Abstract
Purpose
To clarify the effects of rikkunshito on acid reflux, non-acid reflux, and esophageal clearance in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Methods
We enrolled seven patients with vomiting and/or stridor (median 6 years; 1 month–17 years), with a percent total time of esophageal pH <4.0 (reflux index) over 4.0 %. Rikkunshito (TJ-43; Tsumura Co, Tokyo, Japan) was given in three divided doses before meals. We retrospectively investigated its efficacy using pH-multichannel intraluminal impedance before and 7 (6–10) days after starting treatment. Statistical analyses were conducted using Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results
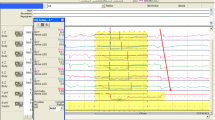
In the pH analyses alone, the median number of acid reflux episodes >5 min (14 versus 10, p = 0.046) and median acid-clearance time (184 versus 134 s, p = 0.03) decreased significantly, although median decrease in reflux index did not reach significance (16.0 versus 17.9 %, p = 0.06). In the combined impedance and pH analyses, the median number (36 versus 36, p = 0.03) and median duration (1.9 versus 1.1 %, p = 0.046) of acid reflux decreased significantly; non-acid reflux and bolus clearance time did not change.
Conclusion
Rikkunshito effectively reduced acid reflux, but not esophageal clearance, in patients with GERD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawahara H, Dent J, Davidson G (1997) Mechanisms responsible for gastroesophageal reflux in children. Gastroenterology 113:399–408
Kawai M, Kawahara H, Hirayama S et al (2004) Effect of baclofen on emesis and 24-h esophageal pH in neurologically impaired children with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 38:317–323
Kawahara H, Mitani Y, Nomura M et al (2009) Impact of rikkunshito, an herbal medicine, on delayed gastric emptying in profoundly handicapped patients. Pediatr Surg Int 25:987–990
Kawahara H, Kubota A, Hasegawa T et al (2007) Effects of rikkunshito on the clinical symptoms and esophageal acid exposure in children with symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatr Surg Int 23:1001–1005
Salvatore S, Arrigo S, Luini C et al (2010) Esophageal impedance in children: symptom-based results. J Pediatr 157:949–954
Francavilla R, Magistà AM, Bucci N et al (2010) Comparison of esophageal pH and multichannel intraluminal impedance testing in pediatric patients with suspected gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 50:154–160
Sifrim D, Castell D, Dent J et al (2004) Gastro-oesophageal reflux monitoring: review and consensus report on detection and definitions of acid, non-acid, and gas reflux. Gut 53:1024–1031
Rothenberg SS (2013) Two decades of experience with laparoscopic nissen fundoplication in infants and children: a critical evaluation of indications, technique, and results. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 23:791–794
Lobe TE (2007) The current role of laparoscopic surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants and children. Surg Endosc 21:167–174
Martin K, Deshaies C, Emil S (2014) Outcomes of pediatric laparoscopic fundoplication: a critical review of the literature. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28:97–102
Cucchiara S, Staiano A, Boccieri A et al (1990) Effects of cisapride on parameters of esophageal pH test in infants with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut 31:21–25
Yagi M, Homma S, Kubota M et al (2004) The herbal medicine Rikkunshi-to stimulates and coordinates the gastric myoelectric activity in post-operative dyspeptic children after gastrointestinal surgery. Pediatr Surg Int 19:760–765
Morita T, Furuta K, Adachi K et al (2012) Effects of rikkunshito (TJ-43) on esophageal motor function and gastroesophageal reflux. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 18:181–186
Tominaga K, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K et al (2012) Rikkunshito improves symptoms in PPI-refractory GERD patients: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial in Japan. J Gastroenterol 47:284–292
Tominaga K, Kato M, Takeda H et al (2014) A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial of rikkunshito for patients with non-erosive reflux disease refractory to proton-pump inhibitor: the G-PRIDE study. J Gastroenterol. doi:10.1007/s00535-013-0896-9
Vicente Y, da Rocha C, Hernandez-Peredo G et al (2002) Esophageal acid clearance: more volume-dependent than motility-dependent in healthy piglets. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 35:173–179
Gourcerol G, Benanni Y, Boueyre E et al (2013) Influence of gastric emptying on gastro-esophageal reflux: a combined pH-impedance study. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:800–e634
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawahara, H., Tazuke, Y., Soh, H. et al. Physiological analysis of the effects of rikkunshito on acid and non-acid gastroesophageal reflux using pH-multichannel intraluminal impedance monitoring. Pediatr Surg Int 30, 927–931 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-014-3565-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-014-3565-z