Abstract
Purpose
The present study aims to define the prognostic impact of the lymph node ratio (LNR) in patients with stage III distal rectal cancer.
Methods
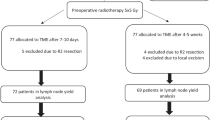
We analyzed data from 501 patients who underwent curative resection (total mesorectal excision, TME) for stage III distal rectal cancer at 12 institutions between 1991 and 1998. Patients were divided into four groups according to quartiles based on LNR.
Results
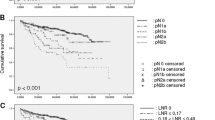
Among the 501 patients, 381 underwent TME with pelvic sidewall dissection (PSD). The median numbers of lymph nodes retrieved with and without PSD were 45 and 17, respectively (P < 0.0001). Forty-nine patients with lymph node retrieved less than 12 were excluded from further analyses. Among various clinicopathological parameters, univariate analysis identified age (P = 0.0059), histological grade (P < 0.0001), depth of tumor invasion (P = 0.0003), and number of positive nodes (P < 0.0001) and LNR (P < 0.0001) as prognostic factors. The Cox proportional hazards model revealed that age (P = 0.014), histological grade (P < 0.0001), depth of tumor invasion (P = 0.0002), and LNR (group 3, P = 0.0012; group 4, P < 0.0001) were independent prognostic factors. When the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) seventh staging system was added as a covariate, both AJCC stage (P < 0.0001) and LNR (P < 0.0001) were independent prognostic factors.
Conclusions
Adding the LNR concept to the AJCC cancer staging system will improve accuracy in evaluating the nodal status of distal rectal cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249
Muto T, Kotake K, Koyama, Y (2001) Colorectal cancer statistics in Japan: data from JSCCR registration, 1974-1993. Int J Clin Oncol 6:171–176
Kotake K, Honjo S, Sugihara K, Kato T, Kodaira S, Takahashi T, Yasutomi M, Muto T, Koyama Y (2003) Changes in colorectal cancer during a 20-year period: an extended report from the multi-institutional registry of large bowel cancer, Japan. Dis Colon Rectum 46:S32–43
Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Macdonald JS, Haller DG, Laurie JA, Goodman PJ, Ungerleider JS, Emerson WA, Tormey DC, Glick JH (1990) Levamisole and fluorouracil for adjuvant therapy of resected colon carcinoma. N Engl J Med 322:352–358
Tepper JE, O'Connell MJ, Niedzwiecki D, Hollis D, Compton C, Benson AB 3rd, Cummings B, Gunderson L, Macdonald JS, Mayer RJ (2001) Impact of number of nodes retrieved on outcome in patients with rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 19:157–163
Wolmark N, Rockette H, Fisher B, Wickerham DL, Redmond C, Fisher ER, Jones J, Mamounas EP, Ore L, Petrelli NJ (1993) The benefit of leucovorin-modulated fluorouracil as postoperative adjuvant therapy for primary colon cancer: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project protocol C-03. J Clin Oncol 11:1879–1887
Wolmark N, Rockette H, Mamounas E, Jones J, Wieand S, Wickerham DL, Bear HD, Atkins JN, Dimitrov NV, Glass AG, Fisher ER, Fisher B (1999) Clinical trial to assess the relative efficacy of fluorouracil and leucovorin, fluorouracil and levamisole, and fluorouracil, leucovorin, and levamisole in patients with Dukes' B and C carcinoma of the colon: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project C-04. J Clin Oncol 17:3553–3559
Zaniboni A (1997) Adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer with high-dose leucovorin and fluorouracil: impact on disease-free survival and overall survival. J Clin Oncol 15:2432–2441
Berger AC, Sigurdson ER, LeVoyer T, Hanlon A, Mayer RJ, Macdonald JS, Catalano PJ, Haller DG (2005) Colon cancer survival is associated with decreasing ratio of metastatic to examined lymph nodes. J Clin Oncol 23:8706–8712
Chin CC, Wang JY, Yeh CY, Kuo YH, Huang WS, Yeh CH (2009) Metastatic lymph node ratio is a more precise predictor of prognosis than number of lymph node metastases in stage III colon cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 24:1297–1302
Kim YS, Kim JH, Yoon SM, Choi EK, Ahn SD, Lee SW, Kim JC, Yu CS, Kim HC, Kim TW, Chang HM (2009) Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in patients with stage III rectal cancer treated with total mesorectal excision followed by chemoradiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:796–802
Moug SJ, Saldanha JD, McGregor JR, Balsitis M, Diament RH (2009) Positive lymph node retrieval ratio optimises patient staging in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 100:1530–1533
Peschaud F, Benoist S, Julie C, Beauchet A, Penna C, Rougier P, Nordlinger B (2008) The ratio of metastatic to examined lymph nodes is a powerful independent prognostic factor in rectal cancer. Ann Surg 248:1067–1073
Rosenberg R, Friederichs J, Schuster T, Gertler R, Maak M, Becker K, Grebner A, Ulm K, Hofler H, Nekarda H, Siewert JR (2008) Prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer is associated with lymph node ratio: a single-center analysis of 3,026 patients over a 25-year time period. Ann Surg 248:968–978
Kobayashi H, Mochizuki H, Sugihara K, Morita T, Kotake K, Teramoto T, Kameoka S, Saito Y, Takahashi K, Hase K, Oya M, Maeda K et al (2007) Characteristics of recurrence and surveillance tools after curative resection for colorectal cancer: a multicenter study. Surgery 141:67–75
Heald RJ, Husband EM, Ryall RD (1982) The mesorectum in rectal cancer surgery—the clue to pelvic recurrence? Br J Surg 69:613–616
Heald RJ, Moran BJ, Ryall RD, Sexton R, MacFarlane JK (1998) Rectal cancer: the Basingstoke experience of total mesorectal excision, 1978–1997. Arch Surg 133:894–899
Martling AL, Holm T, Rutqvist LE, Moran BJ, Heald RJ, Cedemark B (2000) Effect of a surgical training programme on outcome of rectal cancer in the County of Stockholm. Stockholm Colorectal Cancer Study Group, Basingstoke Bowel Cancer Research Project. Lancet 356:93–96
Medical Research Council Rectal Cancer Working Party (1996) Randomised trial of surgery alone versus surgery followed by radiotherapy for mobile cancer of the rectum. Lancet 348:1610–1614
Slanetz CA Jr, Grimson R (1997) Effect of high and intermediate ligation on survival and recurrence rates following curative resection of colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 40:1205–1218, discussion 18–9
Colorectal Cancer Collaborative Group (2001) Adjuvant radiotherapy for rectal cancer: a systematic overview of 8,507 patients from 22 randomised trials. Lancet 358:1291–1304
Kapiteijn E, Marijnen CA, Nagtegaal ID, Putter H, Steup WH, Wiggers T, Rutten HJ, Pahlman L, Glimelius B, van Krieken JH, Leer JW, van de Velde CJ (2001) Preoperative radiotherapy combined with total mesorectal excision for resectable rectal cancer. N Engl J Med 345:638–646
Hojo K, Koyama Y, Moriya Y (1982) Lymphatic spread and its prognostic value in patients with rectal cancer. Am J Surg 144:350–354
Kobayashi H, Mochizuki H, Kato T, Mori T, Kameoka S, Shirouzu K, Sugihara K (2009) Outcomes of surgery alone for lower rectal cancer with and without pelvic sidewall dissection. Dis Colon Rectum 52:567–576
Sugihara K, Kobayashi H, Kato T, Mori T, Mochizuki H, Kameoka S, Shirouzu K, Muto T (2006) Indication and benefit of pelvic sidewall dissection for rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 49:1663–1672
Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Tabah-Fisch I, de Gramont A (2004) Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2343–2351
Andre T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Bonetti A, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Rivera F, de Gramont A (2009) Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol 27:3109–3116
Sierra A, Regueira FM, Hernandez-Lizoain JL, Pardo F, Martinez-Gonzalez MA JAC (2003) Role of the extended lymphadenectomy in gastric cancer surgery: experience in a single institution. Ann Surg Oncol 10:219–226
Bando E, Yonemura Y, Taniguchi K, Fushida S, Fujimura T, Miwa K (2002) Outcome of ratio of lymph node metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 9:775–784
AJCC (American Joint Committee on Cancer) (2010) Cancer Staging Manual, 7th edn. Springer, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, H., Mochizuki, H., Kato, T. et al. Lymph node ratio is a powerful prognostic index in patients with stage III distal rectal cancer: a Japanese multicenter study. Int J Colorectal Dis 26, 891–896 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1173-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1173-0