Abstract
Introduction
Scrotal and inguinal orchiopexy are two commonly used surgical approaches for palpable undescended testis (UDT), each with distinct advantages. However, the optimal approach remains a matter of debate, warranting a comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to guide clinical decision-making.
Materials and methods
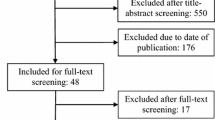
A comprehensive literature search was conducted, adhering to PRISMA guidelines, to select RCTs comparing scrotal and inguinal orchiopexy for palpable UDT. Eight RCTs were selected for meta-analysis. Outcome measures included operative time, hospitalization duration, total complications, wound infection or dehiscence, testicular atrophy or hypotrophy, and testicular re-ascent rate. The evaluation of the study’s quality was conducted by utilizing the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool.
Results
Scrotal orchiopexy showed significantly shorter operative time compared to the inguinal approach (WMD: − 15.06 min; 95% CI: − 21.04 to − 9.08). However, there was no significant difference in hospitalization duration (WMD: − 0.72 days; 95% CI: − 1.89–0.45), total complications (OR: 1.08; 95% CI: 0.70–1.66), wound infection or dehiscence (OR: 0.73; 95% CI: 0.27–1.99), testicular atrophy or hypotrophy (OR: 1.03; 95% CI: 0.38–2.78), and testicular re-ascent (OR: 1.43; 95% CI: 0.67–3.06) between the two approaches. A small proportion of cases (7.3%) required conversion from scrotal to inguinal orchiopexy due to specific anatomical challenges.
Conclusion
Both scrotal and inguinal orchiopexy are safe and effective for palpable UDT, with comparable outcomes in terms of hospitalization and complications. Scrotal orchiopexy offers the advantage of shorter operative time. Clinicians can use this evidence to make informed decisions on the surgical approach for palpable UDT.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Braga LH, Lorenzo AJ, Romao RLP (2017) Canadian Urological Association-Pediatric Urologists of Canada (CUA-PUC) guideline for the diagnosis, management, and followup of cryptorchidism. Can Urol Assoc J 11(7):E251–E260. https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.4585
Marchetti F, Bua J, Tornese G, Piras G, Toffol G, Ronfani L (2012) Management of cryptorchidism: a survey of clinical practice in Italy. BMC Pediatr 12:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-12-4
Caruso AP, Walsh RA, Wolach JW, Koyle MA (2000) Single scrotal incision orchiopexy for the palpable undescended testicle. J Urol 164(1):156–159
Kollin C, Ritzén EM (2014) Cryptorchidism: a clinical perspective. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 11(Suppl 2):240–250
Yu C, Hu Y, Wang L et al (2022) Comparison of single-incision scrotal orchiopexy and traditional two-incision inguinal orchiopexy for primary palpable undescended testis in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2022.805579
Bianchi A, Squire BR (1989) Transscrotal orchidopexy: orchidopexy revised. Pediatr Surg Int 4(3):189–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181983
Lin J, Li D, Chen J, Lin L, Xu Y (2018) Inguinal hernia repair by Bianchi incision in boys: a retrospective study. Pediatr Surg Int 34(3):289–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-017-4217-x
Feng S, Yang H, Li X et al (2016) Single scrotal incision orchiopexy versus the inguinal approach in children with palpable undescended testis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Surg Int 32(10):989–995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3956-4
Na SW, Kim SO, Hwang EC et al (2011) Single scrotal incision orchiopexy for children with palpable low-lying undescended testis: early outcome of a prospective randomized controlled study. Korean J Urol 52(9):637–641. https://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2011.52.9.637
Bhutta MR, Sheikh AH, Qureshi MA, Zubair MA, Majid F (2012) Single incision trans scrotal versus standard inguino-scrotal orchidopexy in children with palpable undescended testis: our experience from april 2007 to april 2010. Pakistan J Med Sci 28(5):827–829
Eltayeb AA (2014) Single high scrotal incision orchidopexy for unilateral palpable testis: a randomised controlled study. African J Paediatr Surg 11(2):143–146. https://doi.org/10.4103/0189-6725.132808
Ben Dhaou M, Zouari M, Zitouni H, Jallouli M, Mhiri R (2015) Traitement chirurgical de la cryptorchidie chez l’enfant: comparaison des voies d’abord scrotale (Bianchi) et inguinale. Progrès en Urol 25(10):598–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.purol.2015.05.005
Talabi AO, Sownde OA, Adejuyigbe O (2018) High (trans) scrotal orchidopexy for palpable undescended testes in children: influence of age and testicular position. African J Urol 24(2):114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afju.2018.02.002
Badbarin D, Mousavi Toomatari SE, Aslanabadi S, Farhadi E, Akhavan SS (2019) A comparative study of single scrotal incision orchiopexy of children with palpable low-lying undescended testis with traditional inguinal method. Adv Pediatr Surg 25(1):14. https://doi.org/10.13029/aps.2019.25.1.14
Nazem M, Hosseinpour M, Alghazali A (2019) Trans-scrotal incision approach versus traditional trans-scrotal incision orchiopexy in children with cryptorchidism: a randomized trial study. Adv Biomed Res 8(1):34. https://doi.org/10.4103/abr.abr_26_19
McGrath M, Kim J, Farrokhyar F, Braga LH (2021) Randomized controlled trial of scrotal versus inguinal orchidopexy on postoperative pain. J Urol 205(3):895–901. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000001379
Cloutier J, Moore K, Nadeau G, Bolduc S (2011) Modified scrotal (Bianchi) mid raphe single incision orchiopexy for low palpable undescended testis: early outcomes. J Urol 185(3):1088–1092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2010.10.039
Ali MS, Khan N, Uddin MB, Hossain MS, Mushtabshirah L (2019) High transverse scrotal incision orchiopexy for undescended testes. Mymensingh Med J 28(3):542–546
Takahashi M, Kurokawa Y, Nakanishi R et al (2009) Low transscrotal orchidopexy is a safe and effective approach for undescended testes distal to the external inguinal ring. Urol Int 82(1):92–96. https://doi.org/10.1159/000176033
Al-Mandil M, Khoury AE, El-Hout Y, Kogon M, Dave S, Farhat WA (2008) Potential complications with the prescrotal approach for the palpable undescended testis? A comparison of single prescrotal incision to the traditional inguinal approach. J Urol 180(2):686–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2008.04.040
Russinko PJ, Siddiq FM, Tackett LD, Caldamone AA (2003) Prescrotal orchiopexy: an alternative surgical approach for the palpable undescended testis. J Urol 170(6 Pt 1):2436–2438. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000097160.15802.23
Bassel YS, Scherz HC, Kirsch AJ (2007) Scrotal incision orchiopexy for undescended testes with or without a patent processus vaginalis. J Urol 177(4):1516–1518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2006.11.075
Gordon M, Cervellione RM, Morabito A, Bianchi A (2010) 20 years of transcrotal orchidopexy for undescended testis: results and outcomes. J Pediatr Urol 6(5):506–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2009.10.016
Sutton PA, Greene OJ, Adamson L, Singh SJ (2011) Scrotal fixation in the management of low undescended testes. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg 16(4):142–144. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-9261.86871
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Irfan Wahyudi: conceptualization, methodology, validation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation. Putu Angga Risky Raharja: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft preparation. Gerhard Reinaldi Situmorang: methodology, writing—review andediting. Arry Rodjani: methodology, writing—review and editing. All the authors reviewed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wahyudi, I., Raharja, P.A.R., Situmorang, G.R. et al. Comparison of scrotal and inguinal orchiopexy for palpable undescended testis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pediatr Surg Int 40, 74 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-024-05655-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-024-05655-7