Abstract
Introduction
Coexistence of multiple seizure types, inclusion of the motor cortex in the epileptogenic zone, and poor delimitation of the abnormal cortex make most patients with polymicrogyria (PMG) unlikely candidates for epilepsy surgery (Guerrini R et al., Epilepsy and malformations of the cerebral cortex in Epileptic syndromes in infancy, childhood and adolescence, 2005).
Case report
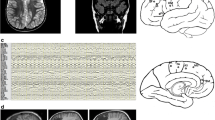
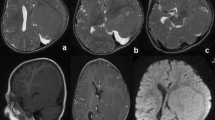
We present here a child with frontal PMG and intractable epilepsy evaluated with advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and neurophysiologic techniques. Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography showed severe involvement of neighboring white matter tracts besides the cortex. The evaluation also included functional MRI, chronic subdural electroencephalogram monitoring, and intra-operative motor mapping. The patient had a decrease in seizure frequency and an increase in his developmental skills after the surgery.
Conclusion
Advanced neuroradiologic and neurophysiologic techniques are required to provide an effective and safe resection of the epileptogenic cortex in cortical dysplasias.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo D, de Araujo DB, Pontes-Neto OM, Escorsi-Rosset S, Simao GN, Wichert-Ana L, Velasco TR, Sakamoto AC, Leite JP, Santos AC (2006) Language and motor fMRI activation in polymicrogyric cortex. Epilepsia 47(3):589–592
Brodtkorb E, Andersen K, Henriksen O, Myhr G, Skullerud K (1998) Focal, continuous spikes suggest cortical developmental abnormalities. Clinical, MRI and neuropathological correltes. Acta Neurol Scand 98:377–385
Burneo JG, Kuzniecky RI, Bebin M, Knowlton RC (2004) Cortical reorganization in malformations of cortical development: a magnetoencephalographic study. Neurology 63(10):1818–1824
Eriksson SH, Rugg-Gunn FJ, Symms MR, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with epilepsy and malformations of cortical development. Brain 124:617–626
Guerrini R, Holthausen H, Parmeggiani L, Parrini E, Chiron C (2005) Epilepsy and malformations of the cerebral cortex. In: Roger J, Bureau M, Dravet C, Genton P, Tassinari CA, Wolf P (eds) Epileptic syndromes in infancy, childhood and adolescence. John Libbey, Eurotext Montrouge, pp 493–518
Jack CR Jr, Thompson RM, Butts RK, Sharbrough FW, Kelly PJ, Hanson DP, Riederer SJ, Ehman RL, Hangrandreou NJ, Cascino GD (1994) Sensory motor cortex: correlation of presurgical mapping with functional MR imaging and invasive cortical mapping. Radiology 190(1):85–92
Jacobs KM, Hwang BJ, Prince DA (1999) Focal epileptogenesis in a rat model of polymicrogyria. J Neurophysiol 81:159–173
Janszky J, Ebner A, Kruse B, Mertens M, Jokeit H, Seitz RJ, Witte OW, Tuxhorn I, Woermann FG (2003) Functional organization of the brain with malformations of cortical development. Ann Neurol 53(6):759–767
Kobayashi E, Bagshaw AP, Jansen A, Andermann F, Andermann E, Gotman J, Dubeau F (2005) Intrinsic epileptogenicity in polymicrogyric cortex suggested by EEG-fMRI BOLD responses. Neurology 64:1263–1266
Kuzniecky RI, Barkovich AJ (2001) Malformations of cortical development and epilepsy. Brain Dev 23:2–11
Lee CC, Jack CR, Riederer SJ (1998) Mapping of the central sulcus with functional MR: active versus passive activation tasks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:847–852
Lee SK, Kim DI, Kim J, Kim DJ, Kim HD, Kim DS, Mori S (2005) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography:a new method of describing aberrant fiber connections in developmental CNS anomalies. Radiographics 25:53–68
Majos A, Tybor K, Stefanczyyk L, Goraj B (2005) Cortical mapping by functional magnetic resonance imaging in patients with brain tumors. Eur Radiol 15(6):1148–1158
Marusic P, Najm IM, Ying Z, Prayson R, Rona S, Nair D, Hadar E, Kotagal P, Bej MD, Wyllie E, Bingaman W, Lüders H (2002) Focal cortical dysplasias in eloquent cortex: functional characteristics and correlation with MRI and histopathologic changes. Epilepsia 43(1):27–32
Palmini A, Gambardella A, Andermann F, Dubeau F, da Costa JC, Olivier A, Tampieri D, Gloor P, Quesney F (1995) Intrinsic epileptogenicity of human dysplastic cortex as suggested by corticography and surgical results. Ann Neurol 37:476–487
Paetau R, Saraneva J, Salonen O, Valanne L, Ignatius J, Salenius S (2004) Electromagnetic function of polymicrogyric cortex in congenital bilateral perisylvian syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:717–722
RamacahandranNair R, Otsubo H, Ochi A, Rutka J, Donner EJ (2006) Mirror movements following cortical resection of polymicrogyria in a child with intractable epilepsy. Pediatr Neurol 34:135–138
Rugg-Gunn FJ, Eriksson SH, Symms MR, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging of cryptogenic and acquired partial epilepsies. Brain 124:627–636
Russo GL, Tassi L, Cossu M, Cardinale F, Mai R, Castana L, Colombo N, Bramerio M (2003) Focal cortical resection in malformations of cortical development. Epileptic Disord 5(Suppl 2):S115–S123
Sisodiya SM (2000) Surgery for malformations of cortical development causing epilepsy. Brain 123:1075–1091
Sisodiya SM, Free SL, Stevens JM, Fish DR, Shorvon SD (1995) Widespread cerebral structural changes in patients with cortical dysgenesis and epilepsy. Brain 118:1039–1050
Van Bogaert P, David P, Gillain CA, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Scalais E, Nuttin C, Wetzburger C, Szliwowsi HB, Metens T, Goldman S (1998) Perisylvian dysgenesis: clinical, EEG, MRI and glucose metabolism features in 10 patients. Brain 121:2229–2238
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Dr. Aydın Sav for his comments on the pathological examination of the surgical material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Işık, U., Dinçer, A. & Özek, M.M. Surgical treatment of polymicrogyria with advanced radiologic and neurophysiologic techniques. Childs Nerv Syst 23, 443–448 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0262-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0262-9