Abstract
Purpose
Visceral hypersensitivity is an important pathological mechanism of irritable bowel syndrome. Electroacupuncture (EA) could relieve chronic visceral hypersensitivity (CVH) in rats. However, little information is available about the mechanism. The aim of this study was to confirm the effects of EA at acupoint ST-36 (Zusanli) on CVH induced by the chemical colorectal irritation during postnatal development of rats, and to explore the possible 5-HT3 receptor mechanism.
Methods
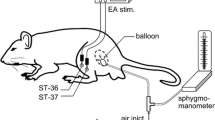
Rats were randomized into four groups, including the normal control group, CVH group, CVH with EA group, and CVH with sham EA group. The abdominal electromyogram (EMG) in response to colorectal distension was selected as the index for measurement of visceral hypersensitivity. 5-HT3 receptors were analyzed through reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction and western blot.
Results
EA at ST-36 significantly decreased evoked EMG. The expression of 5-HT3 receptor in the colon was increased in rats with CVH, and decreased after EA treatment.
Conclusions
EA at acupoint ST-36 attenuates CVH in rats and decreases 5-HT3 receptor level in the colon. Decreased 5-HT3 receptor level in the colon may mediate the beneficial effect of EA in rats with CVH.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuiken SD, Tytgat GN, Boeckxstaens GE (2005) Review article: drugs interfering with visceral sensitivity for the treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders—the clinical evidence. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 21:633–651
Cui KM, Li WM, Gao X, Chung K, Chung JM, Wu JC (2005) Electro-acupuncture relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia in rats. Neurosci Lett 376:20–23
Tian XY, Bian ZX, Hu XG, Zhang XJ, Liu L, Zhang HQ (2006) Electro-acupuncture attenuates stress-induced defecation in rats with chronic visceral hypersensitivity via serotonergic pathway. Brain Res 1088:101–108
Ulett GA, Han S, Han JS (1998) Electroacupuncture: mechanisms and clinical application. Biol Psychiatry 44:129–138
Lux G, Hagel J, Bäcker P, Bäcker G, Vogl R, Ruppin H, Domschke S, Domschke W (1994) Acupuncture inhibits vagal gastric acid secretion stimulated by sham feeding in healthy subjects. Gut 35:1026–1029
Espejo EF, Gil E (1998) Antagonism of perpheral 5-HT4 receptors reduces visceral and cutaneous pain in mice and induces visceral an algesia after simultaneous inactivation of 5-HT3 receptors. Brain Res 788:20–24
Koziowski CM, Green A, Grundy D, Boissonade FM, Bountra C (2000) The 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist alosetron inhibits the colorectal distention induced depressor response and spinal c-fos expression in the anesthetised rat. Gut 46:474–480
Winston J, Shenoy M, Medley D, Naniwadekar A, Pasricha PJ (2007) The vanilloid receptor initiates and maintains colonic hypersensitivity induced by neonatal colon irritation in rats. Gastroenterology 132:615–627
Mayer EA, Collins SM (2002) Evolving pathophysiologic models of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterology 122:2032–2048
Al-chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha PJ (2000) A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology 119:1276–1285
La JH, Kim TW, Sung TS, Kang JW, Kim HJ, Yang IS (2003) Visceral hypersensitivity and altered colonic motility after subsidence of inflammation in a rat model of colitis. World J Gastroenterol 9:2791–2795
Xu GY, Winston JH, Chen JD (2009) Electroacupuncture attenuates visceral hyperalgesia and inhibits the enhanced excitability of colon specific sensory neurons in a rat model of IBS. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:1302–e125
Ezzo J, Berman B, Hadhazy VA, Jadad AR, Lao L, Singh BB (2000) Is acupuncture effective for the treatment of chronic pain? A systematic review. Pain 86:217–225
Tian SL, Wang XY, Ding GH (2008) Repeated electro-acupuncture attenuates chronic visceral hypersensitivity and spinal cord NMDA receptor phosphorylation in a rat irritable bowel syndrome model. Life Sci 83:356–363
Iwa M, Strickland C, Nakade Y, Pappas TN, Takahashi T (2005) Electroacupuncture reduces rectal distension-induced blood pressure changes in conscious dogs. Dig Dis Sci 50:1264–1270
McLean PG, Borman RA, Lee K (2007) 5-HT in the enteric nervous system: gut function and neuropharmacology. Trends Neurosci 30:9–13
Liu HR, Wang XM, Zhou EH, Shi Y, Li N, Yuan LS, Wu HG (2009) Acupuncture at both ST 25 and ST37 improves the pain threshold of chronic visceral hypersensitivity rats. Neurochem Res 34(11):1914–1918
Zhou EH, Liu HR, Wu HG, Shi Y, Wang XM, Tan LY, Yao LQ, Zhong YS, Jiang Y, Zhang LL (2009) Suspended moxibustion relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia via serotonin pathway in the colon. Neurosci Lett 451(2):144–147
Crowell MD (2004) Role of serotonin in the pathophysiology of the irritable bowel syndrome. Br J Pharmacol 141:1285–1293
Prior A, Read NW (1993) Reduction of rectal sensitivity and post-prandial motility by granisetron, a 5HT3-receptor antagonist, in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 7:175–180
Delvaux M, Louvel D, Marmet JP, Campos-Oriola R, Frexinos J (1998) Effect of alosetron on responses to colonic distension in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 12:849–855
Ma XP, Tan LY, Yang Y, Wu HG, Jiang B, Liu HR, Yang L (2009) Effect of electro-acupuncture on substance P, its receptor and corticotropin-releasing hormone in rats with irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 15(41):5211–5217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dan Chu and Pengfei Cheng contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, D., Cheng, P., Xiong, H. et al. Electroacupuncture at ST-36 relieves visceral hypersensitivity and decreases 5-HT3 receptor level in the colon in chronic visceral hypersensitivity rats. Int J Colorectal Dis 26, 569–574 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-010-1087-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-010-1087-2