Abstract
Purpose
Interleukin 23 (IL-23) affects tumor growth by regulating Th cells and plays a vital role in immunosuppression in tumor tissues. However, whether tumor cells are IL-23R positive or whether IL-23 has the potential to influence the growth of cancer cells directly remains unclear. The aim of this study was to clarify the molecular expression patterns of IL-23, IL-23R, and Forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) in normal tissues adjacent to cancer, in intestinal polyps (IP), and in colorectal carcinoma (CRC), and to infer the relationship between the expression patterns of these three molecules and the progress of intestinal tumors from adenomatous polyps to colorectal cancer.
Methods
The levels of IL-23A, IL-23R, and FOXP3 were evaluated in normal tissues adjacent to cancer (NT, n = 13), IP (n = 26), and CRC (n = 13) using real-time PCR, ELISA, western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry.
Results
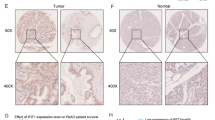
The expression of IL-23 and FOXP3 increased progressively from NT through to CRC. Immunohistochemistry staining showed that IL-23R was highly positive in carcinoma cells of the CRC group, whereas it was partially positive in cells of other groups. In addition, the human CRC cell line SW-480 exhibited weak IL-23R immunocytochemical positivity.
Conclusions
We propose that the IL-23/IL-23R pathway is a potential route to facilitate the malignant progression of cancers. The relationship between IL-23 and FOXP3 in the microenvironment of carcinoma led us to deduce that these two molecules may interact with each other. Although the exact mechanism underlying this interaction remains a mystery, we are convinced that these two molecules are relevant in cancer progression and that IL-23 could be a potential target for cancer immunotherapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B et al (2000) Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 13:715–725. doi:10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00070-4
Parham C, Chirica M, Timans J et al (2002) A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J Immunol 168:5699–5708
Lankford CS, Frucht DM (2003) A unique role for IL-23 in promoting cellular immunity. J Leukoc Biol 73:49–56. doi:10.1189/jlb.0602326
Langowski JL, Zhang X, Wu L et al (2006) IL-23 promotes tumour incidence and growth. Nature 442:461–465. doi:10.1038/nature04808
Wei S, Kryczek I, Zou W (2006) Regulatory T-cell compartmentalization and trafficking. Blood 108:426–431. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-01-0177
Coffer PJ, Burgering BM (2004) Forkhead-box transcription factors and their role in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 4:889–899. doi:10.1038/nri1488
Yagi H, Nomura T, Nakamura K et al (2004) Crucial role of foxp3 in the development and function of human CD25 + CD4 + regulatory T cells. Int Immunol 16:1643–1656. doi:10.1093/intim/dxh165
Beyer M, Schultze JL (2006) Regulatory T cells in cancer. Blood 108:804–811. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-02-002774
Stanilov N, Miteva L, Mintchev N, Stanilova S (2009) High expression of Foxp3, IL-23p19 and surviving mRNA in colorectal carcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis 24:151–157. doi:10.1007/s00384-008-0588-8
Salama P, Phillips M, Grieu F et al (2009) Tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:186–192. doi:10.1200/jco.2008.18.7229
Sinicrope FA, Rego RL, Ansell SM, Knutson KL, Foster NR, Sargent DJ (2009) Intraepithelial effector (CD3+)/regulatory (FoxP3+) T-cell ratio predicts a clinical outcome of human colon carcinoma. Gastroenterology 137:1270–1279. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.06.053
Frey DM, Droeser RA, Viehl CT et al (2010) High frequency of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells predicts improved survival in mismatch repair-proficient colorectal cancer patients. Int J Cancer 126:2635–2643. doi:10.1002/ijc.24989
Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA, Ward E (2009) Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin 59:366–378. doi:10.3322/caac.20038
Malvicini M, Rizzo M, Alaniz L et al (2009) A novel synergistic combination of cyclophosphamide and gene transfer of interleukin-12 eradicates colorectal carcinoma in mice. Clin Cancer Res 15:7256–7265. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-09-1861
Fukuda M, Ehara M, Suzuki S, Ohmori Y, Sakashita H (2010) IL-23 promotes growth and proliferation in human squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Int J Oncol 36:1355–1365. doi:10.3892/ijo_00000620
Kortylewski M, Xin H, Kujawski M et al (2009) Regulation of the IL-23 and IL-12 balance by Stat3 signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 15:114–123. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2008.12.018
Jared EL, Troy RT, Lisa AS et al (2006) Analysis of FOXP3 reveals multiple domains required for its function as a transcriptional repressor. J Immunol 177:3133–3142
Estelle B, Maryam D, Mohamed O (2005) Foxp3 interacts with nuclear factor of activated T cells and NF-κB to repress cytokine gene expression and effector functions of T helper cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5138–5143. doi:10.1073/pnas.0501675102
Philip PA, Chris S, Sofia B et al (2010) Interleukin-23 drives intestinal inflammation through direct activity on T cells. Immunity 33:279–288. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2010.08.010
Jung DJ, Jin DH, Hong SW et al (2010) Foxp3 expression in p53-dependent DNA damage responses. J Biol Chem 285:7995–8002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.047985
Elson CO, Cong Y, Weaver CT, Schoeb TR, TK McClanah an, Fick RB, Kastelein RA (2007) Monoclonal anti-interleukin 23 reverses active colitis in a T cell-mediated model in mice. Gastroentryology 13:2359–2370. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.104
Hue S, Ahern P, Buonocore S et al (2006) Interleukin-23 drives innate and T cell-mediated intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med 203:2473–2483. doi:10.1084/jem.20061099
Kullberg MC, Jankovic D, Feng CG et al (2006) IL-23 plays a key role in Helicobacter hepaticus-induced T cell-dependent colitis. J Exp Med 203:2485–2494. doi:10.1084/jem.20061082
Yen D, Cheung J, Scheerens H et al (2006) IL-23 is essential for T cell-mediated colitis and promotes inflammation via IL-17 and IL-6. J Clin Invest 116:1310–1316. doi:10.1172/JCI21404
Che Mat NF, Zhang X, Guzzo C, Gee K (2010) Interleukin-23-induced interleukin-23 receptor subunit expression is mediated by the Janus Kinase/signal transducer and activation of transcription pathway in human CD4 T cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. doi:10.1089/jir.2010.0083
Chan JR, Blumenschein W, Murphy E et al (2006) IL-23 stimulates epidermal hyperplasia via TNF and IL-20R2-dependent mechanisms with implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Exp Med 203:2577–2587. doi:10.1084/jem.20060244
Kaiga T, Sato M, Kaneda H (2007) Systemic administration of IL-23 induces potent antitumor immunity primarily mediated through Th1-type response in association with the endogenously expressed IL-12. J Immunol 178:7571–7758
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant 136050132 from the Startup Foundation of the West China Hospital of Sichuan University. We would like to thank Dr. Wengeng Zhang (Center for Regenerative Developmental Biology, the Forsyth Institute) for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Feng Lan and Le Zhang had equal contributions to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, F., Zhang, L., Wu, J. et al. IL-23/IL-23R: potential mediator of intestinal tumor progression from adenomatous polyps to colorectal carcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis 26, 1511–1518 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1232-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1232-6