073–9085
Pexa A, Boeger RH, Henle T, Schwedhelm E, Deussen A (2008) Effects of moderate hyperhomocysteinaemia induced by 4 weeks methionine-enriched diet on metabolite profile and mesenteric artery function in rats. Br J Nutr 99:993–999
Pineiro R, Iglesias MJ, Gallego R, Raghay K, Eiras S, Rubio J, Dieguez C, Gualillo O, Gonzalez-Juanatey JR, Lago F (2005) Adiponectin is synthesized and secreted by human and murine cardiomyocytes. FEBS Lett 579:5163–5169
Schraw T, Wang ZV, Halberg N, Hawkins M, Scherer PE (2008) Plasma adiponectin complexes have distinct biochemical characteristics. Endocrinology 149:2270–2282
Shin S, Kim S, Oh HE, Kong H, Shin E, Do SG, Jo TH, Park YI, Lee CK, Kim K (2012) Dietary aloe QDM complex reduces obesity-induced insulin resistance and adipogenesis in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. Immune Netw 12:96–103
Vandesompele J, De Peter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:RESEARCH0034
Waki H, Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Kita S, Ito Y, Hada Y, Uchida S, Tsuchida A, Takekawa S, Kadowaki T (2005) Generation of globular fragment of adiponectin by leukocyte elastase secreted by monocytic cell line THP-1. Endocrinology 146:790–796
Waldron GJ, Cole WC (1999) Activation of vascular smooth muscle K+ channels by endothelium-derived relaxing factors. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 26:180–184
Wolf AM, Wolf D, Avila MA, Moschen AR, Berasain C, Enrich B, Rumpold H, Tilg H (2006) Up-regulation of the anti-inflammatory adipokine adiponectin in acute liver failure in mice. J Hepatol 44:537–543
Xu A, Chan KW, Hoo RL, Wang Y, Tan KC, Zhang J, Chen B, Lam MC, Tse C, Cooper GJ, Lam KS (2005) Testosterone selectively reduces the high molecular weight form of adiponectin by inhibiting its secretion from adipocytes. J Biol Chem 280:18073–18080
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A, Yokomizo T, Kita S, Sugiyama T, Miyagishi M, Hara K, Tsunoda M, Murakami K, Ohteki T, Uchida S, Takekawa S, Waki H, Tsuno NH, Shibata Y, Terauchi Y, Froguel P, Tobe K, Koyasu S, Taira K, Kitamura T, Shimizu T, Nagai R, Kadowaki T (2003) Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 423:762–769
Yokota T, Meka CS, Medina KL, Igarashi H, Comp PC, Takahashi M, Nishida M, Oritani K, Miyagawa J, Funahashi T, Tomiyama Y, Matsuzawa Y, Kincade PW (2002) Paracrine regulation of fat cell formation in bone marrow cultures via adiponectin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest 109:1303–1310
Zatschler B, Dieterich P, Muller B, Kasper M, Rauen U, Deussen A (2009) Improved vessel preservation after 4 days of cold storage: experimental study in rat arteries. J Vasc Surg 50:397–406
Zhang Q, Sun H, Jiang Y, Ding L, Wu S, Fang T, Yan G, Hu Y (2013) MicroRNA-181a suppresses mouse granulosa cell proliferation by targeting activin receptor IIA. PLoS ONE 8:e59667
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Peggy Barthel, Antje Messer and Birgit Zatschler for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by MeDDrive grant program of the Medical Faculty Carl Gustav Carus at Dresden University of Technology [33-60.232 to A.E.]. TiProtec® storage solution was a kind gift from Dr. F. Köhler GmbH.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebner, A., Poitz, D.M., Alexiou, K. et al. Secretion of adiponectin from mouse aorta and its role in cold storage-induced vascular dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol 108, 390 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-013-0390-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-013-0390-9