Abstract
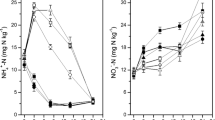
Yak and Tibetan sheep graze extensively on natural grasslands in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, and large amounts of excrement are directly deposited onto alpine grasslands. However, information on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from this excrement is limited. This study evaluated the short-term effects of yak and Tibetan sheep dung on nitrous oxide (N2O), methane (CH4), and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from alpine steppe soil at a water holding capacity (WHC) of 40 or 60 % and from alpine meadow soil at a WHC of 60 or 80 % under laboratory conditions. Cumulative N2O emissions over a 15-day incubation period at low soil moisture conditions ranged from 111 to 232 μg N2O–N kg soil−1 in the yak dung treatments, significantly (P < 0.01) higher than that of sheep dung treatments (28.7 to 33.7 μg N2O–N kg soil−1) and untreated soils (1.04–6.94 μg N2O–N kg soil−1). At high soil moisture conditions, N2O emissions were higher from sheep dung than yak dung and non-treated soils. No significant difference was found between the yak dung and non-treated alpine meadow soil at 80 % WHC. Low N2O emission in the yak dung treatment from relatively wet soil was probably due to complete denitrification to N2. Yak dung markedly (P < 0.001) increased CH4 and CO2 emissions, likely being the main source of these two gases. The addition of sheep dung markedly (P < 0.001) elevated CO2 emissions. Dung application significantly (P < 0.01) increased global warming potential, particularly for alpine steppe soil. In conclusion, our findings suggest that yak and Tibetan sheep dung deposited on alpine grassland soils may increase GHG emissions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alotaibi K, Schoenau J (2013) Greenhouse gas emissions and nutrient supply rates in soil amended with biofuel production by-products. Biol Fertil Soils 49:129–141
Carter MR (1993) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Castaldi S, de Grandcourt A, Rasile A, Skiba U, Valentini R (2010) CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes from soil of a burned grassland in Central Africa. Biogeoscience 7:3459–3471
Chadwick DR, Pain BF (1997) Methane fluxes following slurry applications to grassland soils: laboratory experiments. Agric Ecosyst Environ 63:51–60
Chadwick DR, Pain BF, Brookman SKE (2000) Nitrous oxide and methane emissions following application of animal manures to grassland. J Environ Qual 29:277–287
Chen W, Wolf B, Brüggemann N, Butterbach-Bahl K, Zheng X (2011) Annual emissions of greenhouse gases from sheepfolds in inner Mongolia. Plant Soil 340:291–301
Dalal R, Gibson I, Menzies N (2009) Nitrous oxide emission from feedlot manure and green waste compost applied to Vertisols. Biol Fert Soils 45:809–819
Diaz DAR, Sawyer JE, Mallarino AP (2008) Poultry manure supply of potentially available nitrogen with soil incubation. Agron J 100:1310–1317
Dick J, Kaya B, Soutoura M, Skiba U, Smith R, Niang A, Tabo R (2008) The contribution of agricultural practices to nitrous oxide emissions in semi-arid Mali. Soil Use Manage 24:292–301
Du Y, Cui Y, Xu X, Liang D, Long R, Cao G (2008) Nitrous oxide emissions from two alpine meadows in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 311:245–254
Dubeux JCB, Sollenberger LE, Mathews BW, Scholberg JM, Santos HQ (2007) Nutrient cycling in warm-climate grasslands. Crop Sci 47:915–928
Flessa H, Beese F (2000) Laboratory estimates of trace gas emissions following surface application and injection of cattle slurry. J Environ Qual 29:262–268
Flessa H, Dorsch P, Beese F, Konig H, Bouwman AF (1996) Influence of cattle wastes on nitrous oxide and methane fluxes in pasture land. J Environ Qual 25:1366–1370
Geng Y, Wang Y, Yang K, Wang S, Zeng H, Baumann F, Kuehn P, Scholten T, He JS (2012) Soil respiration in Tibetan alpine grasslands: belowground biomass and soil moisture, but not soil temperature, best explain the large-scale patterns. PLoS One 7:e34968
Granli T, Bockman OC (1994) Nitrous oxide from agriculture. Norw J Agric Sci 12 (Suppl.):1–128
Hayakawa A, Akiyama H, Sudo S, Yagi K (2009) N2O and NO emissions from an Andisol field as influenced by pelleted poultry manure. Soil Biol Biochem 41:521–529
Haynes RJ, Williams PH (1993) Nutrient cycling and soil fertility in the grazed pasture ecosystem. Adv Agron 49:119–199
Hoeft I, Steude K, Wrage N, Veldkamp E (2012) Response of nitrogen oxide emissions to grazer species and plant species composition in temperate agricultural grassland. Agric Ecosyst Environ 151:34–43
Holst J, Liu C, Yao Z, Brueggemann N, Zheng X, Han X, Butterbach-Bahl K (2007) Importance of point sources on regional nitrous oxide fluxes in semi-arid steppe of Inner Mongolia, China. Plant Soil 296:209–226
Holter P (1991) Concentration of oxygen, carbon dioxide and methane in the air within dung pats. Pedobiologia 35:381–386
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Jarvis SC, Lovell RD, Panayides R (1995) Patterns of methane emission from excreta of grazing animals. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1581–1588
Jiang C, Yu G, Fang H, Cao G, Li Y (2010) Short-term effect of increasing nitrogen deposition on CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Atmos Environ 44:2920–2926
Jost D, Joergensen R, Sundrum A (2013) Effect of cattle faeces with different microbial biomass content on soil properties, gaseous emissions and plant growth. Biol Fertil Soils 49:61–70
Li WJ, Li JH, Knops JMH, Wang G, Jia JJ, Qin YY (2009) Plant communities, soil carbon, and soil nitrogen properties in a successional gradient of sub-alpine meadows on the eastern Tibetan Plateau of China. Environ Manage 44:755–765
Lin X, Wang S, Ma X, Xu G, Luo C, Li Y, Jiang G, Xie Z (2009) Fluxes of CO2, CH4, and N2O in an alpine meadow affected by yak excreta on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau during summer grazing periods. Soil Biol Biochem 41:718–725
Linn DM, Doran JW (1984) Effect of water-filled pore space on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide production in tilled and nontilled soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:1267–1272
Lovell RD, Jarvis SC (1996) Effect of cattle dung on soil microbial biomass C and N in a permanent pasture soil. Soil Biol Biochem 28:291–299
Lu XY, Fan JH, Yan Y, Wang XD (2011) Soil water soluble organic carbon under three alpine grassland types in Northern Tibet, China. Afr J Agric Res 6:2066–2071
Lu XY, Yan Y, Fan JH, Wang XD (2012) Gross nitrification and denitrification in alpine grassland ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Arct Antarct Alp Res 44:188–196
Ma X, Wang S, Wang Y, Jiang G, Nyren P (2006) Short-term effects of sheep excrement on carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and methane fluxes in typical grassland of Inner Mongolia. New Zeal J Agr Res 49:285–297
Maljanen M, Virkajarvi P, Martikainen PJ (2012) Dairy cow excreta patches change the boreal grass swards from sink to source of methane. Agr Food Sci 21:91–99
McDowell RW, Stewart I (2005) Phosphorus in fresh and dry dung of grazing dairy cattle, deer, and sheep: Sequential fraction and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance analyses. J Environ Qual 34:598–607
Miller DJ (1990) Grasslands of the Tibetan Plateau. Rangelands 12:159–163
O'Halloran IP, Cade-Menun BJ (2006) Total and organic phosphorus. In: Carter MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 265–292
Olayinka A (2001) Effect of co-applied cow dung and inorganic nitrogen on microbial respiration in soil under laboratory conditions. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 32:3229–3242
Pare MC, Bedard-Haughn A (2013) Soil organic matter quality influences mineralization and GHG emissions in cryosols: a field-based study of sub- to high Arctic. Glob Change Biol 19:1126–1140
Pei Z, Ouyang H, Zhou C, Xu X (2003) Fluxes of CO2, CH4 and N2O from alpine grassland in the Tibetan Plateau. J Geogr Sci 13:27–34
Pratt PF (1965) Digestion with hydrofluoric and perchloric acids for total potassium and sodium. In: Black CA (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Agronomy Monograph No. 9. Part 2. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, pp. 1019–1021
Price SJ, Kelliher FM, Sherlock RR, Tate KR, Condron LM (2004) Environmental and chemical factors regulating methane oxidation in a New Zealand forest soil. Aust J Soil Res 42:767–776
Saggar S, Bolan NS, Bhandral R, Hedley CB, Luo J (2004) A review of emissions of methane, ammonia, and nitrous oxide from animal excreta deposition and farm effluent application in grazed pastures. New Zeal J Agr Res 47:513–544
Saggar S, Hedley CB, Giltrap DL, Lambie SM (2007) Measured and modelled estimates of nitrous oxide emission and methane consumption from a sheep-grazed pasture. Agric Ecosyst Environ 122:357–365
Simek M, Jisova L, Hopkins DW (2002) What is the so-called optimum pH for denitrification in soil? Soil Biol Biochem 34:1227–1234
Thomas KL, Lloyd D, Boddy L (1994) Effects of oxygen, pH and nitrate concentration on denitrification by Pseudomonas species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 118:181–186
Torri D, Poesen J, Monaci F, Busoni E (1994) Rock fragment content and fine soil bulk density. Catena 23:65–71
Vallejo A, Garcia-Torres L, Diez JA, Arce A, Lopez-Fernandez S (2005) Comparison of N losses (NO3 −, N2O, NO) from surface applied, injected or amended (DCD) pig slurry of an irrigated soil in a Mediterranean climate. Plant Soil 272:313–325
Van Groenigen JW, Velthof GL, Oenema O, Van Groenigen KJ, Van Kessel C (2010) Towards an agronomic assessment of N2O emissions: a case study for arable crops. Eur J Soil Sci 61:903–913
Wachendorf C, Lampe C, Taube F, Dittert K (2008) Nitrous oxide emissions and dynamics of soil nitrogen under 15N-labeled cow urine and dung patches on a sandy grassland soil. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 171:171–180
Wang XD, Yan Y, Cao YZ (2012) Impact of historic grazing on steppe soils on the northern Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 354:173–183
Watanabe T, Osada T, Yoh M, Tsuruta H (1997) N2O and NO emissions from grassland soils after the application of cattle and swine excreta. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 49:35–39
Yamulki S, Jarvis SC, Owen P (1998) Nitrous oxide emissions from excreta applied in a simulated grazing pattern. Soil Biol Biochem 30:491–500
Yamulki S, Jarvis SC, Owen P (1999) Methane emission and uptake from soils as influenced by excreta deposition from grazing animals. J Environ Qual 28:676–682
Yamulki S, Wolf I, Bol R, Grant B, Brumme R, Veldkamp E, Jarvis SC (2000) Effects of dung and urine amendments on the isotopic content of N2O released from grasslands. Rapid Comm Mass Sp 14:1356–1360
Yue G, Zhao L, Zhao Y, Li Y (2010) Research advances of grassland ecosystem CO2 flux on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J Glaciol Geocryol 32:166–174
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jian Xiang, Dr. Shouqin Sun, and Mr. Yiduo for their assistance in the field and in the laboratory. Many thanks also to chief editor P. Nannipieri and two anonymous referees for their helpful comments and suggestions that improved the manuscript greatly. This study was funded by the CAS (Chinese Academy of Sciences) Action-plan for West Development (KZCX2-XB3-08), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41201235) and the Natural Science Foundation of Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Wang, X., Ding, W. et al. Potential short-term effects of yak and Tibetan sheep dung on greenhouse gas emissions in two alpine grassland soils under laboratory conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 49, 1215–1226 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-013-0821-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-013-0821-7