Abstract
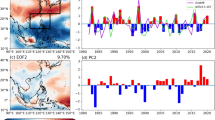
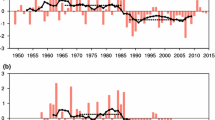
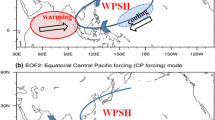
In this study, the anomalous characteristics of observed large-scale synoptic fields in the extreme East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) years are analyzed, and the impact of the local sea surface temperature (SST) anomaly over the western North Pacific (WNP) on the extreme EASM is investigated through sensitivity experiments of 28 years EASM simulations to the local SST over the WNP. The observation analysis reveals that the extreme EASM is influenced more by anomalous large-scale atmospheric features such as monsoon circulations and the western North Pacific subtropical high than the local SST anomaly over the WNP. However, the results of the sensitivity experiments show that the local SST anomaly has an implicit impact on the extreme EASM. The patterns of differences in precipitation between the experiment forced by observed SST in each year and the experiment forced by climatological SST over the WNP are opposite to anomaly patterns of observed precipitation in the extreme EASM years. This is because the SST anomaly over the WNP plays a role in reducing precipitation anomaly by changing surface latent heat flux and monsoon circulations. In particular, the local SST anomaly over the WNP decreases anomalies of large-scale circulations, i.e., the local Hadley and the Walker circulations. Thus, the local SST anomaly over the WNP plays a role in decreasing the interannual variability of the EASM.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonan GB, Oleson KW, Vertenstein M, Levis S, Zeng X, Dai Y, Dickinson RE, Yang Z-L (2002) The land surface climatology of the community land model coupled to the NCAR community climate model. J Clim 15:3123–3149
Briegleb BP (1992) Delta-Eddington approximation for solar radiation in the NCAR community climate model. J Geophys Res 97:7603–7612
Cha D-H, Lee D-K (2009) Reduction of systematic errors in regional climate simulations of the summer monsoon over East Asia and the western North Pacific by applying the spectral nudging technique. J Geophys Res 114:D14108. doi:10.1029/2008JD011176
Cha D-H, Lee D-K, Hong S-Y (2008) Impact of boundary layer processes on seasonal simulation of the East Asian summer monsoon using a regional climate model. Meteorol Atmos Phys 100:53–72
Chang C-P, Zhang Y, Li T (2000) Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I: roles of the subtropical ridge. J Clim 13:4310–4325
Fu C, Wang S, Xiong Z, Gutowski WJ, Lee D-K, McGregor JL, Sato Y, Kato H, Kim J-W, Suh M-S (2005) Regional climate model intercomparison project for Asia RMIP). Bull Am Meteorol Soc 86:257–266
Giorgi F, Marinucci MR (1996) A Investigation of the sensitivity of simulated precipitation to model resolution and its implications for climate studies. Mon Weather Rev 124:148–166
Grell GA, Dudhia J, Stauffer DR (1994) A description of the fifth-generation Penn State/NCAR mesoscale model (MM5), NCAR/TN-398 + STR, NCAR technical note. NCAR, Boulder, CO. 122 pp
Hong S-Y, Kalnay E (2002) The 1998 Oklahoma–Texas drought: mechanistic experiments with NCEP global and regional models. J Clim 15:945–963
Hong S-Y, Noh Y-G, Dudhia J (2006) A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon Weather Rev 134:2318–2341
Huang R-H, Sun F (1992) Impacts of the tropical western Pacific on the East Asian summer monsoon. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 70:243–256
Huang R-H, Zhou LT, Chen W (2003) The progress of recent studies on the variabilities of the East Asian monsoon and their causes. Adv Atmos Sci 20:55–69
Kain JS, Fritsch JM (1990) A one-dimensional entraining/detraining plume model and its application in convective parameterization. J Atmos Sci 47:2784–2802
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W, Woollen J, Yang S-K, Hnilo JJ, Fiorino M, Potter GL (2002) NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83:1631–1643
Kang H-S, Cha D-H, Lee D-K (2005) Evaluation of the mesoscale model/land surface model (MM5/LSM) coupled model for East Asian summer monsoon simulations. J Geophys Res 110:D10105. doi:1029/2004JD005266
Kim J-E, Hong S-Y (2007) Impact of soil moisture anomalies on summer rainfall over East Asia: a regional climate model study. J Clim 20:5732–5743
Kwon M, Jhun J-G, Wang B, An S-I, Kug J-S (2005) Decaldal change in relationship between East Asian and WNP summer monsoons. Geophys Res Lett 32:L16709. doi:10.1029/2005GL023026
Lau K-M, Kim K-M, Yang S (2000) Dynamical and boundary forcing characteristics of regional components of the Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 13:2461–2482
Lee D-K, Cha D-H, Kang HS (2004) Regional climate simulation for the 1998 summer flood over East Asia. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 82:1735–1753
Lee D-K, Cha D-H, Choi S-J (2005a) A sensitivity study of regional climate simulation to convective parameterization schemes for 1998 East Asian summer monsoon. J Terr Atmos Ocean Sci 16:989–1015
Lee E-J, Jhun J-G, Park C-K (2005b) Remote connection of the Northeast Asian summer rainfall variation revealed by a newly defined monsoon index. J Clim 18:4381–4383
Lee E-J, Yeh S-W, Jhun J-G, Moon B-K (2006) Seasonal change in anomalous WNPSH associated with the strong East Asian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 33:L21702. doi:10.1029/2006GL027474
Liang X-Z, Kunkel KE, Samel AN (2001) Development of a regional climate model for U.S. Midwest applications. Part I: sensitivity to buffer zone treatment. J Clim 14:4363–4378
Newell RE (1979) Climate and the ocean. Am Sci 67:405–416
Nitta T (1987) Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impacts on the Northern Hemisphere summer circulation. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 65:373–390
Reisner J, Rasmussen RM, Bruintjes RT (1998) Explicit forecasting of supercooled liquid water in winter storms using the MM5 mesoscale model. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 124:1071–1107
Reynolds RW, Rayner NA, Smith TM, Stokes DC, Wang W (2002) An improved in situ and satellite SST analysis for climate. J Clim 15:1609–1625
Von Storch H, Langerberg H, Feser F (2000) A spectral nudging technique for dynamical downscaling purposes. Mon Weather Rev 128:3664–3673
Waliser DE, Graham NE (1993) Convective cloud systems and warm-pool sea surface temperatures: coupled interactions and self-regulation. J Geophys Res 98:12881–12893
Wang B, Fan Z (1999) Choice of South Asian summer monsoon indices. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 80:629–638
Wang B, Lin H (2002) Rainy season of the Asian-Pacific summer monsoon. J Clim 15:386–398
Wang B, Wu R, Fu X (2000) Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: how does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J Clim 13:1517–1536
Wang B, Wu R, Lau K-M (2001) Interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon: contrasts between the Indian and the western North Pacific-East Asian monsoons. J Clim 14:4037–4090
Wang Y, Sen OL, Wang B (2003) A highly resolved regional climate model (IPRC-RegCM) and its simulation of the 1998 severe precipitation event over China. Part I: model description and verification of simulation. J Clim 16:1721–1738
Wang B, Ding Q, Fu X, Kang I-S, Jin K, Shukla J, Doblas-Reyes F (2005) Fundamental challenge in simulation and prediction of summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 32:L15711. doi:10.1029/2005GL022734
Xue Y, Zeng FJ, Mitchell KE, Janjic ZRE (2001) The impact of land surface processes on simulations of the U.S. hydrological cycle: a case study of the 1993 flood using the SSiB land surface model in the NCEP Eta regional model. Mon Weather Rev 129(12):2833–2860
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Korea Meteorological Administration Research and Development Program under Grant RACS_2010-2016. This study was also partially supported by the BK21 program of the Korean Government Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cha, DH., Jin, CS. & Lee, DK. Impact of local sea surface temperature anomaly over the western North Pacific on extreme East Asian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 37, 1691–1705 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0983-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0983-z