Abstract
Introduction
Brain tumors are a frequent cause of epilepsy in the pediatric population. The last International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) classification of focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) includes a subgroup consisting of tumors with surrounding dysplastic abnormalities (FCD type IIIb). Although its pathogenesis is still unclear, it has several clinical and therapeutic (surgical) implications.
Background
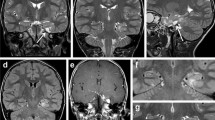
A number of benign tumors (such as dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors and gangliogliomas) frequently present with medically refractory epilepsy associated with cortical dysplasia. In such cases, planning of surgical resection needs to take into consideration not only the tumor but also the whole area of epileptogenicity. The use of intraoperative electrocorticography recordings is reported to result in better postoperative outcomes, since they help delineate the abnormal cerebral cortex that needs to be resected to provide seizure freedom to patients. Clinical, radiological, and pathological features are also discussed herein.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi Y, Yagishita A (2008) Gangliogliomas: characteristic imaging findings and role in the temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroradiology 50(10):829–834
Andres M, Andre VM, Nguyen S, Salamon N, Cepeda C, Levine MS, Leite JP, Neder L, Vinters HV, Mathern GW (2005) Human cortical dysplasia and epilepsy: an ontogenetic hypothesis based on volumetric MRI and NeuN neuronal density and size measurements. Cereb Cortex 15:194–210
Barba C, Coras R, Giordano F, Buccoliero AM, Genitori L, Blümcke I, Guerrini R (2011) Intrinsic epileptogenicity of gangliogliomas may be independent from co-occurring focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsy Res 97(1–2):208–213
Blumcke I, Aronica E, Urbach H, Alexopoulos A, Gonzalez–Martinez JA (2014) A neuropathology–based approach to epilepsy surgery in brain tumors and proposal for a new terminology use for long–term epilepsy–associated brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol 128:39–54
Blumcke I (2009) Neuropathology of focal epilepsies: a critical review. Epilepsy Behav 15:34–39
Blumcke I, Thom M, Aronica E, Armstrong DD, Vinters HV, Palmini A, Jacques TS, Avanzini G, Barkovich AJ, Battaglia G, Becker A, Cepeda C, Cendes F, Colombo N, Crino P, Cross JH, Delalande O, Dubeau F, Duncan J, Guerrini R, Kahane P, Mathern G, Najm I, Ozkara C, Raybaud C, Represa A, Roper SN, Salamon N, Schulze-Bonhage A, Tassi L, Vezzani A, Spreafico R (2011) The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: a consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission. Epilepsia 52(1):158–174
Cendes F, Cook MJ, Watson C, Andermann F, Fish DR, Shorvon SD, Bergin P, Free S, Dubeau F, Arnold DL (1995) Frequency and characteristics of dual pathology in patients with lesional epilepsy. Neurology 45:2058–2064
Cosgrove GR (2001) Epilepsy surgery for tumors, vascular malformations, trauma, and cerebrovascular disease. In: Luders HO, Comair YG (eds) Epilepsy surgery, 2nd edn. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1197–1205
Cossu M, Fuschillo D, Bramerio M, Galli C, Gozzo F, Pelliccia V, Casaceli G, Tassi L, Lo Russo G (2013) Epilepsy surgery of focal cortical dysplasia-associated tumors. Epilepsia 54(Suppl 9):115–122
De Oliveira RS, Santos MV, Terra VC, Sakamoto AC, Machado HR (2011) Tailored resections for intractable rolandic cortex epilepsy in children: a single-center experience with 48 consecutive cases. Childs Nerv Syst 27(5):779–785
Ellika SK, Jain R, Patel SC et al (2007) Role of perfusion CT in glioma grading and comparison with conventional MR imaging features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1981
Englot DJ, Berger MS, Barbaro NM, Chang EF (2012) Factors associated with seizure freedom in the surgical resection of glioneuronal tumors. Epilepsia 53(1):51–57
Englot DJ, Berger MS, Barbaro NM, Chang EF (2011) Predictors of seizure freedom after resection of supratentorial low-grade gliomas. A review. J Neurosurg 115(2):240–244
Leach JL, Miles L, Henkel DM, Greiner HM, Kukreja MK, Holland KD, Rose DF, Zhang B, Mangano FT (2014) Magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in the resection region correlate with histopathological type, gliosis extent, and postoperative outcome in pediatric cortical dysplasia. J Neurosurg Pediatr 14(1):68–80
Lombardi D, Marsh R, de Tribolet N (1997) Low grade glioma in intractable epilepsy: lesionectomy versus epilepsy surgery. Acta Neurochir Suppl 68:70–74
Pellock JM, Bourgeois BFD, Dodson WE (2008) Pediatric epilepsy diagnosis and therapy, 3rd edn. Demos Medical, New York
Qiu B, Ou S, Song T, Hu J, You L, Wang Y, Wang Y (2014) Intraoperative electrocorticography-guided microsurgical management for patients with onset of supratentorial neoplasms manifesting as epilepsy: a review of 65 cases. Epileptic Disord 16(2):175–184
Shapiro WR (2011) Clinical features: neurology of brain tumor and paraneoplastic disorders. In: Winn HR (ed) Youmans neurological surgery, 6th edn. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1197–1205
Sugano H, Shimizu H, Sunaga S (2007) Efficacy of intraoperative electrocorticography for assessing seizure outcomes in intractable epilepsy patients with temporal-lobe-mass lesions. Seizure 16(2):120–127
Taylor DC, Falconer MA, Bruton CJ, Corsellis JA (1971) Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:369–387
Winn HR (2011) Youmans neurological surgery, 6th edn. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, M.V., de Oliveira, R.S. & Machado, H.R. Approach to cortical dysplasia associated with glial and glioneuronal tumors (FCD type IIIb). Childs Nerv Syst 30, 1869–1874 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2519-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2519-z