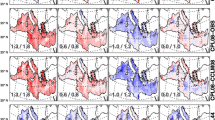
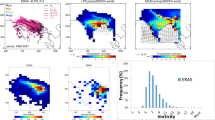
Abstract
The Mediterranean Sea water budget (MWB) is a key parameter, as it controls the Mediterranean Sea water loss and thus the Atlantic Water inflow and the Mediterranean general circulation. More accurately, the MWB controls the net flow through the Strait of Gibraltar, which implies both inflow and outflow. Generally considered at the basin scale and over long-term periods, the MWB is in fact characterized by a large variability in space and time, induced by the complex topography of the region, mesoscale processes and (short) intense events in the ocean and atmosphere compartments. In this study, we use an ocean-atmosphere coupled system at mesoscale able to represent such phenomena, to evaluate the MWB atmospheric components: Evaporation (E) and Precipitation (P). We compare two companion regional simulations: an uncoupled atmospheric run using the ERA-interim Sea Surface Temperature (SST) reanalysis and a coupled run using the MORCE system with the two-way coupling between the NEMO-MED12 eddy-resolving ocean model and the non-hydrostatic Weather Research and Forecasting atmospheric model. We first evaluate the SST validity against satellite data and evidence the coupled system ability in representing SST mesoscale structures, characteristics of the Mediterranean circulation and of small-scale ocean processes, despite a colder mean value and a lower amplitude of the annual cycle. Then, the comparison aims to examine the coupled processes effects (meaning the impacts of the interactive high-resolution and high-frequency SST) on E and P and on their variability. The comparison highlights that the SST is the controlling factor for E and P budgets, with reduction by 6 and 3 % in the coupled run compared to the uncoupled run, respectively. The modifications propagate until 750 km inland far from the Mediterranean coast, as towards the Atlantic Ocean and the Black Sea. This indicates that coupling plays a major role in distributing water at mesoscale. The coupling directly modifies the seasonal variability. It also significantly decreases extreme evaporation and precipitation occurences and intensities. This extreme events mitigation in the coupled run contributes for ~50 % to the decrease in the E and P budgets.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson A, Bakan S, Fennig K, Grassl H, Klepp C-P, Schulz J (2007) Hamburg ocean atmosphere parameters and fluxes from satellite data—HOAPS-3—twice daily composite. Electron Publ World Data Center Clim. doi:10.1594/WDCC/HOAPS3_DAILY
Artale V, Calmanti S, Carillo A, Dell’Aquila A, Herrmann M, Pisacane G, Ruti PM, Saninno G, Struglia MV, Giorgi F, and the PROTHEUS group (2009) An atmosphere-ocean regional climate model for the Mediterranean area: assessment of present climate simulation. Clim Dyn 35(5):721–740. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0691-8
Barnier BG, Madec T, Penduff J-M, Molines A-M, Tréguier J, Le Sommer A, Beckmann A, Biastoch C, Böning J, Dengg C, Derval E, Durand S, Gulev E, Rémy C, Talandier S, Theetten ME, Maltrud J, McClean B, De Cuevas (2006) Impact of partial steps and momentum advection schemes in a global ocean circulation model at eddy-permitting resolution. Ocean Dyn 56(5–6):543–567. doi:10.1007/s10236-006-0082-1
Baschek B, Send U, Lafuente JG, Candela J (2001) Transport estimates in the Strait of Gibraltar with a tidal inverse model. J Geophys Res 112:31033–31044
Béranger K, Barnier B, Guev S, Crépon M (2006) Comparing 20 years of precipitation estimates from different sources over the world. Ocean Dyn 56:104–138
Béranger K, Driller Y, Houssais M-N, Testor P, Bourdallé-Badie R, Alhammoud B, Bozec A, Mortier L, Bouruet-Aubertot P, Crépon M (2010) Impact of the spatial distribution of the atmospheric forcing on water mass formation in the Mediterranean Sea. J Geophys Res 115:C12041. doi:10.1029/2009JC005648
Berthou S, Mailler S, Drobinski P, Arsouze T, Bastin S, Béranger K, Lebeaupin Brossier C (2014) Sensitivity of an intense rain event between an atmosphere-only and and atmosphere-ocean regional coupled model: 19 September 1996. Q J R Meteorol Soc. doi:10.1002/qj.2355
Béthoux J-P (1979) Budgets of the Mediterranean Sea. Their dependence on the local climate and on the characteristics of the Atlantic waters. Oceanol Acta 2:157–163
Beuvier J, Sevault F, Herrmann M, Kontoyiannis H, Ludwig W, Rixen M, Stanev E, Béranger K, Somot S (2010) Modelling the Mediterranean Sea interannual variability during 1961–2000: focus on the Eastern Mediterranean Transient (EMT). J Geophys Res 115:C08517. doi:10.1029/2009JC005850
Beuvier J, Lebeaupin Brossier C, Béranger K, Arsouze T, Bourdallé-Badie R, Deltel C, Drillet Y, Drobinski P, Ferry N, Lyard F, Sevault F, Somot S (2012a) MED12, oceanic component for the modelling of the regional Mediterranean earth system. Mercator Ocean Quart Newslett 46:60–66
Beuvier J, Béranger K, Lebeaupin Brossier C, Somot S, Sevault F, Drillet Y, Bourdallé-Badie R, Ferry N, Levier B, Lyard F (2012b) Spreading of the Western Mediterranean Deep Water after winter 2005: time-scales and deep cyclone transport. J Geophys Res 117:C07022. doi:10.1029/2011JC007679
Blanke B, Delecluse P (1993) Variability of the tropical Atlantic ocean simulated by a general circulation model with two different mixed layer physics. J Phys Oceanogr 23:1363–1388
Boukthir M, Barnier B (2000) Seasonal and inter-annual variations in the surface freshwater flux in the Mediterranean Sea from the ECMWF re-analysis project. J Mar Syst 24:343–354
Brankart J-M, Brasseur P (1998) The general circulation in the Mediterranean Sea: a climatological approach. J Mar Syst 18:41–70. doi:10.1016/S0924-7963(98)00005-0
Bryden HL, Stommel HM (1984) Limiting processes that determine basic features of the circulation in the Mediterranean-Sea. Oceanol Acta 7:289–296
Bryden HL, Kinder TH (1991) Steady two layer exchange through the strait of Gibraltar. Deep Sea Res 38:S445–S463
Bryden HL, Candela J, Kinder TH (1994) Exchange through the strait of Gibraltar. Progr Oceanogr 33:201–248
Candela J (2001) The Mediterranean water and the global circulation. In: Siedler G, Church J, Gould J (eds) Observing and modelling the global ocean. Academic, San Diego, pp 419–429
Claud C, Alhammoud B, Funatsu BM, Lebeaupin Brossier C, Chaboureau J-P, Béranger K, Drobinski P (2012) A high resolution climatology of precipitation and deep convection over the Mediterranean region from operational satellite microwave data: development and application to the evaluation of the model incertainties. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12:785–798. doi:10.5194/nhess-12-785-2012
Criado-Aldeanueva F, Soto-Navarro J, Garcia-Lafuente J (2012) Seasonal and interannual variability of surface heat and freshwater fluxes in the Mediterranean Sea: budgets and exchange through the Strait of Gibraltar. Int J Climatol 32:286–302
Di Luca A, Flaounas E, Drobinski P, Lebeaupin Brossier C (2014) The atmospheric component of the Mediterranean Sea water budget in a WRF multi-physics ensemble and observations. Dyn Clim. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2058-z
Drobinski P, Anav A, Lebeaupin Brossier C, Samson G, Stéfanon M, and the MORCE team, (2012) Model of the Regional Coupled Earth system (MORCE): application to process and climate studies in vulnerable regions. Environ Model Soft 35:1–18. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2012.01.017
Drobinski P, Ducrocq V, Alpert P, Anagnostou E, Béranger K, Borga M, Braud I, Chanzy A, Davolio S, Delrieu G, Estournel C, Filali Boubrahmi N, Font J, Grubisic V, Gualdi S, Homar V, Ivancan-Picek B, Kottmeier C, Kotroni V, Lagouvardos K, Lionello P, Llasat MC, Ludwig W, Lutoff C, Mariotti A, Richard E, Romera R, Rotunno R, Roussot O, Ruin I, Somot S, Taupier-Letage I, Tintore J, Uijlenhoet R, Wernli H (2013) HyMeX, a 10-year multidisciplinary program on the Mediterranea water cycle. BAMS. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00242.1
Dubois C, Somot S, Calmanti S, Carillo A, Déqué M, Dell’Aquilla A, Elizalde A, Gualdi S, Jacob D, L’Hévéder B, Li L, Oddo P, Sannino G, Scoccimarro E, Sevault F (2012) Future projections of the surface heat and water budgets of the Mediterranean Sea in an ensemble of coupled atmosphere-ocean regional climate models. Clim Dyn 39:1859–1884
Ducharne A, Golaz C, Leblois E, Laval K, Polcher J, Ledoux E, de Marsily G (2003) Development of a high-resolution runoff routing model, calibration and application to assess runoff from the LMD GCM. J Hydrol 280(1–4):207–228
Dudhia J (1989) Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model. J Atmos Sci 46:3077–3107
Elguindi N, Somot S, Déqué M, Ludwig W (2011) Climate change evolution of the hydrological balance of the Mediterranean, Black and Caspians Seas: impact of climate model resolution. Clim Dyn 36:205–228
Fairall CW, Bradley EF, Hare JE, Grachev AA, Edson JB (2003) Bulk parametrization of airsea fluxes: updates and verification for the COARE algorithm. J Clim 16:571–591
Ferry N, Parent L, Garric G, Barnier B, Jourdain NC, and the Mercator team, (2010) Mercator global eddy permitting ocean eeanalysis GLORYS1V1: description and results. Mercator Ocean Quart Newslett 36:15–28
Feudale L, Shukla J (2007) Role of the Mediterranean SST in enhancing the European heat wave of summer 2003. Geophys Res Lett 34:L03811. doi:10.1029/2006GL027991
Flaounas E, Drobinski P, Vrac M, Bastin S, Lebeaupin Brossier C, Stéfanon M, Borga M, Calvet J-C (2013) Precipitation and temperature space-time variability and extremes in the Mediterranean region: evaluation of dynamical and statistical downscaling methods. Clim Dyn 40:2687–2705. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1558-y
Giordani H, Planton S (2000) Modeling and analysis of ageostrophic circulation over the Azores Oceanic Front during the SEMAPHORE experiment. Mon Weather Rev 128:2270–2287
Giorgi F, Jones C, Asrar GR (2009) Addressing climate information needs at the regional level: the CORDEX framework. WMO Bull 58:175–183
Herrmann MS, Somot S (2011) Representation of spatial and temporal varaibility of daily wind speed and of intense wind events over the Mediterranean Sea using dynamical downscaling: impact of regional climate model configuration. Nat Haz Earth Syst Sci 11:1983–2001
Hewitt CD, Griggs DJ (2004) Ensembles-based predictions of climate changes and their impacts. EOS, 85, 566 pp
Hong SY, Dudhia J, Chen S-H (2004) A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation. Mon Wea Rev 132:103–120
Kain JS (2004) The Kain-Fritsch convective parameterization: an update. J Appl Meteorol 43:170–181
Krinner G, Viovy N, De Noblet-Ducoudré N, Ogée J, Polcher J, Friedlingstein P, Ciais P, Sitch S, Colin Prentice I (2005) A dynamic global vegetation model for studies of the coupled atmosphere–biosphere system. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 19:1–33
Lafuente JG, Delgado J, Vargas JM, Vargas M, Plaza F, Sarhan T (2002) Low frequency varaibility of the exchanged flows through the Strait of Gibraltar during CANIGO. Deep-Sea Res 49:4051–4067
Lebeaupin Brossier C, Béranger K, Deltel C, Drobinski P (2011) The Mediterranean Sea response to different space-time resolution atmospheric forcings using perpetual mode sensitivity simulations. Ocean Model 36(1–2):1–25
Lebeaupin Brossier C, Drobinski P, Béranger K, Bastin S, Orain F (2013) Ocean memory effect on the dynamics of coastal heavy precipitation preceded by a Mistral event in the North-Western Mediterranean. Quart J R Meteorol Soc 139:1583–1597. doi:10.1002/qj.2049
Levitus S, Antonov JI, Boyer TP (2005) Warming of the World Ocean. Geophys Res Lett 32:L02604. doi:10.1029/2004GL021592
Lévy M, Establier A, Madec G (2001) Choice of an advection scheme for biogeochemical models. Geophys Res Lett 28(19):3725–3728. doi:10.1029/2001GL012947
Lyard FF, Lefevre T Letellier, Francis O (2006) Modelling the global ocean tides: modern insights from FES2004. Ocean Dyn 56(5–6):394–415
Madec G (2008) NEMO ocean engine, Note du Pole de modélisation, Institut Pierre-Simon Laplace (IPSL), France, No 27 ISSN No 1288–1619
Mariotti A, Struglia MV, Zeng N, Lau K-M (2002) The hydrological cycle in the Mediterranean Region and implications for the water budget of the Mediterranean Sea. J Clim 15:1674–1690
Marshall J, Schott F (1999) Open-Ocean convection: observations, theory, and models. Rev Geophys 37(1):1–64
Marullo S, Buongiorno Nardelli B, Guarracino M, Santoreli R (2007) Observing the Mediterranean Sea from space: 21 years of Pathfinder-AVHRR sea surface temperature (1985 to 2005): re-analysis and validation. Ocean Sci 3:299–310
Millot C, Taupier-Letage I (2005) Circulation in the Mediterranean Sea. In: The handbook of environmental chemistry, vol 5K. Springer, Berlin, pp 29–66. doi:10.1007/b107143
Mlawer EJ, Taubnam SJ, Brown PD, Iacono MJ, Clough SA (1997) A validated correlated k-model for the longwave. J Geophys Res 102:16663–16682
Monin AS, Obukhov AM (1954) Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere. Contrib Geophys Inst Acad Sci USSR 151:163–187
Noh Y, Cheon WG, Hong S-Y, Raasch S (2003) Improvement of the K-profile model for the planetary boundary layer based on large eddy simulation data. Bound Layer Meteorol 107:401–427
Omrani H, Drobinski P, Dubos T (2012a) Investigation of indiscriminate nudging and predictability in a nested quasi-geostrophic model. Q J R Meteorol Soc 138:158–169. doi:10.1002/qj.907
Omrani H, Drobinski P, Dubos T (2012b) Spectral nudging in regional climate modelling: how strongly should we nudge? Q J R Meteorol Soc 138:1808–1813. doi:10.1002/qj.1894
Omrani H, Drobinski P, Dubos T (2013) Optimal nudging strategies in regional climate modelling: investigation in a Big-Brother experiment over the European and Mediterranean regions. Clim. Dyn 41(9–10):2451–2470
Pettenuzzo D, Large WG, Pinardi N (2010) On the corrections of ERA-40 surface flux products consistent with the Mediterranean heat and water budgets and the connection basin surface total heat flux and NAO. J Geophys Res 115:C06022. doi:10.1029/2009JC005631
Pullen J, Doyle JD, Signell RP (2006) Two-way air-sea coupling: a study over the Adriatic. Mon Wea Rev 134(5):1465–1483
Romanou A, Tselioudis G, Zerefos CS, Clayson C-A, Curry JA, Andersson A (2010) Evaporation-precipitation variability over the Mediterranean and the Black Seas from satellite and reanalysis estimates. J Clim 23:5268–5287
Ruti P, Somot S, Dubois C, Calmanti S, Ahrens B, Alias A, Aznar R, Bartholy J, Bastin S, Branger K, Brauch J, Calvet J-C, Carillo A, Decharme B, Dell’Aquila A, Djurdjevic V, Drobinski P, Elizalde-Arellano A, Gaertner M, Galn P, Gallardo C, Giorgi F, Gualdi S, Harzallah A, Herrmann M, Jacob D, Khodayar S, Krichak S, Lebeaupin C, L’Heveder B, Li L, Liguro G, Lionello P, Onol B, Rajkovic B, Sannino G, Sevault F (2014) MED-CORDEX initiative for Mediterranean climate studies, BAMS (in revision)
Salameh T, Drobinski P, Dubos T (2010) The effect of indiscriminate nudging time on large and small scales in regional climate modelling: application to the Mediterranean basin. Q J R Meteorol Soc 136:170–182
Sanchez-Gomez E, Somot S, Josey SA, Dubois C, Elguindi N, Déqué M (2011) Evaluation of Mediterranean Sea water and heat budgets simulated by an ensemble of high-resolution climate models. Clim Dyn 37:2067–2086
Simons A, Uppala S, Dee D, Kobayashi S (2007) ERA-interim: new ECMWF reanalysis products from 1989 onwards. ECMWF Newslett 110:25–35
Skamarock WC, Klemp JB, Dudhia J, Gill DO, Barker DM, Duda MG, Huang X-Y, Wang W, Powers JG (2008) A description of the advanced research WRF Version 3, 125pp, NCAR Tech. Note NCAR/TN-475+STR
Soto-Navarro JF, Criado-Aldeanueva J, Garcia-Lafuente, Sanchez-Roman A (2010) Estimation of the Atlantic inflow through the strait of Gibraltar from climatological and in-situ data. J Geophys Res 115 (C10023). doi:10.1029/2010JC006302
Stauffer DR, Seaman NL (1990) Use of four-dimensional data assimilation in a limited-area mesoscale model. Part I: experiments with synoptic scale data. Mon Wea Rev 118:1250–1277
Stéfanon M, Drobinski P, D’Andrea F, Lebeaupin Brossier C, Bastin S (2014) Soil moisture-temperature feedbacks during heat waves over Western Europe. Clim Dyn 42(5–6):1309–1324
Tsimplis MN, Bryden HL (2000) Estimation of the transport through the Strait of Gibraltar. Deep Sea Res I 47:2219–2242
Valcke S (2006) OASIS3 User Guide (prism_2–5). CERFACS Technical Report TR/CMGC/06/73, PRISM Report No 3, Toulouse, France. 60 pp
Acknowledgments
This work is a contribution to the MORCE-MED project funded by the GIS “Climat, Environnement et Société”. This work also contributes to the HyMeX program (HYdrological cycle in The Mediterranean EXperiment—www.hymex.org) through INSU-MISTRALS support, to the Med-CORDEX initiative (A COordinated Regional climate Downscaling EXperiment—Mediterranean region—www.medcordex.eu), to the MED-ICCBIO project (funded by the GIS “Climat, Environnement et Société”) and to the SiMed project (Simulation of the Mediterranean Sea) funded by the “Groupe Mission Mercator Coriolis” program, with granted access to the HPC resources of IDRIS/GENCI (under allocation i2011010227). The authors are very grateful to Jonathan Beuvier, Guillaume Samson (Mercator-Océan), Sébastien Masson, Gurvan Madec (LOCEAN), Sophie Valcke, Laure Coquart and Eric Maisonnave (CERFACS) for their useful collaboration in the development of ocean-atmosphere coupling (WRF-OASIS-NEMO) within the MORCE system. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the Climserv team from IPSL who provides us the ERA-interim reanalysis and collects the HOAPS product, the Gruppo di Oceanografia da Satellite (GOS/ISAC-CNR) with ENEA who freely provide the OISST reanalysis from the MFSTEP project. The authors acknowledge Ségolène Berthou, Sylvain Mailler (LMD) and Thomas Arsouze (ENSTA-Paristech) for fruitful discussions during the review process. Cindy Lebeaupin Brossier finally thanks Samuel Somot and Sophie Belamari (GAME-CNRM/GMGEC) who allow the finalization of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebeaupin Brossier, C., Bastin, S., Béranger, K. et al. Regional mesoscale air–sea coupling impacts and extreme meteorological events role on the Mediterranean Sea water budget. Clim Dyn 44, 1029–1051 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2252-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2252-z