Abstract
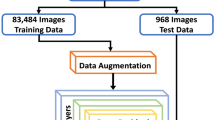
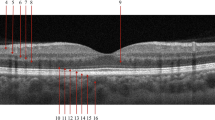
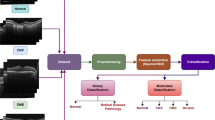
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a noninvasive imaging technique that enables the visualization of tissue microstructure in vivo. Recent studies have suggested that OCT can be used for detecting and monitoring retinal changes over time in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an auto-immune disease that damages various organs, including the eye itself. This research work discusses the potential of using OCT as a screening tool for SLE. OCT provides a detailed view of the retina, allowing the detection of subtle changes that may indicate early-stage SLE-related eye disease to screen SLE patients. The use of OCT as a screening tool may help to identify lupus erythematosus retinopathy (LR) and facilitate earlier interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes. In addition, we used deep learning-based automated screening using OCT images of SLE patients. We present a novel deep-learning model combining a pre-trained CNN, a multi-scale module, a pooling module, and an FC classifier. Our prediction model for SLE disease has outperformed the state-of-the-art method using the in-house dataset from Peking Union Medical College Hospital. Our model achieved a higher AUC indicating a high correlation between the ground truth and predicted output. However, further studies are needed to determine the sensitivity and specificity of OCT in detecting SLE and to establish appropriate screening protocols for this patient population.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the data also forming part of an ongoing study, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Altan, G.: Deepoct: An explainable deep learning architecture to analyze macular edema on OCT images. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 34, 101091 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2021.101091
Aringer, M., Costenbader, K., Daikh, D., et al.: European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71(9), 1400–1412 (2019)
Aronson, A.J., Ordoñez, N.G., Diddie, K.R., et al.: Immune-complex deposition in the eye in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch. Intern. Med. 139(11), 1312–1313 (1979)
Au, A., O’Day, J.: Review of severe vaso-occlusive retinopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus and the antiphospholipid syndrome: associations, visual outcomes, complications and treatment. Clin. Experiment. Ophthalmol. 32(1), 87–100 (2004)
Azevedo, L.: Lupus retinopathy: new data from latin america. ec ophthalmol [inter- net]. 2019 [cited 2019 dec 21]; 10(12), 01–04 (2019)
Bergmeister, R.: Uber primare und mil- iare tuberkulose der retina. Wiener Med Woch 79, 1116–1119 (1929)
Butendieck, R.R., Parikh, K., Stewart, M., et al.: Systemic lupus erythematosus-associated retinal vasculitis. J. Rheumatol. 39(5), 1095–1096 (2012)
Cancro, M.P., D’Cruz, D.P., Khamashta, M.A., et al.: The role of b lymphocyte stimulator (blys) in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Investig. 119(5), 1066–1073 (2009)
Ceccarelli, F., Natalucci, F., Picciariello, L., et al.: Application of machine learning models in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. J. Molecular Sci. 24(5), 4514 (2023).
Cervera, R., Piette, J.C., Font, J., et al.: Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Arthritis Rheumat. Official J. Am. College Rheumatol. 46(4), 1019–1027 (2002)
Gao, N., Li, M., Li, Y., et al.: Retinal vasculopathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 26(11), 1182–1189 (2017)
Gordon, C., Isenberg, D.: Systemic lupus erythematosus. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2016)
Guo, S., Liu, H., Gao, Y., et al.: Analysis of vascular changes of fundus in behcet’s uveitis by widefield swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography and fundus fluorescein angiography. Retina. pp 10–1097 (2022)
Hanane, M., Mounir, B., Rachid, Z., et al.: Severe ischemic retinopathy in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus without antiphospholipid syndrome: a case report. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 29(2), 169–171 (2015)
Hao, H., Zhao, Y., Yan, Q., et al.: Angle-closure assessment in anterior segment oct images via deep learning. Med. Image Anal. 69, 101956 (2021)
Hasan, R., Langner, H., Ritter, M., et al.: Investigating the robustness of pre-trained networks on oct-dataset. Actual Problems Syst. Softw. Eng. (2019)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778 (2016)
Hong-Kee, N., Mei-Fong, C., Azhany, Y. et al.: Antiphospholipid syndrome in lupus retinopathy. Clin. Ophthalmol. pp 2359–2363 (2014)
Huang, D., Swanson, E.A., Lin, C.P., et al.: Optical coherence tomography. Science 254(5035), 1178–1181 (1991)
Jabs, D.A., Fine, S.L., Hochberg, M.C., et al.: Severe retinal vaso-occlusive disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch. Ophthalmol. 104(4), 558–563 (1986)
Jorge, A.M., Smith, D., Wu, Z., et al.: Exploration of machine learning methods to predict systemic lupus erythematosus hospitalizations. Lupus 31(11), 1296–1305 (2022)
Karpik, A.G., Schwartz, M.M., Dickey, L.E., et al.: Ocular immune reactants in patients dying with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 35(3), 295–312 (1985)
Kegerreis, B., Catalina, M.D., Bachali, P., et al.: Machine learning approaches to predict lupus disease activity from gene expression data. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 9617 (2019)
Koonce, B., Koonce, B.: Resnet 34. Convolutional Neural Networks with Swift for Tensorflow: Image Recognition and Dataset Categorization, pp 51–61 (2021)
Lee, W.J., Cho, H.Y., Lee, Y.J., et al.: Intravitreal bevacizumab for severe vaso-occlusive retinopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 33, 247–251 (2013)
Leone, P., Prete, M., Malerba, E., et al.: Lupus vasculitis: an overview. Biomedicines 9(11), 1626 (2021)
Leuchten, N., Hoyer, A., Brinks, R., et al.: Performance of antinuclear antibodies for classifying systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic literature review and meta-regression of diagnostic data. Arthritis Care Res. 70(3), 428–438 (2018)
Li, F., Chen, H., Liu, Z., et al.: Deep learning-based automated detection of retinal diseases using optical coherence tomography images. Biomed. Opt. Express 10(12), 6204–6226 (2019)
Li, X., Bai, L., Ge, Z., et al.: Early diagnosis of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus by deep learning enhanced magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Med. Imag. Health Inform. 11(5), 1341–1347 (2021)
Liu, G.Y., Utset, T.O., Bernard, J.T.: Retinal nerve fiber layer and macular thinning in systemic lupus erythematosus: an optical coherence tomography study comparing sle and neuropsychiatric sle. Lupus 24(11), 1169–1176 (2015)
Liu, R., Wang, Y., Xia, Q., et al.: Retinal thickness and microvascular alterations in the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus: a new approach. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 12(1), 823 (2022)
Matthiesen, R., Lauber, C., Sampaio, J.L., et al.: Shotgun mass spectrometry-based lipid profiling identifies and distinguishes between chronic inflammatory diseases. EBioMedicine 70, 103504 (2021)
Mimier-Janczak, M., Kaczmarek, D., Janczak, D., et al.: Optical coherence tomography angiography as a new tool for evaluation of the subclinical retinal involvement in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus—a review. J. Clin. Med. 10(13), 2887 (2021)
Mizuno, Y., Nishide, M., Wakabayashi, T., et al.: Octa, a sensitive screening for asymptomatic retinopathy, raises alarm over systemic involvements in patients with sle. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 79(2), e17–e17 (2020)
Montehermoso, A., Cervera, R., Font, J. et al.: Association of antiphospholipid anti-bodies with retinal vascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism, Elsevier, pp 326–332 (1999)
Palejwala, N.V., Walia, H.S., Yeh, S.: Ocular manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus: a review of the literature. Autoimmune Dis. 2012, 290898 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/290898
Pan, L., Tin, S., Boey, M., et al.: The sensitivity and specificity of autoantibodies to the sm antigen in the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Acad. Med. Singapore 27(1), 21–23 (1998)
Pelegrín, L., Morató, M., Araújo, O., Figueras-Roca, M., Zarranz-Ventura, J., Adán, A., Cervera, R., Casaroli-Marano, R.P., Budi, V., Barrera-López, L., Ríos, J., Hernández-Rodríguez, J., Espinosa, G.: Preclinical ocular changes in systemic lupus erythematosus patients by optical coherence tomography. Rheumatology. 62(7), 2475–2482 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keac626
Rajabi, E., Sahebari, M., Thomas, T.: Analyzing systemic lupus erythematosus publications using neural network–based multi-label classification algorithms. Lupus 31(7), 820–827 (2022)
Sahu, D.K.: An unusual presentation of lupus retinopathy. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 56(1), 72 (2008)
Seth, G., Chengappa, K., Misra, D.P., et al.: Lupus retinopathy: a marker of active systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 38(8), 1495–1501 (2018)
Shen, Z., Savvides, M.: Meal v2: Boosting vanilla resnet-50 to 80%+ top-1 accuracy on imagenet without tricks. arXiv preprint arXiv:200908453 (2020)
Shi, W.Q., Han, T., Liu, R., et al.: Retinal microvasculature and conjunctival vessel alterations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus—an optical coherence tomography angiography study. Front. Med., p 2467 (2021)
Shulman, S., Shorer, R., Wollman, J., et al.: Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and neuropsychiatric manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 26(13), 1420–1425 (2017)
Silpa-Archa, S., Lee, J.J., Foster, C.S.: Ocular manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 100(1), 135–141 (2016)
Sivaraj, R., Durrani, O., Denniston, A., et al.: Ocular manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 46(12), 1757–1762 (2007)
Stafford-Brady, F.J., Urowitz, M.B., Gladman, D.D., et al.: Lupus retinopathy. Arthrit. Rheumatism Official J. Am. College Rheumatol. 31(9), 1105–1110 (1988)
Stanga, P.E., Lim, J.I., Hamilton, P.: Indocyanine green angiography in chorioretinal diseases: indications and interpretation: an evidence-based update. Ophthalmology 110(1), 15–21 (2003)
Stojanowski, J., Konieczny, A., Rydzyńska K, et al.: Artificial neural network-an effective tool for predicting the lupus nephritis outcome. BMC Nephrol. 23(1), 1–11 (2022)
Ushiyama, O., Ushiyama, K., Koarada, S., et al.: Retinal disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 59(9), 705–708 (2000)
Viedma, I.A., Alonso-Caneiro, D., Read, S.A., et al.: Deep learning in retinal optical coherence tomography (OCT): A comprehensive survey. Neurocomputing 507, 247–264 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.08.021
Wang, J., Deng, G., Li, W., et al.: Deep learning for quality assessment of retinal OCT images. Biomed. Opt. Express 10(12), 6057–6072 (2019)
Zhao, Y., Smith, D., Jorge, A.: Comparing two machine learning approaches in predicting lupus hospitalization using longitudinal data. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 16424 (2022)
Zhou, Y., Wang, M., Zhao, S., Yan, Y.: Machine learning for diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 7167066 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7167066
Zhu, X., Xiong, Y., Dai, J., et al.: Deep feature flow for video recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2349–2358 (2017)
Zou, K.H., O’Malley, A.J., Mauri, L.: Receiver-operating characteristic analysis for evaluating diagnostic tests and predictive models. Circulation 115(5), 654–657 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Masood, A., Li, T. et al. Deep learning-enabled automatic screening of SLE diseases and LR using OCT images. Vis Comput 39, 3259–3269 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02945-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02945-4