Abstract
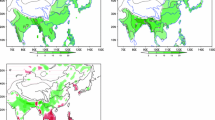
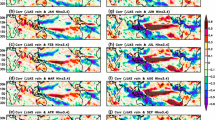
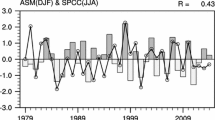
Using National Centers for Environmental Prediction/National Centre for Atmospheric Research (NCEP/NCAR) reanalysis data and monthly Hadley Center sea surface temperature (SST) data, and selecting a representative East Asian winter monsoon (EAWM) index, this study investigated the relationship between EAWM and East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) using statistical analyses and numerical simulations. Some possible mechanisms regarding this relationship were also explored. Results indicate a close relationship between EAWM and EASM: a strong EAWM led to a strong EASM in the following summer, and a weak EAWM led to a weak EASM in the following summer. Anomalous EAWM has persistent impacts on the variation of SST in the tropical Indian Ocean and the South China Sea, and on the equatorial atmospheric thermal anomalies at both lower and upper levels. Through these impacts, the EAWM influences the land-sea thermal contrast in summer and the low-level atmospheric divergence and convergence over the Indo-Pacific region. It further affects the meridional monsoon circulation and other features of the EASM. Numerical simulations support the results of diagnostic analysis. The study provides useful information for predicting the EASM by analyzing the variations of preceding EAWM and tropical SST.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi, X. Q., 1993: IAP9L AGCM models and climate numerical simulation. Ph. D. dissertation, Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 210pp.
Chang, C.-P., and K.-M. Lau, 1982: Short-term planetary-scale interaction over the tropics and the midlatitudes during northern winter, Part I: Contrast between active and inactive periods. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 993–946.
Chen, J., and S. Q. Sun, 1999: Eastern Asian winter monsoon anomaly and variation of global circulation Part I: a comparison study on strong and weak winter monsoon. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 23, 101–111. (in Chinese)
Chen, L. X., Q. G. Zhu, and H. B. Luo, 1991: East Asian Monsoon. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 362pp. (in Chinese).
Chen, W., H. F. Graf, and R. H. Huang, 2000: Interannual variability of East Asian winter monsoon and its relation to the summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 17, 48–60.
Cui, X. P., and Z. B. Sun, 1999: East Asian winter monsoon index and its variation analysis. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 22, 321–324. (in Chinese)
Ding, Y. H., 1994: Monsoon over China. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 419pp.
Gao, H., 2007: Comparison of four East Asian winter monsoon indices. Acta Meteorological Sinica, 65, 272–279. (in Chinese)
Guo, Q. Y., 1983: The summer monsoon intensity index in East Asia and its variation. Acta Geographica Sinica, 38, 207–217. (in Chinese)
Guo, Q. Y., 1985: The variations of East Asian summer monsoon and the rainfall in China. Tropical Meteorology, 1, 44–51. (in Chinese)
Jhun, J. G., and E. J. Lee., 2004: A new East Asian winter monsoon index and associated characteristics of the winter monsoon. J. Climate, 15, 711–726.
Kistler, R., and Coauthors, 2001: The NCEP-NCAR 50-year reanalysis: Monthly means CD-ROM and documentation. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 82, 247–268.
Li, C. Y., 1988: Frequent strong East Asia trough activities and the occurrence of the El Niño. Science in China (B), 6, 667–674. (in Chinese)
Li, C. Y., and J. Hu, 1987: Studies on interaction between atmospheric circulation and El Niño. Scientia Atmospherica Sinica, 11, 359–364. (in Chinese)
Li, J. P., and Q. C. Zeng, 2002: A unified monsoon index. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29(8), 1274, doi: 10.1029/2001GL013874.
Li, J. P., and Q. C. Zeng, 2003: A new monsoon index and the geographical distribution of the global monsoons. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20, 299–302.
Li, J. P., and Q. C. Zeng, 2005: A new monsoon index, its interannual variability and relation with monsoon precipitation. Climatic and Environmental Research, 10(3), 351–365. (in Chinese)
Li, Y., and S. Yang, 2010: A dynamical index for the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Climate, 23, 4255–4262.
Liang, X. Z., 1996: Description of a nine-level grid point atmospheric general circulation model. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 13, 269–298.
Rayner, N. A., D. E. Parker, E. B. Horton, C. K. Folland, L. V. Alexander, D. P. Rowell, E. C. Kent, and A. Kaplan, 2003: Global analyses of SST, sea ice and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D14), 4407, doi: 10.1029/2002JD002670.
Shi, N., 1996: Features of the East Asian winter monsoon intensity on multiple time scale in recent 40 years and their relation to climate. Journal of Applied meteorological Science, 7, 175–181. (in Chinese)
Sun, B. M., and S. Q. Sun, 1996: The role of SST in the East Asian winter monsoon affecting summer drought/flooding in the Yangtze River-Huaihe River valleys. The Processes of Disastrous Climate and Its Diagnostics, Huang, Ed., China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 46–53. (in Chinese)
Sun, S. Q., and B. M. Sun, 1995: The relationship between the anomalous winter monsoon circulation over East Asia and summer drought/flooding in the Yangtze and Huaihe River valley. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 53, 438–450. (in Chinese)
Wang, L., and W. Chen, 2010: How well do existing indices measure the strength of the East Asian winter monsoon? Adv. Atmos. Sci., 27, 855–870.
Wu, B. Y., and R. H. Huang, 1999: Effects of the Extremes in the North Atlantic Oscillation on East Asia Winter Monsoon. Scientia Atmospherica Sinica, 23, 641–651. (in Chinese)
Yan, H. M., and Z. N. Xiao, 2000: The numerical simulation of the Indian Ocean SSTA influence on climatic variations over Asian monsoon region. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 16, 18–27. (in Chinese)
Yan, H. M., W. Duan, and Z. N. Xiao, 2003: A study on relation between East Asian winter monsoon and climate change during raining season in China. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 19, 367–376. (in Chinese)
Yan, H. M., W. Zhou, H. Yang, and Y. Cai, 2009: Definition of a East Asian winter monsoon index and its variation characteristics. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 32, 367–376. (in Chinese)
Yang, H., J. Chen, and S. Q. Sun, 2005a: Numerical experiment on the El Niño event stimulated by the East Asian winter monsoon. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 29, 321–333. (in Chinese)
Yang, H., J. Chen, and S. Q. Sun, 2005b: Numerical experiment on the interseasonal connection of circulation. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 29, 396–408. (in Chinese)
Zhang, Q. Y., and Y. Wang, 2006: The response of East Asian monsoon circulation between winter and summer to sea surface temperature over the Pacific Ocean. Climatic and Environmental Research, 11, 487–498. (in Chinese)
Zhang, R. H., and Q. Li, 2004: Impact of sea temperature variability of tropical oceans on East Asian monsoon. Meteorological Monthly, 30, 22–26. (in Chinese)
Zhang, Y., K. R. Sperber, and J. S. Boyle, 1997: Climatology and interannual variation of the East Asian monsoon: A diagnostic study of the 86/87 and 91/92 events. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 49–62.
Zhao, Z. G., 1999: Summer Drought and Flood of China and Environment Field. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 297pp. (in Chinese)
Zhou, B. T., and H. J. Wang, 2006: Relationship between the boreal spring Hadley circulation and the summer precipitation in the Yangtze River valley. J. Geophys. Res., 111, doi: 10.1029/2005JD007006.
Zhou, W., C. Y. Li, and X. Wang, 2007: Possible connection between Pacific oceanic interdecadal pathway and East Asian winter monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, doi: 10.1029/2006GL027809.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Yang, H., Yuan, Y. et al. Relationship between East Asian winter monsoon and summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 28, 1345–1356 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-0014-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-0014-y