Abstract
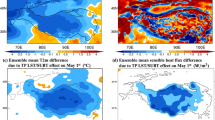
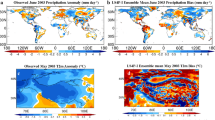
Recent observational and modeling studies have demonstrated the substantial influence of the Tibetan Plateau (TP) spring land surface temperature (LST) and subsurface temperature (SUBT) on downstream summer droughts/floods events in East Asia, highlighting the potential application of LST/SUBT on sub-seasonal to seasonal prediction (S2S). In this study, we employ the National Centers for Environment Prediction—Global Forecast System/Simplified Simple Biosphere model version 2 (GFS/SSiB2) to investigate the potential role of the late spring warm LST anomaly over the TP on the extraordinary June 1998 flood in the south of the Yangtze River region. Numerical experiments indicate that the warmer (above normal) May LST over the TP may contribute to the extreme flood of 1998 over the south of the Yangtze River region, with the LST reproducing about 57% and 64% of observed above-normal rainfall anomaly over the south of the Yangtze River region and southeastern China, respectively. Further analyses reveal a possible effect of springtime TP’s LST on summer southern and eastern Asian rainfall and identify some hot spots, suggesting that the TP’s spring LST effect is not only limited to the Yangtze River region, but to a much larger scale. The imposed warm LST/SUBT over the TP triggers a strong wave activities propagating eastward along the upper-level westerly jet, associated with an increase of the atmospheric baroclinic instability as well as a strengthening and southeastward movement of the South Asian high, leading to intensified moisture convergence and convective instability favorable to the excessive rainfall in the downstream region of East Asia. The results of the 1998 case have also been compared with the results from year of 2003, which had a very cold spring LST anomaly over the TP and a severe downstream June 2003 drought (flood) in southern (northern) of the Yangtze River Basin area. Simulation results provide further evidence of the great importance of the TP spring land surface temperature anomaly in regulating summer extreme hydroclimatic events (e.g. droughts and floods) in South and East Asia. The present study suggests that consideration of LST/SUBT anomalies has a strong potential for more skillful S2S prediction of extreme hydroclimatic events such as floods, droughts and heatwaves over both Southern and Eastern Asia.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar SA, Diallo I (2021) Modelling the Tropical African Climate using a state-of-the-art coupled regional climate-vegetation model. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05892-9
Arakawa A, Schubert WH (1974) Interaction of a cumulus cloud ensemble with the large scale environment. Part I. J Atmos Sci 31:674–701
Ashfaq M (2020) Topographic controls on the distribution of summer monsoon precipitation over South Asia. Earth Syst Environ 4:667–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-020-00196-0〹
Bamba A, Diallo I et al (2018) Effect of the African greenbelt position on West African summer climate: a regional climate modeling study. Theor Appl Climatol 137(1–2):309–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2589-z
Bamzai A, Shukla J (1999) Relation between Eurasian snow cover, snow depth and the Indian summer monsoon: an observational study. J Clim 12:3117–3132. https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/clim/12/10/1520-0442_1999_012_3117_rbescs_2.0.co_2.xml
Bao Q, Yang J, Liu Y, Wu G, Wang B (2010) Roles of anomalous Tibetan Plateau warming on the severe 2008 winter storm in central-southern China. Mon Weather Rev 138:2375–2384. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009MWR2950.1
Chen D, Sun JQ, Gao Y (2019) Distinct impact of the Pacific multi-decadal oscillation on precipitation in Northeast China during April in different Pacific multi-decadal oscillation phases. Int J Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6291
China Meteorological Administration [CMA] (1999) National weather and climate review and impact assessment. China meteorological yearbook. Meteorological Press, Beijing, pp 257–274
Choi YW, Ahn JB (2019) Possible mechanisms for the coupling between late spring sea surface temperature anomalies over tropical Atlantic and East Asian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 53:6995–7009
Chow KC, Chan JCL, Shi X, Liu Y, Ding Y (2008) Time-lagged effects of spring Tibetan Plateau soil moisture on the monsoon over China in early summer. Int J Climatol 28:55–67
Chun H-Y, Baik J-J (1998) Momentum flux by thermally induced internal gravity waves and its approximation for large-scale models. J Atmos Sci 55:3299–3310
Clough SA, Shephard MW, Mlawer E, Delamere JS, Iacono M, Cady-Pereira K, Boukabara S, Brown PD (2005) Atmospheric radiative transfer modeling: a summary of the AER codes. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Trans 91:233–244
CMA (2004) National weather and climate review and impact assessment. China meteorological yearbook. Meteorological Press, Beijing, pp 446–467 (In Chinese)
Deng X, Sun Z (1994) Characteristics of temporal evolution of northern storm tracks (in Chinese). J Nanjing Inst Meteorol 17(2):165–170. https://doi.org/10.13878/j.cnki.dqkxxb.1994.02.006
Dey B, Kumar OSRUB (1983) An apparent relationship between Eurasian snow cover and the advanced period of the Indian summer monsoon. J Appl Meteorol 21:1929–1932. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1982)021%3c1929:AARBES%3e2.0.CO;2
Diallo I, Giorgi F, Sukumaran S, Stordal F, Giuliani G (2015) Evaluation of RegCM4 driven by CAM4 over Southern Africa: mean climatology, interannual variability and daily extremes of wet season temperature and precipitation. Theor Appl Climatol 121(3–4):749–766
Diallo I, Giorgi F, Stordal F (2018) Influence of Lake Malawi on regional climate from a double-nested regional climate model experiment. Clim Dyn 50(9–10):3397–3411. https://doi.org/10.1007/sOO382-017-3811-x
Diallo I, Xue Y, Li Q et al (2019) Dynamical downscaling the impact of spring Western US land surface temperature on the 2015 flood extremes at the Southern Great Plains: effect of domain choice, dynamic cores and land surface parameterization. Clim Dyn 53:1039–1061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04630-6
Dickinson RE (1988) The force-restore model for surface temperatures and its generalizations. J Clim 1:1086–1097. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1988)001%3c1086:TFMFST%3e2.0.CO;2
Ding R, Ha KJ, Li J (2010) Interdecadal shift in the relationship between the East Asian summer monsoon and the tropical Indian Ocean. Clim Dyn 34:1059–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-009-0555-2
Duan AM, Wu GX (2005) Role of the Tibetan Plateau thermal forcing in the summer climate patterns over subtropical Asia. Clim Dyn 24:793–807
Duan AM, Li F, Wang MR, Wu GX (2011) Persistent weakening trend in the spring sensible heat source over the Tibetan Plateau and its impact on the Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 24:5671–5682
Fan Y, van den Dool H (2008) A global monthly land surface air temperature analysis for 1948–present. J Geophys Res 113:D01103
Fasullo J (2004) A stratified diagnosis of the Indian Monsoon-Eurasian snow cover relationship. J Clim 17:1110–1122. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017%3c1110:ASDOTI%3e2.0.CO;2
Gao C, Li G, Bei X, Li X (2020) Effect of spring soil moisture over the Indo-China Peninsula on the following summer extreme precipitation events over the Yangtze River basin. Clim Dyn 45:3845–3861
Ge J, You Q, Zhang Y (2019) Effect of Tibetan Plateau heating on summer extreme precipitation in eastern China. Atmos Res 218:364–371
Gelaro R, McCarty W, Suàrez MJ et al (2017) The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J Clim 30(14):5419–5454. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0758.1
Good EJ, Ghent DJ, Bulgin CE, Remedios JJ (2017) A spatiotemporal analysis of the relationship between near-surface air temperature and satellite land surface temperatures using 17 years of data from the ATSR series. J Geophys Res Atmos 122(17):9185–9210. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD026880
Han S, Shi CX, Xu B et al (2019) Development and evaluation of hourly and kilometer resolution retrospective and real-time surface meteorological blended forcing dataset (SMBFD) in China. J Meteorol Res 33:1168–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-9042-9
Harris I, Osborn TJ, Jones PD, Lister DH (2020) Version 4 of the CRU TS monthly high-resolution gridded multivariate climate dataset. Sci Data 7:109
Hertwig E, von Storch J-S, Handorf D, Dethloff K, Fast I, Krismer T (2015) Effect of horizontal resolution on ECHAM6-AMIP performance. Clim Dyn 45:185–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2396-x
Hong SY, Pan HL (1996) Non-local boundary layer vertical diffusion in a medium range forecast model. Mon Weather Rev 124:2322–2339
Hong SY, Pan HL (1998) Convective trigger function for a mass-flux cumulus parameterization scheme. Mon Weather Rev 126:2599–2620
Hoskins B (1991) Toward a PV-h view of the general circulation. Tellus 43:27–35
Hoskins BJ, Ambrizzi T (1993) Rossby wave propagation on a realistic longitudinaly varying flow. J Atmos Sci 50:1661–1671
Hoskins BJ, Valdes PJ (1990) On the existence of storm-tracks. J Atmos Sci 47:1854–1864. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1990)047%3c1854:OTEOST%3e2.0.CO;2
Hsu HH, Liu X (2003) Relationship between the Tibetan Plateau heating and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 30(20):2066. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017909
Hu Q, Feng S (2004) A role of the soil enthalpy in land memory. J Clim 17(18):3633–3643
Huang RH, Sun FY (1992) Impact of the tropical western Pacific on the East Asian summer monsoon. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 70:243–256
Huang RH, Xu YH, Wang PF (1998) The features of the particularly severe flood over the Changjiang (Yangtze River) basin during the summer of 1998 and exploration of its causes. Clim Environ Res 3:300–313 (In Chinese)
Huang RH, Chen JL, Huang G (2007) Characteristics and variations of the East Asian monsoon system and its impacts on climate disasters in China. Adv Atmos Sci 24:993–1023
Huang H, Xue Y, Chilukoti N, Liu Y, Chen G, Diallo I (2020) Assessing global and regional effects of reconstructed land use and land cover change on climate since 1950 using a coupled land-atmosphere-ocean model. J Clim 33:8997–9013. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0108.1
Jiang DB, Ding ZL, Drange H, Gao YQ (2008a) Sensitivity of East Asian climate to the progressive uplift and expansion of the Tibetan Plateau under the Mid-Pliocene boundary conditions. Adv Atmos Sci 25(5):709–722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-008-0709-x
Jiang T, Kundzewicz ZW, Su B (2008b) Changes in monthly precipitation and flood hazard in the Yangtze River basin, China. Int J Climatol 28:1471–1481. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1635
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, Collins W, Deaven D, Gandin L, Iredell M, Saha S, White G, Woollen J, Zhu Y, Leetmaa A, Reynolds R, Chelliah M, Ebisuzaki W, Higgins W, Janowiak J, Mo KC, Ropelewski C, Wang J, Jenne R, Joseph D (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–471. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077%3C0437:TNYRP%3E2.0.CO;2
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W, Woollen J, Yang SK, Hnilo JJ, Fiorino M, Potter GL (2002) NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83:1631–1643
Koster RD, Dirmeyer PA, Guo Z, Bonan G, Chan E, Cox P, Gordon CT, Kanae S, Kowalczyk E, Lawrence D, Liu P, Lu CH, Malyshev S, McAvaney B, Mitchell K, Mocko D, Oki T, Oleson K, Pitman A, Sud YC, Taylor CM, Verseghy D, Vasic R, Xue Y, Yamada T (2004) Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science 305:1138–1140
Kripalani RH, Kulkarni A, Sabade SS (2003) Western Himalayan snow cover and Indian monsoon rainfall: a re-examination with INSAT and NCEP/NCAR data. Theor Appl Climatol 74:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-002-0699-z
Lau KM (1992) East Asian summer monsoon rainfall variability and climate teleconnection. J Meteor Soc Jpn 70:211–240
Lau K, Weng H (2001) Coherent modes of global SST and summer rainfall over China: an assessment of the regional impacts of the 1997 98 El Nin˜o. J Clim 14:1294–1308. https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/clim/14/6/1520-0442_2001_014_1294_cmogsa_2.0.co_2.xml
Lee S, Lee M-I (2019) Effects of surface vegetation on the intensity of East Asian summer monsoon as revealed by observation and model experiments. Int J Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6420
Lee S, Lee M-I (2020) Effects of surface vegetation on the intensity of East Asian summer monsoon as revealed by observation and model experiments. Int J Climatol 40:3634–3648. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6420
Lee J, Xue Y, De Sales F et al (2019) Evaluation of multi-decadal UCLA-CFSv2 simulation and impact of interactive atmospheric-ocean feedback on global and regional variability. Clim Dyn 52:3683–3707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4351-8
Li C, Yanai M (1996) The onset and interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon in relation to land–sea thermal contrast. J Clim 9:358–375
Li H, Dai A, Zhou T, Lu J (2010) Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to historical SST and atmospheric forcing during 1950–2000. Clim Dyn 34(4):501–514
Lin R, Zhu J, Zheng F (2016) Decadal shifts of East Asian summer monsoon in a climate model free of explicit GHGs and aerosols. Sci Rep 6:38546. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38546
Liu XD, Yin ZY (2002) Sensitivity of East Asian monsoon climate to the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 183(3–4):223–245
Liu YM, Wu GX, Hong JL, Dong BW, Duan AM, Bao Q, Zhou LJ (2012) Revisiting Asian monsoon formation and changes associated with Tibetan Plateau forcing: II. Change. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1335-y
Liu Y, Xue Y, Li Q, Lettenmaier D, Zhao P (2020) Investigation of the variability of near-surface temperature anomaly and its causes over the Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res Atmos 125:650. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020jd032800
Lu R (2000) Anomalies in the tropics associated with the heavy rainfall in East Asia during the summer of 1998. Adv Atmos Sci 17(2):205–220
Ministry of Water Resources of China (1999) China’s 98 Great Flood. China Water Resources Yearbook. China Water Resources and Hydropower Press, Beijing, pp 518–523
Mlawer EJ, Taubman SJ, Brown PD, Iacono MJ, Clough SA (1997) Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J Geophys Res Atmos 102:16663–16682
Moorthi S, Pan HL, Caplan P (2001) Changes to the 2001 NCEP operational MRF/AVN global analysis/forecast system. NWS Tech Proc Bull 484:1–14
Nitta T (1987) Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impact on the Northern Hemisphere summer circulation. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 65:373–390
Notaro M, Chen GS, Liu Z (2011) Vegetation feedbacks to climate in the global monsoon regions. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JCLI4237.1
Pan H-L, Wu W-S (1995) Implementing a mass flux convective parameterization package for the NMC medium-range forecast model. In: NMC Office Note 409, NCEP/EMC, Camp Springs, Md, p 40
Pincus R, Barker HW, Morcrette JJ (2003) A fast, flexible, approximate technique for computing radiative transfer in inhomogeneous cloud fields. J Geophys Res 108:4376
Ren X, Yang D, Yang X-Q (2015a) Characteristics and mechanisms of the subseasonal eastward extension of the South Asian High. J Clim 28(17):6799–6822
Ren Z, Zhang M, Wang S, Qiang F, Zhu X, Dong L (2015b) Changes in daily extreme precipitation events in South China from 1961 to 2011. J Geogr Sci 25:58–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-015-1153-3
Saha S, Moorthi S, Pan HL, Wu X, Wang J, Nadiga S, Tripp P, Kistler R, Woollen J, Behringer D, Liu H (2010) The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 91:1015–1057. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010BAMS3001.1
Saha S, Moorthi S, Wu X, Wang J, Nadiga S, Tripp P, Behringer D, Hou YT, Chuang HY, Iredell M, Ek M (2014) The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J Clim 27:2185–2208. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00823.1
Sampe T, Xie SP (2010) Large-scale dynamics of the Meiyu-Baiu rainband: environmental forcing by the westerly jet. J Clim 23:113–134
Sellers PJ, Randall DA, Collatz GJ, Berry JA, Field CB, Dazlich DA, Zhang C, Colello GD, Bounoua L (1996) A revised land surface parametrization (SiB2) for atmospheric GCMs. Part I: model formulation. J Clim 9:676–705
Seol KH, Hong SY (2009) Relationship between the Tibetan Snow in spring and the East Asian summer monsoon in 2003: a global and regional modeling study. J Clim 22:2095–2110
Shen H, He S, Wang H (2019) Effect of summer Arctic sea ice on the reverse August precipitation anomaly in Eastern China between 1998 and 2016. J Clim 32:3389–3407
Skamarock WC, Klemp JB, Dudhia J, Gill D, Barker D, Duda M, Huang X, Wang W, Powers J (2008) A description of the advanced research WRF version 3. In: NCAR technical note, NCAR/TN-475?STR, p 125
Song F, Zhou T (2014) The climatology and inter-annual variability of East Asian summer monsoon in CMIP5 coupled models: does air-sea coupling improve the simulations? J Clim 27:8761–8777. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00396.1
Song F, Zhou T (2015) The crucial role of internal variability in modulating the decadal variation of the east Asian summer monsoon–ENSO relationship during the twentieth Century. J Clim 28:7093–7107. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-14-00783.1
Takaya Y, Ishikawa I, Kobayashi C, Endo H, Ose T (2020) Enhanced Meiyu-Baiu rainfall in Early Summer 2020: aftermath of the 2019 super IOD event. Geophys Res Lett 47(22):e2020GL090671
Tian S-F, Yasunari T (1992) Time and space structure of interannual variations in summer rainfall over China. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 70:585–596
Ullah W, Guojie W, Gao Z et al (2021) Observed linkage between Tibetan Plateau soil moisture and South Asian summer precipitation and the possible mechanism. J Clim 34(1):361–377
Vallis GK, Gerber EP (2008) Local and hemispheric dynamics of the North Atlantic oscillation, annular patterns and the zonal index. Dyn Atmos Oceans 44:184–212
Wallace JM, Lim GH, Blackmon ML (1988) Relationship between cyclone tracks, anticyclone tracks and baroclinic waveguides. J Atmos Sci 45:439–462
Wan BC, Gao ZQ, Chen F, Lu CG (2017) Impact of Tibetan Plateau surface heating on persistent extreme precipitation events in Southeastern China. Mon Weather Rev 145(9):3485–3505. https://doi.org/10.1175/Mwr-D-17-0061.1
Wang B (ed) (2006) The Asian monsoon. Springer, Berlin
Wang B, Wu R, Fu X (2000) Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: how does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J Clim 13:1517–1536. https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/clim/13/9/1520-0442_2000_013_1517_peathd_2.0.co_2.xml
Wang Y, Zhai P, Tian H (2006) Characteristics of high temperature variation in southern China in recent 40 years and high temperature events in 2003. Meteorol Mon 10:27–33 (In Chinese)
Wang B, Bao Q, Hoskins B, Wu G, Liu Y (2008) Tibetan Plateau warming and precipitation changes in East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 35:L14702. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL034330
Wang Z, Duan A, Wu G (2014) Time-lagged impact of spring sensible heat over the Tibetan Plateau on the summer rainfall anomaly in East China: case studies using the WRF model. Clim Dyn 42:2885–2898
Wang PX, Wang B, Cheng H et al (2017) The global monsoon across time scales: mechanisms and outstanding issues. Earth Sci Rev 174:84–121
Wu J, Gao X (2013) A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets. Chin J Geophy 56:1102–1111 (In Chinese)
Wu G, Liu Y (2016) Impacts of the Tibetan Plateau on Asian climate. Meteorol Monogr 56:7–1
Wu TW, Qian ZA (2003) The relationship between the Tibetan winter snow and the Asian summer monsoon and rainfall: an observational investigation. J Clim 16:2038–2051. https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/clim/16/12/1520-0442_2003_016_2038_trbttw_2.0.co_2.xml
Wu R, Hu Z, Kirtman B (2003) Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J Clim 16(22):3742–3758. https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/clim/16/22/1520-0442_2003_016_3742_eoerai_2.0.co_2.xml
Wu Z, Wang B, Li J, Jin FF (2009) An empirical seasonal prediction model of the east Asian summer monsoon using ENSO and NAO. J Geophys Res 114:D18120. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009jd011733
Wu GX, Liu YM, He B, Bao Q, Duan AM, Jin FF (2012) Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Sci Rep 2:404
Xiao Z, Duan A (2016) Impacts of Tibetan Plateau snow cover on the interannual variability of the East Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 29:8495–8514
Xu Z, Fan K, Wang H (2015) Decadal variation of summer precipitation over china and associated atmospheric circulation after the late 1990s. J Clim 28:4086–4106
Xue Y, Sellers PJ, Kinter JL, Shukla J (1991) A simplified biosphere model for global climate studies. J Clim 4(3):345–364
Xue Y, Juang HM, Li W, Prince S, DeFries R, Jiao Y, Vasic R (2004) Role of land surface processes in monsoon development: East Asia and West Africa. J Geophys Res 109:D03105. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JD003556
Xue Y, De Sales F, Vasic R, Mechoso CR, Arakawa A, Prince S (2010) Global and seasonal assessment of interactions between climate and vegetation biophysical processes: a GCM study with different land-vegetation representations. J Clim 23:1411–1433
Xue Y, Vasic R, Janjic Z, Liu YM, Chu PC (2012) The impact of spring subsurface soil temperature anomaly in the western US on North American summer precipitation: a case study using regional climate model downscaling. J Geophys Res Atmos 117(D11):D11103
Xue Y, Oaida CM, Diallo I, Neelin JD, Li S, De Sales F, Gu Y, Robinson D, Vasic R, Yi L (2016a) Spring land temperature anomalies in northwestern US and the summer drought over Southern Plains and adjacent areas. Environ Res Lett 11:044018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/4/044018
Xue Y, De Sales F, Lau WKM, Boone A, Kim KM, Mechoso CR, Wang G, Kucharski F, Schiro K, Hosaka M, Li S, Druyan LM, Sanda IS, Thiaw W, Zeng N, Comer RE, Lim YK, Mahanama S, Song G, Gu Y, Hagos SM, Chin M, Schubert S, Dirmeyer P, Leung LR, Kalnay E, Kitoh A, Lu CH, Mahowald NM, Zhang Z (2016b) West African monsoon decadal variability and surface-related forcings: second West African Monsoon Modeling and Evaluation Project Experiment (WAMME II). Clim Dyn 47:3517–3545
Xue Y, Diallo I, Li W, Neelin JD, Chu P-C, Vasic R, Guo W, Li Q, Robinson DA, Zhu Y, Fu C, Oaida CM (2018) Spring land surface and subsurface temperature anomalies and subsequent downstream late spring-summer droughts/floods in North America and East Asia. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JD028246
Xue Y, Yao T, Boone AA, Diallo I et al (2021) Impact of initialized land surface temperature and snowpack on subseasonal to seasonal prediction project, phase I (LS4P-I): organization and experimental design. Geosci Model Dev 14:4465–4494. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-14-4465-2021
Yanai M, Wu GX (2006) Effects of the Tibetan Plateau. In: Wang B (ed) The Asian Monsoon. Springer, New York, pp 513–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-37722-0_13
Yao T et al (2019) Recent third pole’s rapid warming accompanies cryospheric melt and water cycle intensification and interactions between monsoon and environment: multi-disciplinary approach with observation, modeling and analysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 100(3):423–444. https://doi.org/10.1175/bams-d-17-0057.1
Yasunari T, Miwa T (2006) Convective cloud systems over the Tibetan Plateau and their impact on meso-scale disturbances in the Meiyu/Baiu frontal zone: a case study in 1998. J Meteor Soc Jpn 84:783–803
You QL, Min J, Zhang W, Pepin N, Kang S (2015) Comparison of multiple datasets with gridded precipitation observations over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim Dyn 45(3):791–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2310-6
Yu L, Xue Y, Diallo I (2021) Vegetation greening in China and its effect on summer regional climate. Sci Bull 66(1):13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2020.09.003
Zhan XW, Xue YK, Collatz GJ (2003) An analytical approach for estimating CO2 and heat fluxes over the Amazonian region. Ecol Model 162:97–117
Zhang L, Zhou T (2015) Drought over East Asia: a review. J Clim 28(8):150203142724009
Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Fan S (2016) Development of hourly precipitation datasets for national meteorological stations in China. Torrential Rain Disasters 35(2):182–186
Zhao Q, Carr FH (1997) A prognostic cloud scheme for operational NWP models. Mon Weather Rev 125:1931–1953
Zhao TB, Fu CB (2006) Preliminary comparison and analysis between ERA-40, NCEP-2 reanalysis and observations over China. Clim Environ Res 11:14–32. https://doi.org/10.3969/jissn.1006-9585.2006.01.002.(inChinese)
Zhao P, Zhang X, Zhou X, Ikeda M, Yin Y (2004) The sea ice extent anomaly in the North Pacific and its impact on the East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. J Clim 17:3434–3447. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017%3c3434:TSIEAI%3e2.0.CO;2
Zheng F, Li J, Li Y, Zhao S, Deng D (2016) Influence of the summer NAO on the spring-NAO-based predictability of the East Asian summer monsoon. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 55:1459–1476
Zhisheng A, Kutzbach JE, Prell WL, Porter S (2001) Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature 411:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/35075035
Zhou ZQ, Xie SP, Zhang RH (2021) Historic Yangtze flooding of 2020 tied to extreme Indian Ocean conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118:2022255118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2022255118
Zhu W, Sun ZB (2000) Impacts of Kuroshio SSTA on storm track over North Pacific in winter. Q J Appl Meteor 11:145–153
Zuo Z, Yang S, Zhang R, Jiang P, Zhang L, Wang F (2013) Long-term variations of broad-scale Asian summer monsoon circulation and possible causes. J Clim 26:8947–8961
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (Grant No AGS-1849654). The authors would like to thank the Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) at the University of Texas at Austin for providing invaluable computer time for the model simulations, as well as the anonymous reviewers’ and the editor for providing very constructive comments/suggestions to help improve the paper. All the model runs described in this study were carried out at the TACC stampede 2. All simulations datasets analyzed in this study are archived in the Department of Geography at the University of California—Los Angeles and can be obtained upon request by contacting the corresponding author (idiallo.work@gmail.com or ismailladiallo@gmail.com).
Funding
The U.S. National Science Foundation (Grant No AGS-1849654).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Availability of data and material
The reference datasets are downloaded from open sources. The gridded observational datasets (CMA) are available from http://data.cma.cn/site/index.html (http://data.cma.cn/en; for English). All simulations datasets and processed datasets are available upon request from the corresponding author (ismailladiallo@gmail.com or idiallo.work@gmail.com).
Code availability
All analysis code is available upon request from the corresponding author (ismailladiallo@gmail.com or idiallo.work@gmail.com).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diallo, I., Xue, Y., Chen, Q. et al. Effects of spring Tibetan Plateau land temperature anomalies on early summer floods/droughts over the monsoon regions of South East Asia. Clim Dyn 62, 2659–2681 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-06053-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-06053-8