Abstract
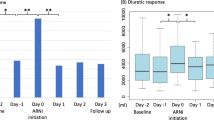
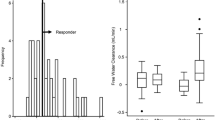
A nonrandomized controlled study was conducted to evaluate the effect of lipo-prostaglandin E1 (lipo-PGE1) on cystatin C (CysC), β2-microglobulin (B2MG), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in patients with decompensated heart failure (DHF) and renal dysfunction. A total of 286 enrolled patients with DHF and renal dysfunction were nonrandomly assigned a 7-day standard treatment without (n = 146) or with (n = 140) lipo-PGE1 intervention. According to the baseline eGFR, patients were further classified into mild, moderate, and severe renal dysfunction subgroups. By the end of study period, there was no evidence of an immense improvement in B2MG, CysC, and eGFR in response to standard treatment (all P > 0.05). On the contrary, a noticeable decrease of B2MG and CysC was observed in patients receiving lipo-PGE1 intervention, as well as an increase in eGFR (all P < 0.05). Moreover, lipo-PGE1 intervention led to greater changes in renal function variables from baseline than with standard management (all P < 0.05). Most important, the favorable renal protective effects of lipo-PGE1 were maintained in three subgroups. Lipo-PGE1 intervention brought a substantial renoprotective benefit to hospitalized DHF patients as compared with standard therapy, suggesting it might offer a promising therapeutic option for the management of renal dysfunction associated with DHF.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scrutinio D, Passantino A, Santoro D, Catanzaro R (2011) The cardiorenal anaemia syndrome in systolic heart failure: prevalence, clinical correlates, and long-term survival. Eur J Heart Fail 13:61–67
House AA, Anand I, Bellomo R, Cruz D, Bobek I, Anker SD, Aspromonte N, Bagshaw S, Berl T, Daliento L, Davenport A, Haapio M, Hillege H, McCullough P, Katz N, Maisel A, Mankad S, Zanco P, Mebazaa A, Palazzuoli A, Ronco F, Shaw A, Sheinfeld G, Soni S, Vescovo G, Zamperetti N, Ponikowski P, Ronco C; Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Consensus Group (2010) Definition and classification of cardio-renal syndromes: workgroup statements from the 7th ADQI Consensus Conference. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:1416–1420
Kimura H, Hiramitsu S, Miyagishima K, Mori K, Yoda R, Kato S, Kato Y, Morimoto S, Hishida H, Ozaki Y (2010) Cardio-renal interaction: impact of renal function and anemia on the outcome of chronic heart failure. Heart Vessels 25:306–312
Heywood JT, Fonarow GC, Costanzo MR, Mathur VS, Wigneswaran JR, Wynne J, ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee Investigators (2007) High prevalence of renal dysfunction and its impact on outcome in 118,465 patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: a report from the ADHERE database. J Card Fail 13:422–430
Smith GL, Lichtman JH, Bracken MB, Shlipak MG, Phillips CO, DiCapua P, Krumholz HM (2006) Renal impairment and outcomes in heart failure: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:1987–1996
Takagi A, Iwama Y, Yamada A, Aihara K, Daida H (2010) Estimated glomerular filtration rate is an independent predictor for mortality of patients with acute heart failure. J Cardiol 55:317–321
Yagi H, Kawai M, Komukai K, Ogawa T, Minai K, Nagoshi T, Ogawa K, Sekiyama H, Taniguchi I, Yoshimura M (2011) Impact of chronic kidney disease on the severity of initially diagnosed coronary artery disease and the patient prognosis in the Japanese population. Heart Vessels 26:370–378
Damman K, Jaarsma T, Voors AA, Navis G, Hillege HL, van Veldhuisen DJ, COACH investigators, (2009) Both in- and out-hospital worsening of renal function predict outcome in patients with heart failure: results from the Coordinating Study Evaluating Outcome of Advising and Counseling in Heart Failure (COACH). Eur J Heart Fail 11:847–854
Kawai K, Kawashima S, Miyazaki T, Tajiri E, Mori M, Kitazaki K, Shirotani T, Inatome T, Yamabe H, Hirata K, Yokoyama M (2010) Serum β2-microglobulin concentration as a novel marker to distinguish levels of risk in acute heart failure patients. J Cardiol 55:99–107
Damman K, van der Harst P, Smilde TD, Voors AA, Navis G, van Veldhuisen DJ, Hillege HL (2012) Use of cystatin C levels in estimating renal function and prognosis in patients with chronic systolic heart failure. Heart 98:319–324
Jungbauer CG, Birner C, Jung B, Buchner S, Lubnow M, von Bary C, Endemann D, Banas B, Mack M, Böger CA, Riegger G, Luchner A (2011) Kidney injury molecule-1 and N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase in chronic heart failure: possible biomarkers of cardiorenal syndrome. Eur J Heart Fail 13:1104–1110
Lassus JP, Nieminen MS, Peuhkurinen K, Pulkki K, Siirilä-Waris K, Sund R, Harjola VP; FINN-AKVA study group (2010) Markers of renal function and acute kidney injury in acute heart failure: definitions and impact on outcomes of the cardiorenal syndrome. Eur Heart J 31:2791–2798
Maréchaux S, Six-Carpentier MM, Bouabdallaoui N, Montaigne D, Bauchart JJ, Mouquet F, Auffray JL, Le Tourneau T, Asseman P, LeJemtel TH, Ennezat PV (2011) Prognostic importance of comorbidities in heart failure with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Heart Vessels 26:313–320
Fukuta H, Ohte N, Wakami K, Asada K, Goto T, Mukai S, Kimura G (2011) Reduced renal function is associated with combined increases in ventricular-systolic stiffness and arterial load in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization for coronary artery disease. Heart Vessels 26:10–16
Damman K, Kalra PR, Hillege H (2010) Pathophysiological mechanisms contributing to renal dysfunction in chronic heart failure. J Ren Care 36:18–26
House AA (2010) Pharmacological therapy of cardiorenal syndromes and heart failure. Contrib Nephrol 164:164–172
Koniari K, Nikolaou M, Paraskevaidis I, Parissis J (2010) Therapeutic options for the management of the cardiorenal syndrome. Int J Nephrol 2011:194910
Sun D, Liu CX, Ma YY, Zhang L (2011) Protective effect of prostaglandin E1 on renal microvascular injury in rats of acute aristolochic acid nephropathy. Ren Fail 33:225–232
McCullough PA, Tumlin JA (2009) Prostaglandin-based renal protection against contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Circulation 120:1749–1751
Wang H, Deng JL, Yue J, Li J, Hou YB (2010) Prostaglandin E1 for preventing the progression of diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:CD006872
Tian J, Chen JH, Li Q, He Q, Lin WQ (2005) Lipid peroxidation in IgA nephropathy and the effect of lipo-prostaglandin E1. J Nephrol 18:243–248
Nakayama Y, Inoue T, Kohda Y, Inoue H, Izumi Y, Tomita K, Nonoguchi H (2008) Long-term observation of renal function on combination therapy with prostaglandin and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor for chronic kidney disease. Clin Nephrol 69:402–407
Moertl D, Berger R, Huelsmann M, Bojic A, Pacher R (2005) Short-term effects of levosimendan and prostaglandin E1 on hemodynamic parameters and B-type natriuretic peptide levels in patients with decompensated chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 7:1156–1163
Serra W, Musiari L, Ardissino D, Gherli T, Montanari A (2011) Benefit of prostaglandin infusion in severe heart failure: preliminary clinical experience of repetitive administration. Int J Cardiol 146:10–15
Shen J, He B, Wang B (2005) Effects of lipo-prostaglandin E1 on pulmonary hemodynamics and clinical outcomes in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 128:714–719
Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, Strömberg A, van Veldhuisen DJ, Atar D, Hoes AW, Keren A, Mebazaa A, Nieminen M, Priori SG, Swedberg K, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG) (2008) ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). Eur J Heart Fail 10:933–989
Miller WG (2008) Reporting estimated GFR: a laboratory perspective. Am J Kidney Dis 52:645–648
Stevens LA, Coresh J, Schmid CH, Feldman HI, Froissart M, Kusek J, Rossert J, Van Lente F, Bruce RD 3rd, Zhang YL, Greene T, Levey AS (2008) Estimating GFR using serum cystatin C alone and in combination with serum creatinine: a pooled analysis of 3,418 individuals with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 51:395–406
Felker GM, Lee KL, Bull DA, Redfield MM, Stevenson LW, Goldsmith SR, LeWinter MM, Deswal A, Rouleau JL, Ofili EO, Anstrom KJ, Hernandez AF, McNulty SE, Velazquez EJ, Kfoury AG, Chen HH, Givertz MM, Semigran MJ, Bart BA, Mascette AM, Braunwald E, O’Connor CM, NHLBI Heart Failure Clinical Research Network (2011) Diuretic strategies in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. N Engl J Med 364:797–805
Huang CL, Wu YW, Wang SS, Tseng CD, Chiang FT, Hsu KL, Lee CM, Tzen KY (2011) Continuous intravenous infusion of prostaglandin E1 improves myocardial perfusion reserve in patients with ischemic heart disease assessed by positron emission tomography: a pilot study. Ann Nucl Med 25:462–468
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge with deep gratitude the assistance and guidance of all colleagues in the Emergency Department.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest for any authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Z.-Q. Hou and Z.-X. Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, ZQ., Sun, ZX., Su, CY. et al. Effect of lipo-prostaglandin E1 on cystatin C, β2-microglobulin, and estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with decompensated heart failure and renal dysfunction: a single-center, nonrandomized controlled study. Heart Vessels 28, 589–595 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-012-0286-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-012-0286-x