Abstract
Purpose
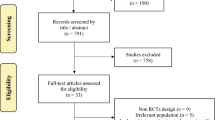
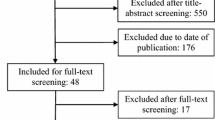
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety between single-incision, transscrotal orchidopexy, and the traditional inguinal orchidopexy in children.
Methods
A systematic search of the electronic databases was conducted to identify studies compared the transscrotal orchidopexy (SO) and inguinal orchidopexy (IO) for children. Parameters, such as operative time, the incidence of patent processus vaginalis, and postoperative complications, including wound infection, testicular atrophy, testicular reascent, hernia, or hydrocele, were pooled and compared by meta-analysis.
Results
Among the 1376 children with palpable undescended testes (UDTs) included in the eight studies, 697 had received SO and 679 IO. There were shorter operative times with the SO approach compared with IO. However, no significant difference was found between SO and IO in the incidence of patent processus vaginalis and postoperative complications, including wound infection, testicular atrophy, testicular reascent, and hernia.
Conclusion
SO is a safe and effective surgical approach alternative to IO for pediatric UDTs. Compared with IO, SO has the advantage of shorter operative times. Besides, the incidence of postoperative wound infection may be slightly lower in SO. We suggest that SO should be considered as an acceptable option for children with UDTs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thong M, Lim C, Fatimah H (1998) Undescended testes: incidence in 1,002 consecutive male infants and outcome at 1 year of age. Pediatr Surg Int 13:37–41
Bianchi A, Squire BR (1989) Transscrotal orchidopexy:orchidopexy revised. Pediatr Surg Int 4:189–192
Lais A, Ferro F (1995) Trans-scrotal approach for surgical correction of cryptorchidism and congenital anomalies of the processus vaginalis. Eur Urol 29(2):235–238
Al-Mandil M, Khoury AE, El-Hout Y et al (2008) Potential complications with the prescrotal approach for the palpable undescended testis? A comparison of single prescrotal incision to the traditional inguinal approach. J Urol 180(2):686–689
Lee HR, Lee YS, Kim HS et al (2009) A comparison between single scrotal incision orchiopexy and the inguinal approach in patients with palpable undescended testes distal to the external inguinal ring. Korean J Urol 50(11):1133–1137
Takahashi M, Kurokawa Y, Nakanishi R et al (2009) Low transscrotal orchidopexy is a safe and effective approach for undescended testes distal to the external inguinal ring. Urol Int 82(1):92–96
Na SW, Kim SO, Hwang EC et al (2011) Single scrotal incision orchiopexy for children with palpable low-lying undescended testis: early outcome of a prospective randomized controlled study. Korean J Urol 52(9):637–641
Cuda SP, Srinivasan AK, Kalisvaart J et al (2011) Evolution of single practice trends in the surgical approach to the undescended testicle. J Urol 185(6):2451–2454
Cloutier J, Moore K, Nadeau G et al (2011) Modified scrotal (Bianchi) mid raphe single incision orchiopexy for low palpable undescended testis: early outcomes. J Urol 185(3):1088–1092
Eltayeb AA (2014) Single high scrotal incision orchidopexy for unilateral palpable testis: a randomised controlled study. Afr J Paediatr Surg 11(2):143–146
Ben DM, Zouari M, Zitouni H et al (2015) Comparison of the inguinal and scrotal approaches for the treatment of cryptorchidism in children. Progres en urologie: journal de l’Association francaise d’urologie et de la Societe francaise d’urologie 25(10):598–602
Caruso AP, Walsh RA, Wolach JW et al (2000) Single scrotal incision orchiopexy for the palpable undescended testicle. J Urol 164:156–158
Parsons JK, Ferrer F, Docimo SG (2003) The low scrotal approach to the ectopic or ascended testicle: prevalence of a patent processus vaginalis. J Urol 169:1832–1833
Dayanç M, Kibar Y, Tahmaz L et al (2004) Scrotal incision orchiopexy for undescended testis. Urology 64(6):1216–1218
Russinko PJ, Siddiq FM, Tackett LD et al (2003) Prescrotal orchiopexy: an alternative surgical approach for the palpable undescended testis. J Urol 170(6):2436–2438
Dayanc M, Kibar Y, Irkilata HC et al (2007) Long-term outcome of scrotal incision orchiopexy for undescended testis. Urology 70(4):786–788
Bassel YS, Scherz HC, Kirsch AJ (2007) Scrotal incision orchiopexy for undescended testes with or without a patent processus vaginalis. J Urol 177(4):1516–1518
Gordon M, Cervellione RM, Morabito A et al (2010) 20 years of transcrotal orchidopexy for undescended testis: results and outcomes. J Pediatr Urol 6:506–512
Acknowledgments
The manuscript had been proofread by Mr.Zhiqiang Zhong, Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, S., Yang, H., Li, X. et al. Single scrotal incision orchiopexy versus the inguinal approach in children with palpable undescended testis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Surg Int 32, 989–995 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3956-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3956-4