Abstract
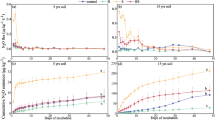
Earthworms can significantly accelerate soil nitrification and N2O emissions by stimulating microbial communities in the soil and their gut. However, the response of earthworm-mediated N transformation to nitrification inhibitors (e.g., 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate, DMPP) is mostly unknown. In this study, soils with or without earthworms were treated with four different concentrations of DMPP (0%, 1%, 2%, and 3%), and samples were collected at six different time points (days 3, 5, 7, 14, 21, and 30 of incubation). The presence of earthworms resulted in the highest soil NH4+ content and lowest NO3– content in DMPP-treated soil, which could be attributed to the highest ureC gene abundance and lowest soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) abundance. Approximately 75% of the earthworm-induced N2O emission could be suppressed by DMPP application, and earthworms also resulted in weak correlations between soil N-related gene abundance (bacterial amoA and nirK) and N2O emission, while such correlations could be strengthened when both DMPP and earthworms were applied. Besides, DMPP application could also significantly suppresses the nitrification and denitrification functions of earthworm gut microbiota, suggesting that the earthworm-induced N2O emission might be mainly produced by the denitrifier communities within their gut. In addition, the earthworm-induced fluctuations in soil NO3− and NH4+ content further resulted in significant losses of earthworm gut microbial diversity, while such losses could be alleviated by DMPP application, which enhanced the C-, P-, and S-cycling capacities of gut microbiota. Altogether, we suggest that DMPP can effectively inhibit nitrification in earthworm-treated soil, subsequently enhancing the earthworm gut microbiota’s metabolic capacities.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All sequencing data were deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information Sequence Read Archive under the BioProject accession number PRJNA831672.
References
Bachtsevani E, Papazlatani CV, Rousidou C, Lampronikou E, Menkissoglu-Spiroudi U, Nicol GW, Karpouzas DG, Papadopoulou ES (2021) Effects of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on the activity and diversity of the soil microbial community under contrasting soil pH. Biol Fertil Soils 57:1117–1135
Barrena I, Menéndez S, Correa-Galeote D, Vega-Mas I, Bedmar EJ, González-Murua C, Estavillo JM (2017) Soil water content modulates the effect of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria. Geoderma 303:1–8
Bertora C, van Vliet PCJ, Hummelink EWJ, van Groenigen JW (2007) Do earthworms increase N2O emissions in ploughed grassland? Soil Biol Biochem 39:632–640
Bertrand M, Barot S, Blouin M, Whalen J, de Oliveira T, Roger-Estrade J (2015) Earthworm services for cropping systems. A Review. Agron Sustain Dev 35:553–567
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, Da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo J, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang L, Kaehler BD, Kang KB, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu YX, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik AV, Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS 2nd, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, van der Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan Y, Wang M, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Knight R, Caporaso JG (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583
Chen M, Wang W, Feng Y, Zhu X, Zhou H, Tan Z, Li X (2014) Impact resistance of different factors on ammonia removal by heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium Aeromonas sp. HN-02. Bioresour Technol 167:456–461
Coleman DC, Crossley DA Jr, Hendrix PF (2004) Fundamentals of soil ecology, 2nd edn. Elsevier, New York
Daims H, Lucker S, Wagner M (2016) A new perspective on microbes formerly known as nitrite-oxidizing bacteria. Trends Microbiol 24:699–712
Davidson EA, Hart SC, Shanks CA, Firestone MK (1991) Measuring gross nitrogen mineralization, and nitrification by 15 N isotopic pool dilution in intact soil cores. J Soil Sci 42:335–349
Decaëns T, Rangel A, Asakawa N, Thomas R (1999) Carbon and nitrogen dynamics in ageing earthworm casts in grasslands of the eastern plains of Colombia. Biol Fertil Soils 30:20–28
Drake HL, Horn MA (2007) As the worm turns: the earthworm gut as a transient habitat for soil microbial biomes. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:169–189
Duan YF, Kong XW, Schramm A, Labouriau R, Eriksen J, Petersen SO (2017) Microbial N transformations and N2O emission after simulated grassland cultivation: effects of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP). Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e02019-e2116
Fan X, Yin C, Chen H, Ye M, Zhao Y, Li T, Wakelin SA, Liang Y (2019) The efficacy of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate on N2O emissions is linked to niche differentiation of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria across four arable soils. Soil Biol Biochem 130:82–93
Geisseler D, Scow KM (2014) Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms - a review. Soil Biol Biochem 75:54–63
Goreau TJ, Kaplan WA, Wofsy SC, McElroy MB, Valois FW, Watson SW (1980) Production of NO2- and N2O by nitrifying bacteria at reduced concentrations of oxygen. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:526–532
Haimi J, Boucelham M (1991) Influence of a litter feeding earthworm, Lumbricus rubellus, on soil processes in a simulated coniferous forest floor. Pedobiologia 35:247–256
Han Z, Xu P, Li Z, Lin H, Zhu C, Wang J, Zou J (2022) Microbial diversity and the abundance of keystone species drive the response of soil multifunctionality to organic substitution and biochar amendment in a tea plantation. GCB Bioenergy 14:481–495
Hart SC, Nason GE, Myrold DD, Perry DA (1994) Dynamics of gross nitrogen transformations in an old-growth forest: the carbon connection. Ecology 75:880–891
Hau HH, Gralnick JA (2007) Ecology and biotechnology of the genus Shewanella. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:237–258
He XX, Chen YQ, Liu SJ, Gunina A, Wang XL, Chen W, Shao YH, Shi LL, Yao Q, Li JX, Zou XM, Schimel JP, Zhang WX, Fu SL (2018) Cooperation of earthworm and arbuscular mycorrhizae enhanced plant N uptake by balancing absorption and supply of ammonia. Soil Biol Biochem 116:351–359
Horn MA, Schramm A, Drake HL (2003) The earthworm gut: an ideal habitat for ingested N2O-producing microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1662–1669
Hu J, Zhao H, Wang Y, Yin Z, Kang Y (2020) The bacterial community structures in response to the gut passage of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) feeding on cow dung and domestic sludge: Illumina high-throughput sequencing-based data analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110149
Huang HK, Tseng SK (2001) Nitrate reduction by Citrobacter diversus under aerobic environment. Appl Microbiol Biot 55:90–94
Huang K, Xia H, Cui G, Li F (2017) Effects of earthworms on nitrification and ammonia oxidizers in vermicomposting systems for recycling of fruit and vegetable wastes. Sci Total Environ 578:337–345
Jin BJ, Bi QF, Li KJ, Yu QG, Ni L, Lin XY, Zhu YG (2022a) Long-term combined application of chemical fertilizers and organic manure shapes the gut microbial diversity and functional community structures of earthworms. Appl Soil Ecol 170:104250
Jin BJ, Liu XP, Roux XL, Bi QF, Li KJ, Wu CY, Sun CL, Zhu YG, Lin XY (2022b) Biochar addition regulates soil and earthworm gut microbiome and multifunctionality. Soil Biol Biochem 173:108810
Kleineidam K, Kosmrlj K, Kublik S, Palmer I, Pfab H, Ruser R, Fiedler S, Schloter M (2011) Influence of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in rhizosphere and bulk soil. Chemosphere 84:182–186
Knapp BA, Podmirseg SM, Seeber J, Meyer E, Insam H (2009) Diet-related composition of the gut microbiota of Lumbricus rubellus as revealed by a molecular fingerprinting technique and cloning. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2299–2307
Kong X, Eriksen J, Petersen SO (2018) Evaluation of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) for mitigating soil N2O emissions after grassland cultivation. Agric Ecosyst Environ 259:174–183
Kool DM, Dolfing J, Wrage N, Van Groenigen JW (2011) Nitrifier denitrification as a distinct and significant source of nitrous oxide from soil. Soil Biol Biochem 43:174–178
Kotzerke A, Klemer S, Kleineidam K, Horn MA, Drake HL, Schloter M, Wilke BM (2010) Manure contaminated with the antibiotic sulfadiazine impairs the abundance of nirK- and nirS-type denitrifiers in the gut of the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Biol Fertil Soils 46:415–418
Kou YP, Wei K, Chen GX, Wang ZY, Xu H (2015) Effects of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate and dicyandiamide on nitrous oxide emission in a greenhouse vegetable soil. Plant Soil Environ 61:29–35
Kuypers MMM, Marchant HK, Kartal B (2018) The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:263–276
Lam SK, Suter H, Davies R, Bai M, Mosier AR, Sun JL, Chen DL (2018) Direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions from two intensive vegetable farms applied with a nitrification inhibitor. Soil Biol Biochem 116:48–51
Lavelle P, Spain AV (2001) Soil ecology. Kluwer Academics Publishers, Dordrecht
Li XG, Zhang WJ, Xiao X, Jian HH, Jiang T, Tang HZ, Qi XQ, Wu LF (2018) Pressure-regulated gene expression and enzymatic activity of the two periplasmic nitrate reductases in the deep-sea bacterium Shewanella piezotolerans WP3. Front Microbiol 9:3173
Lubbers IM, van Groenigen KJ, Fonte SJ, Six J, Brussaard L, van Groenigen JW (2013) Greenhouse-gas emissions from soils increased by earthworms. Nat Clim Change 3:187–194
Luo G, Rensing C, Chen H, Liu M, Wang M, Guo S, Ling N, Shen Q, Briones M (2018) Deciphering the associations between soil microbial diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality driven by long-term fertilization management. Funct Ecol 32:1103–1116
Lv B, Cui Y, Wei H, Chen Q, Zhang D (2020) Elucidating the role of earthworms in N2O emission and production pathway during vermicomposting of sewage sludge and rice straw. J Hazard Mater 400:123215
Maienza A, Baath E, Stazi SR, Benedetti A, Grego S, Dell’Abate MT (2014) Microbial dynamics after adding bovine manure effluent together with a nitrification inhibitor (3,4 DMPP) in a microcosm experiment. Biol Fertil Soils 50:869–877
Matthies C, Griesshammer A, Schmittroth M, Drake HL (1999) Evidence for involvement of gut-associated denitrifying bacteria in emission of nitrous oxide (N2O) by earthworms obtained from garden and forest soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3599–3604
Medina-Sauza RM, Alvarez-Jimenez M, Delhal A, Reverchon F, Blouin M, Guerrero-Analco JA, Cerdan CR, Guevara R, Villain L, Barois I (2019) Earthworms building up soil microbiota, a review. Front Environ Sci 7:81
Meier AB, Hunger S, Drake HL (2018) Differential engagement of fermentative taxa in gut contents of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Appl Environ Microbiol 84:01851–01917
OECD (2016) Test No. 222: Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida / Eisenia andrei), OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. OECD Publishing, Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264264496-en
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O'Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2016) Vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.5-7. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan. Accessed 9 Feb 2022
Pass DA, Morgan AJ, Read DS, Field D, Weightman AJ, Kille P (2015) The effect of anthropogenic arsenic contamination on the earthworm microbiome. Environ Microbiol 17:1884–1896
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 4:590–596
Ravindran B, Contreras-Ramos SM, Sekaran G (2015) Changes in earthworm gut associated enzymes and microbial diversity on the treatment of fermented tannery waste using epigeic earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae. Ecol Eng 74:394–401
Rizhiya E, Bertora C, van Vliet PCJ, Kuikman PJ, Faber JH, van Groenigen JW (2007) Earthworm activity as a determinant for N2O emission from crop residue. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2058–2069
Senbayram M, Chen R, Budai A, Bakken L, Dittert K (2012) N2O emission and the N2O/(N2O + N2) product ratio of denitrification as controlled by available carbon substrates and nitrate concentrations. Agric Ecosyst Environ 147:4–12
Shi XZ, Hu HW, Muller C, He JZ, Chen DL, Suter HC (2016) Effects of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate on nitrification and nitrifiers in two contrasting agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:5236–5248
Sorokin DY, Lucker S, Vejmelkova D, Kostrikina NA, Kleerebezem R, Rijpstra WI, Damste JS, Le Paslier D, Muyzer G, Wagner M, van Loosdrecht MC, Daims H (2012) Nitrification expanded: discovery, physiology and genomics of a nitrite-oxidizing bacterium from the phylum Chloroflexi. ISME J 6:2245–2256
Stein LY, Klotz MG (2016) The nitrogen cycle. Curr Biol 26:94–98
Tan X, Yang YL, Li X, Zhou ZW, Liu CJ, Liu YW, Yin WC, Fan XY (2020) Intensified nitrogen removal by heterotrophic nitrification aerobic denitrification bacteria in two pilot-scale tidal flow constructed wetlands: influence of influent C/N ratios and tidal strategies. Bioresour Technol 302:122803
Tao J, Griffiths B, Zhang S, Chen X, Liu M, Hu F, Li H (2009) Effects of earthworms on soil enzyme activity in an organic residue amended rice-wheat rotation agro-ecosystem. Appl Soil Ecol 42:221–226
Thakuria D, Schmidt O, Finan D, Egan D, Doohan FM (2010) Gut wall bacteria of earthworms: a natural selection process. ISME J 4:357–366
Tian D, Niu S (2015) A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ Res Lett 10:024019
Turner S, Pryer KM, Miao VP, Palmer JD (1999) Investigating deep phylogenetic relationships among cyanobacteria and plastids by small subunit rRNA sequence analysis. J Eukaryotic Microbiol 46:327–338
Wang Z, Kong T, Hu S, Sun H, Yang W, Kou Y, Mandlaa XuH (2015) Nitrification inhibitors mitigate earthworm-induced N2O emission—a mesocosm study. Biol Fertil Soils 51:1005–1011
Wang L, Zhang Y, Luo X, Zhang J, Zheng Z (2016a) Effects of earthworms and substrate on diversity and abundance of denitrifying genes (nirS and nirK) and denitrifying rate during rural domestic wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 212:174–181
Wang Z, Peng S, Sun Y, Yao Q, Yu Y, Wu Y (2016b) How gut-stimulated denitrifiers influence soil N2O emission without earthworm activity. Eur J Soil Sci 76:70–73
Wrage N, Velthof GL, van Beusichem ML, Oenema O (2001) Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1723–1732
Wu D, Liu M, Song X, Jiao J, Li H, Hu F (2015a) Earthworm ecosystem service and dis-service in an N-enriched agroecosystem: increase of plant production leads to no effects on yield-scaled N2O emissions. Soil Biol Biochem 82:1–8
Wu Y, Shaaban M, Zhao J, Hao R, Hu R (2015b) Effect of the earthworm gut-stimulated denitrifiers on soil nitrous oxide emissions. Eur J Soil Sci 70:104–110
Wu JT, Bai YF, Lu BK, Zhao W, Forstner C, Menzies NW, Bertsch PM, Wang P, Kopittke PM (2020) Silver sulfide nanoparticles reduce nitrous oxide emissions by inhibiting denitrification in the earthworm gut. Environ Sci Technol 54:11146–11154
Wüst PK, Horn MA, Drake HL (2009a) In situ hydrogen and nitrous oxide as indicators of concomitant fermentation and denitrification in the alimentary canal of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1852–1859
Wüst PK, Horn MA, Henderson G, Janssen PH, Rehm BH, Drake HL (2009b) Gut-associated denitrification and in vivo emission of nitrous oxide by the earthworm families megascolecidae and lumbricidae in New Zealand. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3430–3436
Xu D, Li Y, Howard A, Guan Y (2013) Effect of earthworm Eisenia fetida and wetland plants on nitrification and denitrification potentials in vertical flow constructed wetland. Chemosphere 92:201–206
Xu HJ, Chen H, Wang XL, Zhang YL, Wang JJ, Li N, Li YT (2018) Earthworms stimulate nitrogen transformation in an acidic soil under different Cd contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:564–572
Xue R, Wang C, Liu X, Liu M (2022) Earthworm regulation of nitrogen pools and dynamics and marker genes of nitrogen cycling: a meta-analysis. Pedosphere 32:131–139
Xun W, Liu Y, Li W, Ren Y, Xiong W, Xu Z, Zhang N, Miao Y, Shen Q, Zhang R (2021) Specialized metabolic functions of keystone taxa sustain soil microbiome stability. Microbiome 9:35
Yan P, Wu L, Wang D, Fu J, Shen C, Li X, Zhang L, Zhang L, Fan L, Wenyan H (2020) Soil acidification in Chinese tea plantations. Sci Total Environ 715:136963
Yin C, Fan X, Chen H, Jiang Y, Ye M, Yan G, Peng H, Wakelin SA, Liang Y (2021) 3, 4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate is an effective and specific inhibitor of soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Biol Fertil Soils 57:753–766
Zhang B, Penton CR, Yu Z, Xue C, Chen Q, Chen Z, Yan C, Zhang Q, Zhao M, Quensen JF, Tiedje JM (2021) A new primer set for Clade I nosZ that recovers genes from a broader range of taxa. Biol Fertil Soils 57:523–531
Zhang M, Jin BJ, Bi QF, Li KJ, Sun CL, Lin XY, Zhu YG (2022a) Variations of earthworm gut bacterial community composition and metabolic functions in coastal upland soil along a 700-year reclamation chronosequence. Sci Total Environ 804:149994
Zhang Y, Zhang F, Abalos D, Luo Y, Hui D, Hungate BA, Garcia-Palacios P, Kuzyakov Y, Olesen JE, Jorgensen U, Chen J (2022b) Stimulation of ammonia oxidizer and denitrifier abundances by nitrogen loading: poor predictability for increased soil N2O emission. Global Change Biol 28:2158–2168
Zheng B, Zhu Y, Sardans J, Penuelas J, Su J (2018) QMEC: a tool for high throughput quantitative assessment of microbial functional potential in C, N, P, and S biogeochemical cycling. Sci China Life Sci 61:1451–1462
Zheng Q, Hu Y, Zhang S, Noll L, Bockle T, Dietrich M, Herbold CW, Eichorst SA, Woebken D, Richter A, Wanek W (2019) Soil multifunctionality is affected by the soil environment and by microbial community composition and diversity. Soil Biol Biochem 136:107521
Zhou J, Wu L, Deng Y, Zhi X, Jiang YH, Tu Q, Xie J, Van Nostrand JD, He Z, Yang Y (2011) Reproducibility and quantitation of amplicon sequencing based detection. ISME J 5:1303–1313
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Liang Ni (AES of Zhejiang University) for his help in field experiment management and soil sample collection.
Funding
This work was supported by Zhejiang Province “Agriculture, Rural Areas, Rural People and Nine Institutions” Science and Technology Collaboration Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42077088) and Ningbo Bureau of Science and Technology (2022Z169, 2021Z101). Xipeng Liu was supported by a scholarship from the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• DMPP effectively inhibits nitrification in the earthworm-treated soil.
• Earthworm gut denitrifiers mainly produce earthworm-related N2O.
• DMPP significantly suppresses earthworm gut denitrifiers and related N2O emission.
• DMPP changes the environmental filter function of the earthworm for soil microbes.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, BJ., Liu, XP., Zhang, M. et al. Earthworms enhance the inhibition efficiency of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate on soil nitrification by altering soil AOB communities and gut denitrifier communities. Biol Fertil Soils 59, 747–761 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-023-01744-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-023-01744-2