Abstract
Purpose
Changes of food preference toward foods with low caloric density have been demonstrated after bariatric surgery and may contribute to sustained body weight loss. It has been hypothesized that olfactory perception as an integral part of food selection might be altered after bariatric surgery.
Methods
Sniffin’ Sticks® were used to investigate the olfactory perception of morbidly obese patients undergoing either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB, n = 15) or sleeve gastrectomy (SG, n = 15) before 1, 6, 12, and 24 weeks after surgery. Obese patients without surgical intervention served as controls (CG, n = 12). Results are presented using the testing odor threshold, discrimination, and identification score (TDI; higher scores indicate better olfactory perception). Body weight loss was recorded.
Results
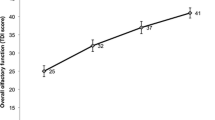
Initial BMI of the SG group (56.04 ± 7.096 kg m−2) was higher compared to the BMI of the RYGB (48.71 ± 6.49 kg m−2) and CG (50.35 ± 6.78 kg m−2); p = 0.011. Body weight loss among the surgical groups was not different (p = 0.011) while controls did not lose weight. Mean baseline TDI scores were significantly lower in the SG group 27.1 ± 3.9 vs. 32.6 ± 3.6 (RYGB) and 32.1 ± 5.3 (CG), respectively, whereas there were after 24 weeks no changes in RYGB and CG patients; the TDI score in the SG group increased significantly to 31.1 ± 3.5 (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
Our data suggest that a substantial body weight loss per se does not affect olfactory perception. However, our results point towards improved olfactory perception after sleeve gastrectomy but not Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berghöfer A, Pischon T, Reinhold T, Apovian CM, Sharma AM, Willich SN (2008) Obesity prevalence from a European perspective: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 8(1):200. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-8-200
Gray LJ, Cooper N, Dunkley A, Warren FC, Ara R, Abrams K, Davies MJ, Khunti K, Sutton A (2012) A systematic review and mixed treatment comparison of pharmacological interventions for the treatment of obesity. Obes Rev 13(6):483–498. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00981.x
Ho M, Garnett SP, Baur L, Burrows T, Stewart L, Neve M, Collins C (2012) Effectiveness of lifestyle interventions in child obesity: systematic review with meta-analysis. Pediatrics 130(6):e1647–e1671. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-1176
Sjostrom L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M, Torgerson J, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, Dahlgren S, Larsson B, Narbro K, Sjostrom CD, Sullivan M, Wedel H (2004) Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med 351(26):2683–2693
Jurowich C, Germer CT, Seyfried F, Thalheimer A (2012) Metabolic surgery. Chirurg 83(6):583–598. doi:10.1007/s00104-011-2239-9, quiz 599–600
Bueter M, Seyfried F, Germer CT (2010) Why patients lose weight after bariatric operations. Zentralbl Chir 135(1):28–33. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1224697
Laurenius A, Larsson I, Bueter M, Melanson KJ, Bosaeus I, Forslund HB, Lonroth H, Fandriks L, Olbers T (2012) Changes in eating behaviour and meal pattern following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Int J Obes (Lond) 36(3):348–355. doi:10.1038/ijo.2011.217
Chambers AP, Wilson-Perez HE, McGrath S, Grayson BE, Ryan KK, D’Alessio DA, Woods SC, Sandoval DA, Seeley RJ (2012) Effect of vertical sleeve gastrectomy on food selection and satiation in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 303(8):E1076–E1084. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00211.2012
Wilson-Perez HE, Chambers AP, Sandoval DA, Stefater MA, Woods SC, Benoit SC, Seeley RJ (2013) The effect of vertical sleeve gastrectomy on food choice in rats. Int J Obes (Lond) 37(2):288–295. doi:10.1038/ijo.2012.18
Miras AD, le Roux CW (2013) Mechanisms underlying weight loss after bariatric surgery. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(10):575–584. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2013.119
Saeidi N, Nestoridi E, Kucharczyk J, Uygun MK, Yarmush ML, Stylopoulos N (2012) Sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass exhibit differential effects on food preferences, nutrient absorption and energy expenditure in obese rats. Int J Obes (Lond) 36(11):1396–1402. doi:10.1038/ijo.2012.167
Richardson BE, Vanderwoude EA, Sudan R, Leopold DA, Thompson JS (2012) Gastric bypass does not influence olfactory function in obese patients. Obes Surg 22(2):283–286. doi:10.1007/s11695-011-0487-x
Runkel N, Colombo-Benkmann M, Huttl TP, Tigges H, Mann O, Flade-Kuthe R, Shang E, Susewind M, Wolff S, Wunder R, Wirth A, Winckler K, Weimann A, de Zwaan M, Sauerland S (2011) Evidence-based German guidelines for surgery for obesity. Int J Colorectal Dis 26(4):397–404. doi:10.1007/s00384-011-1136-5
Wolfensberger M, Schnieper I (1999) Sniffin’Sticks: a new system for olfactory assessment in routine clinical practice. Hno 47(7):629–636
Haehner A, Mayer AM, Landis BN, Pournaras I, Lill K, Gudziol V, Hummel T (2009) High test-retest reliability of the extended version of the “Sniffin’ Sticks” test. Chem Senses 34(8):705–711. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjp057
Doty RL, Marcus A, Lee WW (1996) Development of the 12-item Cross-Cultural Smell Identification Test (CC-SIT). Laryngoscope 106(3 Pt 1):353–356
Smeets PA, Charbonnier L, van Meer F, van der Laan LN, Spetter MS (2012) Food-induced brain responses and eating behaviour. Proc Nutr Soc 71(4):511–520. doi:10.1017/S0029665112000808
Yeomans MR (2006) Olfactory influences on appetite and satiety in humans. Physiol Behav 87(4):800–804. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.01.029
Richardson BE, Vander Woude EA, Sudan R, Thompson JS, Leopold DA (2004) Altered olfactory acuity in the morbidly obese. Obes Surg 14(7):967–969. doi:10.1381/0960892041719617
Miras AD, le Roux CW (2010) Bariatric surgery and taste: novel mechanisms of weight loss. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 26(2):140–145. doi:10.1097/MOG.0b013e328333e94a
le Roux CW, Bueter M, Theis N, Werling M, Ashrafian H, Lowenstein C, Athanasiou T, Bloom SR, Spector AC, Olbers T, Lutz TA (2011) Gastric bypass reduces fat intake and preference. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301(4):R1057–1066
Bueter M, Miras AD, Chichger H, Fenske W, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Unwin RJ, Lutz TA, Spector AC, le Roux CW (2011) Alterations of sucrose preference after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Physiol Behav 104(5):709–721
Scholtz S, Miras AD, Chhina N, Prechtl CG, Sleeth ML, Daud NM, Ismail NA, Durighel G, Ahmed AR, Olbers T, Vincent RP, Alaghband-Zadeh J, Ghatei MA, Waldman AD, Frost GS, Bell JD, le Roux CW, Goldstone AP (2013) Obese patients after gastric bypass surgery have lower brain-hedonic responses to food than after gastric banding. Gut. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305008
Brady S, Lalli P, Midha N, Chan A, Garven A, Chan C, Toth C (2013) Presence of neuropathic pain may explain poor performances on olfactory testing in diabetes mellitus patients. Chem Senses 38(6):497–507. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjt013
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Kathrin Bischof and Kathrin Hohl for their skillful assistance during the data recruitment, and we thank Dr. Imme Haubitz for the statistical analysis. Additionally, we thank Dr. Dieter Schneider for his guidance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jurowich, C.F., Seyfried, F., Miras, A.D. et al. Does bariatric surgery change olfactory perception? Results of the early postoperative course. Int J Colorectal Dis 29, 253–260 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-013-1795-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-013-1795-5