Abstract
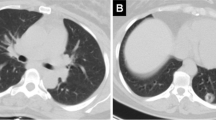
Pulmonary hydatidosis is more frequently encountered in children than in adults. Chemotherapy with oral administration of particular antihelminthic agents (mebendazole and albendazole) has proved to be effective. This treatment, however, may be associated with serious complications that require surgical management. The aim of this study was to define the limitations of medical treatment, the subsequent complications, and their management. During a 16-year period (1985–2001), 36 children with pulmonary hydatidosis (Echinococcus cysticus) were medically treated. Oral antihelminthic agents (mebendazole until 1992 and albendazole thereafter) were given to all these patients. During this treatment, 11 patients developed complications requiring surgical intervention. In seven children, pleural empyema, or the presence of inflammatory residual fluid, was noted. The remaining four developed pulmonary abscess combined with fluid collection within the pleural cavity. In all complicated cases, the mean size of the cysts exceeded 6 cm in diameter at the beginning of medical treatment. At operation, suturing of communicating bronchi was insecure due to inflammation. Postoperatively, three patients had air leakage from the bronchial tree, requiring continuous suction and prolonged hospitalization. One patient presented with pneumothorax 4 months postoperatively and was operated on again. Overall, long-term results were good. We concluded that a) large pulmonary hydatid cysts should not be treated medically, b) incomplete expectoration of the cyst contents after the parasite death may lead to infection through bronchial communication, and c) patients surgically treated for complications following medical treatment are hospitalized twice as long as patients surgically treated in the first place.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mutaf O, Arikan A, Yazici M (1994) Pulmonary hydatidosis in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg 4:70–73
Karpathios T, Syriopoulou V, Nikolaidou P et al. (1984) Mebendazole in the treatment of hydatid cysts. Arch Dis Child 59:894–896
Messaritakis J, Psychou P, Nikolaidou P et al. (1991) High mebendazole doses in pulmonary and hepatic hydatid disease. Arch Dis Child 66:532–533
Todorov T, Mechkov G, Vutova K et al (1992) Factors influencing the response to chemotherapy in human cystic echinococcosis. WHO Bulletin 70:347–58
Reuter S, Kratzer W, Kurz S, Wellinghausen N, Kern P (1998) Chemotherapy of alveolar echinococcosis with benzimidasoles. A prospective long-term study. Med Klin 8:463–467
Nahmias J, Goldsmith R, Soilbelman M, El-On J (1994) Three to five years follow up after albendazole treatment of 68 patients with cystic echinococcosis (hydatic disease). Ann Trop Med Parasitol 3:295–304
Galanakis E, Besis S, Pappa C, Nicolopoulos P, Lapatsanis P (1997) Treatment of complicated pulmonary echinococcosis with albendazole in childhood. Scand J Infect Dis 6:638–640
Kammener W, Judge D (1976) Chemotherapy of hydatid disease (Echinococcus granulosus) in mice with mebendazole and bithionol. Am J Trop Med Hyg 25:714–717
Franchi C, Di Vico B, Teggi A (1999) Long term evaluation of patients with hydatidosis treated with benzimidazole carbamates. Clin Infect Dis 2:304–309
Halezeroglu S, Celik M, Uysal A et al. (1991) Giant hydatid cysts of the lung. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 102:427–430
Morris D, Dykes P, Marriner S et al. (1985) Albendazole-objective evidence of response in human hydatid disease. JAMA 253:2053–2057
Celic M, Senol C, Keles M et al. (2000) Surgical treatment of pulmonary hydatid disease in children: report of 122 cases. J Pediatr Surg 12:1710–1713
Solak H, Ozgen G, Yüksek T et al. (1988) Surgery in hydatid cyst of the lung. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 22:101–104
Ozçelik C, Inci I, Toprak M et al (1994) Surgical treatment of pulmonary hydatidosis in children: experience in 92 patients. J Pediatr Surg 29:392–395
Salih O, Topcuoglu M, Celik S et al (1998) Surgical treatment of hydatid cysts of the lung: analysis of 405 patients. Can J Surg 41:131–135
Elburjo M, Gani EA (1995) Surgical management of pulmonary hydatid cysts in children. Thorax 50:396–398
Rebhandl W, Turnbull J, Felberbauer FX et al. (1999) Pulmonary echinococcosis (hydatidosis) in children: results of surgical treatment. Pediatr Pulmonol 5:336–40
Gargouri M, Ben AN, Ben CF et al. (1990) Percutaneous treatment of hydatid cysts (Echinococcus granulosus). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 13:169–173
Akhan O, Özmen M, Dinçer A et al. (1994) Percutaneous treatment of pulmonary hydatid cysts. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 17:271–5
Lamy A, Cameron B, LeBlanc J et al. (1993) Giant hydatid lung cysts in the Canadian Northwest: Outcome of conservative treatment in three children. J Pediatr Surg 28:1140–1143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keramidas, D., Mavridis, G., Soutis, M. et al. Medical treatment of pulmonary hydatidosis: complications and surgical management. Ped Surgery Int 19, 774–776 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-003-1031-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-003-1031-4