Abstract
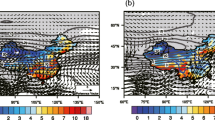
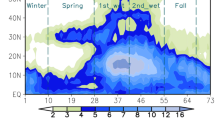
This study proposes primary diagnostic metrics to evaluate the integrated structure of interdecadal changes of East Asian climate in mid-summer (July–August) over the recent half-century (1955–2000) in numerical models. The metrics are applied to comprehensively examine the performance of BCC_AGCM (Beijing Climate Center atmospheric general circulation model) version 2.0.1. When forced by historical sea surface temperatures (SST), the ensemble simulation with the BCC_AGCM reasonably reproduced the coherent interdecadal changes of rainfall, temperature and circulation. The main feature of the “southern-flooding-and-northern-drought” rainfall change is captured by the model. Correspondingly, the tropospheric cooling in the upper and middle troposphere, the southward shift of upper level westerly jet and weakening of the low-level southwesterly monsoon flow are also reproduced, as well as their relationships with rainfall changes. One of the main deficiencies of the simulation is that the amplitudes of the changes of tropospheric cooling and large-scale circulation are both much weaker than those in reanalysis, and they are consistent with the rainfall deficiency. Also, the upper and middle troposphere cooling center and decreasing of upper-level westerly jet axis shift westward in the model simulations compared with that in the observations. Overall, although BCC_AGCM shows problems in simulating the interdecadal changes of East Asia climate, especially the amplitude and locations of change centers, it reasonably represents the observed configuration of rainfall variation and the associated coherent temperature and circulation changes. Therefore, it could be further used to discuss the mechanisms of the interdecadal variation in East Asia. Meanwhile, the reasonably reproduced configuration of rainfall and its associated large-scale circulation by SST-forced runs indicate that the interdecadal variations in East Asia could mostly arise from the regional response to the global climate change.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang K-T (2003) Introduction to geographic information systems (in Chinese), 2nd edn. Science Press, Moscow, pp 245–254
Collins WD, Rasch PJ, Boville BA, Hack JJ, McCaa JR, Williamson DL, Briegleb BP, Bitz CM, Lin S-J, Zhang M (2006) The formulation and atmospheric simulation of the community atmosphere model version 3 (CAM3). J Clim 19:2144–2161. doi:10.1175/JCLI3760.1
Ding Y, Chan JCL (2005) The East Asian summer monsoon: an overview. Meteorol Atmos Phys 89:117–142
Gao H, Yang S, Kumar A, Hu Z–Z, Huang B, Li Y, Jha B (2011) Variations of the East Asian Mei-Yu and simulation and prediction by the NCEP climate forecast system. J Clim 24:94–108
Hu Z–Z (1997) Interdecadal variability of summer climate over East Asia and its association with 500 hPa height and global sea surface temperature. J Geophys Res 102:19403–19412. doi:10.1029/97jd01052
Hu Z–Z, Yang S, Wu R (2003) Long-term climate variations in China and global warming signals. J Geophys Res 108:4614. doi:10.1029/2003jd003651
Huang R, Zhou L, Chen W (2003) The progresses of recent studies on the variabilities of the East Asian monsoon and their causes. Adv Atmos Sci 20:55–69
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, Collins W, Deaven D, Gandin L, Iredell M, Saha S, White G, Woollen J, Zhu Y, Chelliah M, Ebisuzaki W, Higgins W, Janowiak J, Mo KC, Ropelewski C, Wang J, Leetmaa A, Reynolds R, Jenne R, Joseph D (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–471
Kang IS et al (2002) Intercomparison of the climatological variations of Asian summer monsoon precipitation simulated by 10 GCMs. Clim Dyn 19:383–395
Li H, Dai A, Zhou T, Lu J (2010) Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to historical SST and atmospheric forcing during 1950–2000. Clim Dyn 34:501–514. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0482-7
Liang J, Yang S, Hu Z–Z, Huang B, Kumar A, Zhang Z (2009) Predictable patterns of the Asian and Indo-Pacific summer precipitation in the NCEP CFS. Clim Dyn 32:989–1001
Liu Y, Wu G, Ren R (2004) Relationship between the subtropical anticyclone and diabatic heating. J Clim 17:682–698
Menon S, Hansen J, Nazarenko L, Luo Y (2002) Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 297:2250–2253. doi:10.1126/science.1075159
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB, Folland CK, Alexander LV, Rowell DP, Kent EC, Kaplan A (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108:4407. doi:10.1029/2002jd002670
Reynolds R, Rayner N, Smith T, Stokes D, Wang W (2002) An improved in situ and satellite SST analysis for climate. J Clim 15:1609–1625
Tao S, Chen L (1987) A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China. In: Chang CP, Krishnamurti TN (eds) Monsoon meteorology. University Press, Oxford
Tao S, Zhao Y, Chen X (1958) The association between Mei-Yu in East Asia and seasonal variation of the general circulation of atmosphere over Asia (In Chinese). Acta Meteorologica Sinica 29:119–134
Trenberth KE, Hurrell JW (1994) Decadal atmosphere-ocean variations in the Pacific. Clim Dyn 9:303–319. doi:10.1007/bf00204745
Wang H (2001) The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s. Adv Atmos Sci 18:376–386. doi:10.1007/bf02919316
Wang B, Ding Q, Fu X, Kang I-S, Jin K, Shukla J, Doblas-Reyes F (2005) Fundamental challenge in simulation and prediction of summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 32:L15711. doi:10.1029/2005GL022734
Wang B, Bao Q, Hoskins B, Wu G, Liu Y (2008) Tibetan Plateau warming and precipitation changes in East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 35:L14702. doi:10.1029/2008gl034330
Wu T (2011) A mass-flux cumulus parameterization scheme for large-scale models: description and test with observations. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-0995-3
Wu T, Yu R, Zhang F (2008) A modified dynamic framework for the atmospheric spectral model and its application. J Atmos Sci 65:2235–2253. doi:10.1175/2007JAS2514.1
Wu T, Yu R, Zhang F, Wang Z, Dong M, Wang L, Jin X, Chen D, Li L (2010) The Beijing Climate Center atmospheric general circulation model: description and its performance for the present-day climate. Clim Dyn 34:123–147. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0487-2
Xu Q (2001) Abrupt change of the mid-summer climate in central east China by the influence of atmospheric pollution. Atmos Environ 35:5029–5040. doi:10.1016/s1352-2310(01)00315-6
Xu M, Chang C-P, Fu C, Qi Y, Robock A, Robinson D, Zhang H-M (2006) Steady decline of East Asian monsoon winds, 1969–2000: evidence from direct ground measurements of wind speed. J Geophys Res 111:D24111. doi:10.1029/2006jd007337
Yu R, Zhou T (2007) Seasonality and three-dimensional structure of interdecadal change in the East Asian monsoon. J Clim 20:5344–5355
Yu R, Wang B, Zhou T (2004) Tropospheric cooling and summer monsoon weakening trend over East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 31:L22212. doi:10.1029/2004gl021270
Zhang Y, Kuang X, Guo W, Zhou T (2006) Seasonal evolution of the upper-tropospheric westerly jet core over East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 33:L11708. doi:11710.11029/12006GL026377
Zhou T, Yu R (2005) Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in China. J Geophys Res 110:D08104. doi:08110.01029/02004JD005413
Zhou T, Yu R, Zhang J, Drange H, Cassou C, Deser C, Hodson DLR, Sanchez-Gomez E, Li J, Keenlyside N, Xin X, Okumura Y (2009) Why the Western Pacific subtropical high has extended westward since the late 1970s. J Clim 22:2199–2215
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful detailed comments. This work was jointly supported by the Major National Basic Research Program of China on Global Change under Grant 2010CB951902 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 40625014 and 40921003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Yu, R., Li, J. et al. The coherent interdecadal changes of East Asia climate in mid-summer simulated by BCC_AGCM 2.0.1. Clim Dyn 39, 155–163 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1154-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1154-6