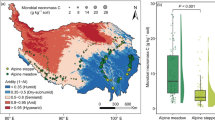
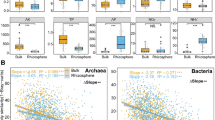
Abstract
The alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (QTP), which is sensitive to global climate change and human activities, is subjected to addition of nutrients such as nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in the soil. The impacts of N or P on ecosystem structure and function depend at least partly on the response of soil fungal communities, although few studies have compared the effects of N and P addition, both separately and together. We examined the responses of composition of the soil fungal community to 3-year experimental nutrient additions (control, N, N plus P, and P) in a typical alpine meadow of the QTP. We found that P addition, regardless of N addition, significantly reduced fungal species richness and changed fungal community composition, while the effect of N was undetectable. Nitrogen plus phosphorus caused a more distinct community than either N or P addition alone. Multivariate regression tree, canonical correspondence analysis, and distance-based multivariate linear model analyses all suggested available P was a key parameter determining the diversity and composition of the fungal community. Other parameters such as dissolved organic N, aboveground net primary productivity of forbs, and dissolved organic C played important but secondary roles. The results indicated an important role of P in structuring soil fungal communities in the alpine meadow. Our results suggest that fungal diversity loss and long-term changes in ecosystem stability can result from fertilization management in the fragile alpine environment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarenkov K, Henrik Nilsson R, Larsson KH, Alexander IJ, Eberhardt U, Erland S, Høiland K, Kjøller R, Larsson E, Pennanen T (2010) The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi-recent updates and future perspectives. New Phytol 186:281–285
A’Bear AD, Boddy L, Jones TH (2012) Impacts of elevated temperature on the growth and functioning of decomposer fungi are influenced by grazing collembola. Glob Chang Biol 18:1823–1832
Ahn H, James RT (2001) Variability, uncertainty, and sensitivity of phosphorus deposition load estimates in south Florida. Water Air Soil Pollut 126:37–51
Alguacil MDM, Lozano Z, Campoy MJ, Roldán A (2010) Phosphorus fertilisation management modifies the biodiversity of AM fungi in a tropical savanna forage system. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1114–1122
Allen EB, Allen MF, Helm DJ, Trappe JM, Molina R, Rincon E (1995) Patterns and regulation of mycorrhizal plant and fungal diversity. Plant Soil 170:47–62
Antoninka A, Reich PB, Johnson NC (2011) Seven years of carbon dioxide enrichment, nitrogen fertilization and plant diversity influence arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a grassland ecosystem. New Phytol 192:200–214
Artursson V, Finlay RD, Jansson JK (2006) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and bacteria and their potential for stimulating plant growth. Environ Microbiol 8:1–10
Aschehoug ET, Metlen KL, Callaway RM, Newcombe G (2012) Fungal endophytes directly increase the competitive effects of an invasive forb. Ecology 93:3–8
Balajee SA, Sigler L, Brandt ME (2007) DNA and the classical way: identification of medically important molds in the 21st century. Med Mycol 45:475–490
Bao Z, Matsushita Y, Morimoto S, Hoshino YT, Suzuki C, Nagaoka K, Takenaka M, Murakami H, Kuroyanagi Y, Urashima Y, Sekiguchi H, Kushida A, Toyota K, Saito M, Tsushima S (2013) Decrease in fungal biodiversity along an available phosphorous gradient in arable Andosol soils in Japan. Can J Microbiol 59:368–373
Beauregard MS, Hamel C, Atul N, St-Arnaud M (2010) Long-term phosphorus fertilization impacts soil fungal and bacterial diversity but not AM fungal community in alfalfa. Microb Ecol 59:379–389
Bindraban PS, Dimkpa C, Nagarajan L, Roy A, Rabbinge R (2015) Revisiting fertilisers and fertilisation strategies for improved nutrient uptake by plants. Biol Fertil Soils 51:1–15
Caceres MD, Legendre P (2009) Associations between species and groups of sites: indices and statistical inference. Ecology 90:3566–3574
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Cassman NA, Leite MF, Pan Y, de Hollander M, van Veen JA, Kuramae EE (2016) Plant and soil fungal but not soil bacterial communities are linked in long-term fertilized grassland. Sci Rep 6:23680. doi:10.1038/srep23680
Chagnon PL, Bradley RL (2013) Evidence that soil nutrient stoichiometry controls the competitive abilities of arbuscular mycorrhizal vs. root-borne non-mycorrhizal fungi. Fungal Ecol 6:557–560
Chen C, Zhang J, Lu M, Qin C, Chen Y, Yang L, Huang Q, Wang J, Shen Z, Shen Q (2016) Microbial communities of an arable soil treated for 8 years with organic and inorganic fertilizers. Biol Fertil Soils 52:455–467
Clarke K, Gorley R, Somerfield P, Warwick R (2014) Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, third ed. PRIMER-E v7, Plymouth, pp 260
Core Team R (2015) R: a language and environment for statistical computing., R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Covacevich F, Echeverría HE, Aguirrezabal LA (2007) Soil available phosphorus status determines indigenous mycorrhizal colonization of field and glasshouse-grown spring wheat from Argentina. Appl Soil Ecol 35:1–9
Crowther TW, Boddy L, Jones TH (2011) Outcomes of fungal interactions are determined by soil invertebrate grazers. Ecol Lett 14:1134–1142
De’ath G (2002) Multivariate regression trees: a new technique for modeling species-environment relationships. Ecology 83:1105–1117
Dinno A (2015) dunn.test: Dunn’s test of multiple comparisons using rank sums. R package version 1.3.2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dunn.test.
Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142
Fang HJ, Cheng SL, Yu GR, Zheng J, Zhang P, Xu MJ, Li Y, Yang XM (2012) Responses of CO2 efflux from an alpine meadow soil on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau to multi-form and low-level N addition. Plant Soil 351:177–190
Fang HJ, Cheng SL, Yu GR, Yang XM, Xu MJ, Wang YS, Li LS, Dang XS, Wang L, Li NY (2014) Nitrogen deposition impacts on the amount and stability of soil organic matter in an alpine meadow ecosystem depend on the form and rate of applied nitrogen. Eur J Soil Sci 65:510–519
Frey SD, Knorr M, Parrent JL, Simpson RT (2004) Chronic nitrogen enrichment affects the structure and function of the soil microbial community in temperate hardwood and pine forests. For Ecol Manage 196:159–171
Gerloff G (1976) Plant efficiencies in the use of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. In: Plant adaptation to mineral stress in problem soils. Proceedings of a workshop held at the National Agricultural Library, Beltsville, Maryland, November 22–23, 1976. Cornell University Agricultural Experiment Station, pp 161–173
Güsewell S, Gessner MO (2008) N:P ratios influence litter decomposition and colonization by fungi and bacteria in microcosms. Funct Ecol 23:211–219
Güsewell S, Verhoeven JTA (2006) Litter N: P ratios indicate whether N or P limits the decomposability of graminoid leaf litter. Plant Soil 287:131–143
Hammel K (1997) Fungal degradation of lignin. In: Cadisch G (ed) Driven by nature: plant litter quality and decomposition. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 33–45
Hedlund K, Santa Regina I, Van der Putten W, Lepš J, Diaz T, Korthals G, Lavorel S, Brown V, Gormsen D, Mortimer S (2003) Plant species diversity, plant biomass and responses of the soil community on abandoned land across Europe: idiosyncracy or above-belowground time lags. Oikos 103:45–58
Hervé M (2015) RVAideMemoire: diverse basic statistical and graphical functions. R package version 0.9-53. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RVAideMemoire.
Jiang C, Yu G, Li Y, Cao G, Yang Z, Sheng W, Yu W (2012) Nutrient resorption of coexistence species in alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau explains plant adaptation to nutrient-poor environment. Ecol Eng 44:1–9
Jiang M, Wang X, Liu SY, Sun X, Zhao C, Liu H (2015) Diversity and abundance of soil animals as influenced by long-term fertilization in grey desert soil, China. Sustainability 7:10837–10853
Johnson D, Vandenkoornhuyse PJ, Leake JR, Gilbert L, Booth RE, Grime JP, Young JPW, Read DJ (2004) Plant communities affect arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal diversity and community composition in grassland microcosms. New Phytol 161:503–515
Kazutaka K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30:772–780
Kennedy AC (1999) Bacterial diversity in agroecosystems. Agric Ecosyst Environ 74:65–76
Kivlin SN, Hawkes CV, Treseder KK (2011) Global diversity and distribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Biol Biochem 43:2294–2303
Lamarque JF, Hess P, Emmons L, Buja L, Washington W, Granier C (2005) Tropospheric ozone evolution between 1890 and 1990. J Geophys Res Atmos 110:D08304. doi:10.1029/2004JD005537
Lemons A, Clay K, Rudgers JA (2005) Connecting plant-microbial interactions above and belowground: a fungal endophyte affects decomposition. Oecologia 145:595–604
Li J, Li Z, Wang F, Zou B, Chen Y, Zhao J, Mo Q, Li Y, Li X, Xia H (2015) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil microbial community in a secondary tropical forest of China. Biol Fertil Soils 51:207–215
Liu L, Gundersen P, Zhang T, Mo J (2012a) Effects of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass and community composition in three forest types in tropical China. Soil Biol Biochem 44:31–38
Liu Y, Shi G, Mao L, Cheng G, Jiang S, Ma X, An L, Du G, Collins Johnson N, Feng H (2012b) Direct and indirect influences of 8 yr of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on Glomeromycota in an alpine meadow ecosystem. New Phytol 194:523–535
Liu X, Zhang Y, Han W, Tang A, Shen J, Cui Z, Vitousek P, Erisman JW, Goulding K, Christie P, Fangmeier A, Zhang F (2013a) Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 494:459–462
Liu L, Zhang T, Gilliam FS, Gundersen P, Zhang W, Chen H, Mo J (2013b) Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on soil microbial communities in a tropical forest. PLoS ONE 8:e61188. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061188
Lombard L, Merwe NAVD, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2015) Generic concepts in Nectriaceae. Stud Mycol 80:189–245
Lü C, Tian H (2007) Spatial and temporal patterns of nitrogen deposition in China: synthesis of observational data. J Geophys Res Atmos 112:229–238
Lukač B, Kramberger B, Meglič V, Verbič J (2012) Importance of non-leguminous forbs in animal nutrition and their ensiling properties: a review. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture 99:3–8
Luo P, Han X, Wang Y, Han M, Shi H, Liu N, Bai H (2015) Influence of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass, dehydrogenase activity, and bacterial and fungal community structure in a brown soil of northeast China. Ann Microbiol 65:533–542
Magoč T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Marschner P, Kandeler E, Marschner B (2003) Structure and function of the soil microbial community in a long-term fertilizer experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 35:453–461
Meidute S, Demoling F, Bååth E (2008) Antagonistic and synergistic effects of fungal and bacterial growth in soil after adding different carbon and nitrogen sources. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2334–2343
Meier CL, Suding KN, Bowman WD (2008) Carbon flux from plants to soil: roots are a belowground source of phenolic secondary compounds in an alpine ecosystem. J Ecol 96:421–430
Mueller RC, Balasch MM, Kuske CR (2014) Contrasting soil fungal community responses to experimental nitrogen addition using the large subunit rRNA taxonomic marker and cellobiohydrolase I functional marker. Mol Ecol 23:4406–4417
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini MT, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2003) Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur J Soil Sci 54:655–670
Narisawa K, Hambleton S, Currah RS (2007) Heteroconium chaetospira, a dark septate root endophyte allied to the Herpotrichiellaceae (Chaetothyriales) obtained from some forest soil samples in Canada using bait plants. Mycoscience 48:274–281
Nemergut DR, Townsend AR, Sattin SR, Freeman KR, Fierer N, Neff JC, Bowman WD, Schadt CW, Weintraub MN, Schmidt SK (2008) The effects of chronic nitrogen fertilization on alpine tundra soil microbial communities: implications for carbon and nitrogen cycling. Environ Microbiol 10:3093–3105
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2015) vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.3-4. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan.
Pena R, Offermann C, Simon J, Naumann PS, Geßler A, Holst J, Dannenmann M, Mayer H, Kögel-Knabner I, Rennenberg H, Polle A (2010) Girdling affects ectomycorrhizal fungal (EMF) diversity and reveals functional differences in EMF community composition in a beech forest. Applied Environ Microbiol 76:1831–1841
Pii Y, Mimmo T, Tomasi N, Terzano R, Cesco S, Crecchio C (2015) Microbial interactions in the rhizosphere: beneficial influences of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on nutrient acquisition process. A review. Biol Fertil Soils 51:403–415
Poggeler S (2011) Evolution of multicopper oxidase genes in coprophilous and non-coprophilous members of the order Sordariales. Curr Genomics 12:95–103
Rinaldi AC, Comandini O, Kuyper TW (2008) Ectomycorrhizal fungal diversity: separating the wheat from the chaff. Fungal Divers 33:1–45
Rineau F, Courty PE (2011) Secreted enzymatic activities of ectomycorrhizal fungi as a case study of functional diversity and functional redundancy. Ann For Sci 68:69–80
Rudgers JA, Fischer S, Clay K (2010) Managing plant symbiosis: fungal endophyte genotype alters plant community composition. J Appl Ecol 47:468–477
Ruiz-González C, Salazar G, Logares R, Proia L, Gasol JM, Sabater S (2015) Weak coherence in abundance patterns between bacterial classes and their constituent OTUs along a regulated river. Front Microbiol 6:1293
Sahrawat KL, Burford JR (1982) Modification of the alkaline permanganate method for assessing the availability of soil nitrogen in upland soils. Soil Sci 133:53–57
Sautour M, Rouget A, Dantigny P, Divies C, Bensoussan M (2001) Prediction of conidial germination of Penicillium chrysogenum as influenced by temperature, water activity and pH. Lett Appl Microbiol 32:131–134
Schachtman DP, Reid RJ, Ayling SM (1998) Phosphorus uptake by plants: from soil to cell. Plant Physiol 116:447–453
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Applied Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Shi XM, Li XG, Long RJ, Singh BP, Li ZT, Li FM (2010) Dynamics of soil organic carbon and nitrogen associated with physically separated fractions in a grassland-cultivation sequence in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biol Fertil Soils 46:103–111
Ståhlberg S (1980) A new extraction method for estimation of plant-available P, K and Mg: a trial application in Swedish cultivated soils. Acta Agric Scand 30:93–107
Stöcklin J, Schweizer K, Körner C (1998) Effects of elevated CO2 and phosphorus addition on productivity and community composition of intact monoliths from calcareous grassland. Oecologia 116:50–56
Sun LJ, Qi YC, Dong YS, He YT, Peng Q, Liu XC, Jia JQ, Guo SF, Cao CC (2014) Interactions of water and nitrogen addition on soil microbial community composition and functional diversity depending on the inter-annual precipitation in a Chinese steppe. J Integr Agric 14:788–799
Sun X, Yu K, Shugart HH, Wang G (2015) Species richness loss after nutrient addition as affected by N: C ratios and phytohormone GA3 contents in an alpine meadow community. J Plant Ecol 2015:rtv037. doi:10.1093/jpe/rtv037
Tedersoo L, Pärtel K, Jairus T, Gates G, Põldmaa K, Tamm H (2009) Ascomycetes associated with ectomycorrhizas: molecular diversity and ecology with particular reference to the Helotiales. Environ Microbiol 11:3166–3178
Tedersoo L, May TW, Smith ME (2010) Ectomycorrhizal lifestyle in fungi: global diversity, distribution, and evolution of phylogenetic lineages. Mycorrhiza 20:217–263
Therneau T, Atkinson B (2014) mvpart: multivariate partitioning. R package version 1.6-1. https://cran.r-project.org/src/contrib/Archive/mvpart/mvpart_1.6-1.tar.gz.
Vicars WC, Sickman JO, Ziemann PJ (2010) Atmospheric phosphorus deposition at a montane site: size distribution, effects of wildfire, and ecological implications. Atmos Environ 44:2813–2821
Viketoft M, Palmborg C, Sohlenius B, Huss-Danell K, Bengtsson J (2005) Plant species effects on soil nematode communities in experimental grasslands. Appl Soil Ecol 30:90–103
Vitousek P, Howarth R (1991) Nitrogen limitation on land and in the sea: how can it occur? Biogeochemistry 13:87–115
Vitousek PM, Porder S, Houlton BZ, Chadwick OA (2010) Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol Appl 20:5–15
Waldrop MP, Zak DR (2006) Response of oxidative enzyme activities to nitrogen deposition affects soil concentrations of dissolved organic carbon. Ecosystems 9:921–933
Waldrop MP, Zak DR, Blackwood CB, Curtis CD, Tilman D (2006) Resource availability controls fungal diversity across a plant diversity gradient. Ecol Lett 9:1127–1135
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang S, Chen HY, Tan Y, Fan H, Ruan H (2016) Fertilizer regime impacts on abundance and diversity of soil fauna across a poplar plantation chronosequence in coastal Eastern China. Sci Rep 6:20816. doi:10.1038/srep20816
Weber CF, Vilgalys R, Kuske CR (2013) Changes in fungal community composition in response to elevated atmospheric CO2 and nitrogen fertilization varies with soil horizon. Front Microbiol 4:78. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2013.00078
Winder RS, Lamarche J, Constabel CP, Hamelin RC (2013) The effects of high-tannin leaf litter from transgenic poplars on microbial communities in microcosm soils. Front Microbiol 4:290. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2013.00290
Xu X, Wanek W, Zhou C, Richter A, Song M, Cao G, Ouyang H, Kuzyakov Y (2014) Nutrient limitation of alpine plants: implications from leaf N:P stoichiometry and leaf δ15N. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 177:378–387
Xu D, Fang X, Zhang R, Gao T, Bu H, Du G (2015) Influences of nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon addition on plant productivity and species richness in an alpine meadow. AoB Plants 7:plv125. doi:10.1093/aobpla/plv125
Yang Z, van Ruijven J, Du G (2011) The effects of long-term fertilization on the temporal stability of alpine meadow communities. Plant Soil 345:315–324
Zeng C, Zhang F, Wang Q, Chen Y, Joswiak DR (2013) Impact of alpine meadow degradation on soil hydraulic properties over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J Hydrol 478:148–156
Zhang P, Tang Y, Hirota M, Yamamoto A, Mariko S (2009) Use of a regression method to partition sources of ecosystem respiration in an alpine meadow. Soil Biol Biochem 41:663–670
Zhao XQ, Zhou XM (1999) Ecological basis of alpine meadow ecosystem management in Tibet: Haibei alpine meadow ecosystem research station. Ambio 28:642–647
Zhao L, Chen DD, Zhao N, Li Q, Cheng Q, Luo CY, Xu SX, Wang SP, Zhao XQ (2015) Responses of carbon transfer, partitioning, and residence time to land use in the plant-soil system of an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biol Fertil Soils 51:781–790
Zhou J, Jiang X, Zhou B, Zhao B, Ma M, Guan D, Li J, Chen SF, Cao FM, Shen DL, Qin J (2016) Thirty four years of nitrogen fertilization decreases fungal diversity and alters fungal community composition in black soil in NorthEast China. Soil Biol Biochem 57:135–143
Acknowledgments
We thank Yuntao Li, Ruibo Sun, Yingying Ni, Kaoping Zhang, and Qian Li for the assistance in sampling work. We also thank the editor and the three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by the National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program, Grant # 2014CB954002), the Strategic Priority Research Program (Grant # XDB15010101) of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41071121).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
(PDF 218 kb)
Online Resource 2
(PDF 278 kb)
Online Resource 3
(PDF 178 kb)
Online Resource 4
(PDF 319 kb)
Online Resource 5
(PDF 218 kb)
Online Resource 6
(PDF 237 kb)
Online Resource 7
(PDF 280 kb)
Online Resource 8
(PDF 175 kb)
Online Resource 9
(PDF 321 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, D., Xiang, X., He, JS. et al. Composition of the soil fungal community is more sensitive to phosphorus than nitrogen addition in the alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biol Fertil Soils 52, 1059–1072 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1142-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1142-4