Abstract
Background
Hydatid disease is endemic in sheep-raising regions of the world. It is caused by the larval stage of a tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. The lifecycle of Echinococcus revolves between sheep and dog. Humans get the infection by ingesting the eggs. Lungs are the second most common site of involvement after the liver. We review our 4-year experience of surgical treatment of pulmonary hydatid cysts.
Methods
Clinical presentation, radiological investigations, operative techniques, postoperative outcome and follow-up of 120 cases of pulmonary hydatid cysts treated surgically were studied between June 2009 and June 2013 at SSKM Hospital, Kolkata.
Results
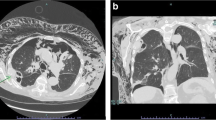
There were 68 males (56.67 %) and 52 females (43.33 %). The median age of presentation was 33 years. A total of 111 patients were from rural areas with farming and cattle raising as their occupation. Lung hydatid cysts are usually asymptomatic before reaching large sizes. Cough and chest pain are often the only symptoms. The right lung was affected in 58.33 % of cases and the left lung was affected in 35 % of cases. The right lower lobe was most commonly involved (26.67 %). Enucleation of the cyst with capitonnage was the preferred technique. The mean duration of hospital stay was 9.3 days. Oral albendazole was used in postoperative period at the dose of 10 mg/kg/day for 3 months. The recurrence rate was 0.33 %.
Conclusions
Surgery in the form of enucleation and capitonnage is the most effective treatment for pulmonary hydatid cyst as it causes removal of the cyst without spillage and maximum preservation of the lung parenchyma. Povidone-iodine is a good scolicidal agent to prevent contamination of the surgical field from spillage of the cyst contents. Albendazole should be used postoperatively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burgos R, Varela A, Castedo E, et al. Pulmonary hydatidosis: surgical treatment and follow-up of 240 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1999;16:628–34.
Dakak M, Genc O, Gurkuk S, Gozubuyuk A, Balkanli K. Surgical treatment for pulmonary hydatidosis(a review of 422 cases). J R Coll Edinb. 2002;47:689–92.
Sayir F, Cobanoglu U, Sehitogullari A, Bilici S. Our eight-year surgical experience in patients with pulmonary cyst hydatid. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2012;5:64–71.
Halioglu M, Saatci I, Akhan O, Ozmen MN, Besim A. Spectrum of imaging findings in pediatrichydatid disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997;169:1627–31.
Wen H, Craig PS. Immunoglobulin G subclass responses in human cystic and alveolar echinococcosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1994;51:741–8.
Zhang W, Li J, McManus DP. Concepts in immunology and diagnosis of hydatid disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003;16:18–36.
Dogan R, Yuksel M, Cetin G, et al. Surgical treatment of hydatid cysts of the lung. Report on 1055 patients. Thorax. 1989;44:192–9.
Barrett NR. Removal of simple univesicular pulmonary hydatid cyst. Lancet. 1994;2:234.
Lichter I. Surgery of pulmonary hydatid cyst—the Barrett technique. Thorax. 1972;27:529.
Turna A, Yilmaz MA, Haciibrahimoglu G, Kutlu CA, Bedirham MA. Surgical treatment of pulmonary hydatid cyst: is capitonnage necessary? Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;74:191–5.
Bilgin M, Oguzkaya F, Akcali Y. Is capitonnage unnecessary in the surgery of intact pulmonary hydatid cyst? ANZ J Surg. 2004;74:40–2.
Celik M, Senol C, Keles M, et al. Surgical treatment of pulmonary hydatid disease in children: report of 122 cases. J Ped Surg. 2000;35:1710–3.
Dhaliwal RS, Kalkat MS. One stage surgical procedure for bilateral lung and liver hydatid cysts. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997;64:338–41.
Salih OK, Topcuglu MS, Celik SK, Ulus T, Tokcan A. Surgical treatment of hydatid cysts of lung: analysis of 405 patients. Can J Surg. 1998;41:131–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohapatra, B., Sivakumar, P., Bhattacharya, S. et al. Surgical treatment of pulmonary hydatidosis: a single-centre experience of four years. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 31, 8–12 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-014-0315-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-014-0315-8