Abstract
Objective
It was reported that there are cardiac stem cells (CSCs) in the rat heart, and they could reconstitute well-differentiated myocardium that are formed by blood-carrying new vessels and myocytes. However, how do the CSCs migrate into the peri-infarcted areas after myocardial infarction (MI)? It remains entirely unknown about the signal transduction involved in the migration of CSCs.
Methods and results
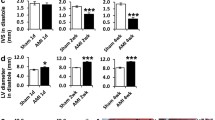
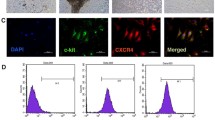
Rat heart MI was induced by left coronary artery ligation. Both immunohistochemical staining and Western blotting analysis was performed to detect the expression of SCF protein, and RT-PCR was conducted for the expression of SCF mRNA. Cardiac stem cells were isolated from rat hearts, and a cardiac stem cell migration assay was performed using a 48-well chemotaxis chamber system. On day 5 after MI in rats, the expression of stem cell factor (SCF) mRNA and protein was significantly increased in the peri-infarcted area, which was matched with more accumulation of CSCs in the region and improvement of cardiac function, which was blocked by p38 MAPK selective inhibitor SB203580. In in vitro experiments, SCF induced CSC migration in a concentration-dependent manner, and the antibody against SCF receptor (c-kit) blocked the SCF-induced CSC migration. Western blot analysis showed that the phosphorylated p38 MAPK (Phospho-p38 MAPK) was highly increased in the SCF-treated CSCs, and the inhibition of p38 MAPK activity significantly attenuated SCF-induced the migration of CSCs.
Conclusion
It demonstrated that SCF/c-kit signaling may mediate the migration of CSCs via activation of p38 MAPK.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anversa P, Kajstura J, Nadal-Ginard B, Leri A (2003) Primitive cells and tissue regeneration. Circ Res 92:579–582
Ayach BB, Yoshimitsu M, Dawood F, Sun M, Arab S, Chen M, Higuchi K, Siatskas C, Lee P, Lim H, Zhang J, Cukerman E, Stanford W, Medin JA, Liu PP (2006) Stem cell factor receptor induces progenitor and natural killer cell-mediated cardiac survival and repair after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2304–2309
Barbash IM, Chouraqui P, Baron J, Feinberg MS, Etzion S, Tessone A, Miller L, Guetta E, Zipori D, Kedes LH, Kloner RA, Leor J (2003) Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infracted myocardium: feasibility, cell migration and body distribution. Circulation 108:863–868
Beltrami AP, Urbanek K, Kajstura J, Yan SM, Finato N, Bussani R, Nadal-Ginard B, Silvestri F, Leri A, Beltrami CA, Anversa P (2001) Evidence that human cardiac myocytes divide after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 344:1750–1757
Beltrami AP, Barlucchi L, Torella D, Baker M, Limana F, Chimenti S, Kasahara H, Rota M, Musso E, Urbanek K, Leri A, Nadal-Ginard B, Anversa P (2003) Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial regeneration. Cell 114:763–776
Cai CL, Liang X, Shi Y, Chu PH, Pfaff SL, Chen J, Evans S (2003) Isl1 identifies a cardiac progenitor population that proliferates prior to differentiation and contributes a majority of cells to the heart. Dev Cell 5:877–889
Chimenti C, Kajstura J, Torella D, Urbanek K, Heleniak H, Colussi C, Di Meglio F, Nadal-Ginard B, Frustaci A, Leri A, Maseri A, Anversa P (2003) Senescence and death of primitive cells and myocytes lead to premature cardiac aging and heart failure. Circ Res 93:604–613
Dawn B, Stein AB, Urbanek K, Rota M, Whang B, Rastaldo R, Torella D, Tang XL, Rezazadeh A, Kajstura J, Leri A, Hunt G, Varma J, Prabhu SD, Anversa P, Bolli R (2005) Cardiac stem cells delivered intravascularly traverse the vessel barrier, regenerate infarcted myocardium, and improve cardiac function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3766–3771
Duronio V, Welham MJ, Abraham S, Dryden P, Schrader JW (1992) p21ras activation via hemopoietin receptors and c-kit requires tyrosine kinase activity but not tyrosine phosphorylation of p21ras GTPase-activating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1587–1591
Engel FB, Hsieh PC, Lee RT, Keating MT (2006) FGF1/p38 MAP kinase inhibitor therapy induces cardiomyocyte mitosis, reduces scarring, and rescues function after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15546–15551
Fazel S, Cimini M, Chen L, Li S, Angoulvant D, Fedak P, Verma S, Weisel RD, Keating A, Li RK (2006) Cardioprotective c-kit+ cells are from the bone marrow and regulate the myocardial balance of angiogenic cytokines. J Clin Invest 116:1865–1877
Galli SJ, Zsebo KM, Geissler EN (1994) The kit ligand, stem cell factor. Adv Immunol 55:1–96
Histov M, Weber C (2006) The therapeutic potential of progenitor cells in ischemic heart diseases—past, present and future. Basic Res Cardiol 101:1–7
Konard L, Munir Keilani M, Cordes A, Voulck-Badouin E, Laible L, Albrecht M, Renneberg N, Aumouller G (2005) Rat sertoli cells express epithelial but also mesenchymal genes after immortalization with SV40. Biochim Biophy Acta 1722:6–14
Kunisada T, Yoshida H, Yamakazi H, Miyamoto A, Hemmi H, Nishimura E, Shultz LD, Nishikawa S, Hayashi S (1998) Transgene expression of steel factor in the basal layer of epidermis promotes survival, proliferation, differentiation and migration of melanocyte precursors. Development 125: 2915–2293
Laflamme MA, Myerson D, Saffitz JE, Murry CE (2002) Evidence for cardiomyocyte repopulation by extracardiac progenitors in transplanted human hearts. Circ Res 90:634–640
Lam V, Kalesnikoff J, Lee CW, Hernandez-Hansen V, Wilson BS, Oliver JM, Krystal G (2003) IgE alone stimulates mast cell adhesion to fibronectin via pathways similar to those used by IgE + antigen but distinct from those used by Steel factor. Blood 102:1405–1413
Leri A, Kajstura J, Anversa P (2005) Cardiac stem cells and mechanisms of myocardial regeneration. Physiol Rev 5:1373–416
Linke A, Mueller P, Nurzynska D, Casarsa C, Torella D, Nascimbene A, Castaldo C, Cascapera S, Bohm M, Quaini F, Urbanek K, Leri A, Hintze TH, Kajstura J, Anversa P (2005) Cardiac stem cells in the dog heart regenerate infarcted myocardium improving cardiac performance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8966–8971
Linnekin D, DeBerry CS, Mou S (1997) Lyn associates with the juxtamembrane region of c-Kit and is activated by stem cell factor in hematopoietic cell lines and normal progenitor cells. J Biol Chem 272:27450–27455
Lewis TS, Shapiro PS, Ahn NG (1998) Signal transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res 74:49–139
Lyngbaek S, Schneider M, Hansen JL, Sheikh SP (2007) Cardiac regeneration by resident stem and progenitor cells in the adult heart. Basic Res Cardiol 102:101–114
Nadal-Ginard B, Kajstura J, Anversa P, Leri A (2003) A matter of life and death: cardiac myocyte apoptosis and regeneration. J Clin Invest 111:1457–1459
Oh H, Bradfute SB, Gallardo TD, Nakamura T, Gaussin V, Mishina Y, Pocius J, Michael LH, Behringer RR, Garry DJ, Entman ML, Schneider MD (2003) Cardiac progenitor cells from adult myocardium: homing, differentiation, and fusion after infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12313–12318
O’Laughlin-Bunner B, Radosevic N, Taylor ML, Shivakrupa, DeBerry C, Metcalfe DD, Zhou M, Lowell C, Linnekin D (2001) Lyn is required for normal stem cell factor-induced proliferation and chemotaxis of primary hematopoietic cells. Blood 98:343–350
Qiu FH, Ray P, Brown K, Barker PE, Jhanwar S, Ruddle FH, Besmer P (1988) Primary structure of c-kit: relationship with the CSF-1/PDGF receptor kinase family—oncogenic activation of v-kit involves deletion of extracellular domain and C terminus. EMBO J 7:1003–1011
Sattler M, Salgia R, Shrikhande G, Verma S, Pisick E, Prasad KV Griffin JD (1997) Steel factor induces tyrosine phosphorylation of CRKL and binding of CRKL to a complex containing ckit, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and p120(CBL). J Biol Chem 272:10248–10253
Serve H, Hsu YC, Besmer P (1994) Tyrosine residue 719 of the c-kit receptor is essential for binding of the P85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase and for c-kit- associated PI 3-kinase activity in COS-1 cells. J Biol Chem 269:6026–6030
Song ZH, Zhong M (2000) CB1 cannabinoid receptor-mediated cell migration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:204–209
Sun L, Lee J, Fine HA (2004) Neuronally expressed stem cell factor induces neural stem cell migration to areas of brain injury. J Clin Invest 113:1364–1374
Sundstrom M, Alfredsson J, Olsson N, Nilsson G (2001) Stem cell factor-induced migration of mast cells requires p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Exp Cell Res 267:144–151
Suto H, Nakae S, Kakurai M, Sedgwick JD, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2006) Mast cell-associated TNF promotes dendritic cell migration. J Immunol 176:4102–4112
Teyssier-Le Discorde M, Prost S, Nandrot E, Kirzenbaum M (1999) Spatial and temporal mapping of c-kit and its ligand, stem cell factor expression during human embryonic haemopoiesis. Br J Haematol 107:247–253
Templin C, Kotlarz D, Marquart F, Faulhaber J, Brendecke V, Schaefer A, Tsikas D, Bonda T, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Ohl L, Naim HY, Foerster R, Drexler H, Limbourg FP (2006) Transcoronary delivery of bone marrow cells to the infarcted murine myocardium: feasibility, cellular kinetics, and improvement in cardiac function. Basic Res Cardiol 101:301–310
Ueda S, Mizuki M, Ikeda H, Tsujimura T, Matsumura I, Nakano K, Daino H, Honda Zi Z, Sonoyama J, Shibayama H, Sugahara H, Machii T, Kanakura Y (2002) Critical roles of c-Kit tyrosine residues 567 and 719 in stem cell factor-induced chemotaxis: contribution of src family kinase and PI3-kinase on calcium mobilization and cell migration. Blood 99:3342–3349
Urbanek K, Rota M, Cascapera S, Bearzi C, Nascimbene A, De Angelis A, Hosota T, Chimenti S, Baker M, Limana F, Nurzynska D, Torella D, Rotatori F, Rastaldo R, Musso E, Quaini F, Leri A, Kajstura J, Anversa P (2005) Cardiac stem cells possess growth factor-receptor systems that after activation regenerate the infarcted myocardium, improving ventricular function and long-term survival. Circ Res 97:663–673
Urbanek K, Torella D, Sheikh F, Nurzynska D, Silvestri F, Beltrami CA, Bussani R, Beltrami AP, Quaini F, Bolli R, Leri A, Kajstura J, Anversa P (2005) Myocardial regeneration by activation of multipotent cardiac stem cells in ischemic heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8692–8697
van Dijk TB, van Den Akker E, Amelsvoort MP, Mano H, Lowenberg B, von Lindern M (2000) Stem cell factor induces phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent Lyn/Tec/Dok-1 complex formation in hematopoietic cells. Blood 96:3406–3413
Vosseller K, Stella G, Yee NS, Besmer P (1997) c-kit receptor signaling through its phosphatidylinositide-3′-kinase-binding site and protein kinase C: role in mast cell enhancement of degranulation, adhesion, and membrane ruffling. Mol Biol Cell 8:909–922
Wang G, Lei M, Lu X, Feng Q (2004) Bone marrow stem cell migration to the infracted myocardium: role of TNF. Faseb J 18:A1286
Wang R, Li J, Yashpal N (2004) Phenotypic analysis of c-kit expression in epithelial monolayers derived from postnatal rat pancreatic islets. J Endocrinol 182:113–122
Witte ON (1990) Steel locus defines new multipotent growth factor. Cell 63:5–6
Yarden Y, Kuang WJ, Yang-Feng T, Coussens L, Munemitsu S, Dull TJ, Chen E, Schlessinger J, Francke U, Ullrich A (1987) Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J 6:3341–3351
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by research grants 30470710 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, NCET-04-0711 from the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, and 2005ABB009 from the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Returned for 1. Revision: 22 August 2007 1. Revision received: 11 October 2007
Returned for 2. Revision: 31 October 2007 2. Revision received: 2 November 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuang, D., Zhao, X., Xiao, G. et al. Stem cell factor/c-kit signaling mediated cardiac stem cell migration via activation of p38 MAPK. Basic Res Cardiol 103, 265–273 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-007-0690-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-007-0690-z