Abstract
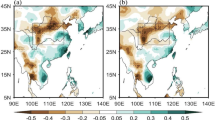
ENSO’s effect on the rainfall in eastern China in the following early summer is investigated by using station precipitation data and the ERA-40 reanalysis data from 1958 to 2002. In June, after the El Niño peak, the precipitation is significantly enhanced in the Yangtze River valley while suppressed in the Huaihe River-Yellow River valleys. This relationship between ENSO and the rainfall in eastern China is established possibly through two teleconnections: One is related to the western North Pacific (WNP) anticyclonic anomaly in the lower troposphere leading to enhanced precipitation in the Yangtze River valley, and the other is related to the southward displacement of the Asian jet stream (AJS) in the upper troposphere resulting in suppressed precipitation in the Huaihe River-Yellow River valleys.
This southward displacement of the AJS is one part of ENSO’s effect on the zonal flow in the whole Northern Hemisphere. After the El Niño peak, the ENSO-related warming in the tropical troposphere persists into the following early summer, increasing the meridional temperature gradient and through the thermal wind balance, leads to the enhancement of westerly flow in the subtropics south of the westerly jet stream and results in a southward displacement of the westerly jet stream.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, C.-P., Y. Zhang, and T. Li, 2000: Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I: Role of the subtropical ridge. J. Climate, 13, 4310–4325.
Chen, L.-X., M. Dong, and Y.-N. Shao, 1992: The characteristics of interannual variations on the East Asian monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 70, 397–421.
Ha, K.-J., and E. Ha, 2006: Climate change and interannual fluctuations in the long-term record of monthly precipitation for Seoul. International Journal of Climatology, 26, 607–618.
Hoerling, M. P., J. S. Whitaker, A. Kumar, and W. Wang, 2001: The midlatitude warming during 1998–2000. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 755–758.
Huang, R., and Y. Wu, 1989: The influence of ENSO on the summer climate change in China and its mechanism. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 6, 21–32.
Huang, R., and F. Sun, 1992: Impacts of the tropical western Pacific on the East Asia summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 70, 243–256.
Kosaka, Y., and H. Nakamura, 2006: Structure and dynamics of the summertime Pacific-Japan (PJ) teleconnection pattern. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 132, 2009–2030.
Lau, K.-M., K.-M. Kim, and S. Yang, 2000: Dynamical and boundary forcing characteristics of regional components of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Climate, 13, 2461–2482.
Lau, K.-M., and H. Weng, 2001: Coherent mode of global SST and summer rainfall over China: An assessment of the regional impacts of the 1997–98 El Niño. J. Climate, 14, 1294–1308.
Lau, N.-C., and M. J. Nath, and H. Wang, 2004: Simulation by a GFDL GCM of ENSO-related variability of the coupled atmosphere-ocean system in the East Asian monsoon region. East Asian Monsoon, C.-P. Chang, Ed., World Scientific Publishing Co., 271–300.
Lim, Y.-K., and K.-Y. Kim, 2007: ENSO impact on the space-time evolution of the regional Asian summer monsoons. J. Climate, 20, 2397–2415.
Lin, Z., and R. Lu, 2005: Interannual meridional displacement of the East Asian upper-tropospheric jet stream in summer. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 22, 199–211.
Lu, R., 2004: Associations among the components of the East Asian summer monsoon system in the meridional direction. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 82, 155–165.
Lu, R., and B. Dong, 2001: Westward extension of North Pacific subtropical high in summer. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 79, 1229–1241.
Nitta, T., 1987: Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impact on the Northern Hemisphere summer circulation. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 65, 243–256.
Seager, R., N. Harnik, and Y. Kushnir, 2003: Mechanisms of hemispherically symmetric climate variability. J. Climate, 16, 2960–2978.
Tanaka, M., 1997: Interannual and interdecadal variation of the western north Pacific monsoon and the East Asian Baiu rainfall and their relationship to ENSO cycle. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 75, 1109–1123.
Uppala, S. M., and Coauthors, 2005: The ERA-40 reanalysis, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 131, 2961–3012.
Wang, B., R. Wu, and X. Fu, 2000: Pacific-east Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536.
Wang, B., R. Wu, and K.-M. Lau, 2001: Interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon: Contrasts between the Indian and the western North Pacific-east Asia monsoons. J. Climate, 14, 4073–4090.
Webster, P. J., V. O. Magana, T. N. Palmer, R. A. Thomas, M. Yanai, and T. Yasunari, 1998: Monsoons: Processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 14451–14510.
Wu, R., Z.-Z. Hu, and B. P. Kirtman, 2003: Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J. Climate, 16, 3742–3758.
Yulaeva, E., and J. M. Wallace, 1994: The signature of ENSO in global temperature and precipitation fields derived from the microwave sounding unit. J. Climate, 7, 1719–1736.
Zhang, R., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto, 1999: A diagnostic study of the impact of El Niño on the precipitation in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 16, 229–241.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Z., Lu, R. The ENSO’s effect on eastern China rainfall in the following early summer. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 26, 333–342 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-0333-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-0333-4